作业复习
期中问题
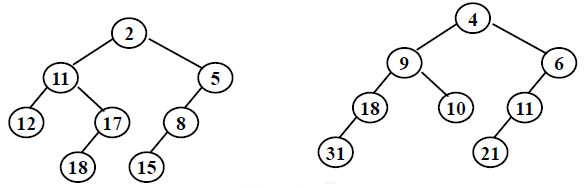
Insert {1,2,3,4,5,6,7} into an initially empty splay tree, then delete 5. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. 3 is the right child of 2
- B. 1 is the left child of 2
- C. 4 is the root
- D. 3 and 6 are siblings
splay的删除??????
Given two words word1 and word2, the minimum number of operations required to transform word1 into word2 is defined as the edit distance between the two words.The operations include:
Inserting a character
Deleting a character
Replacing a character
Example:
Input: word1= "horse", word2 = "ros"Edit Distance: 3Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r') rorse -> rose (remove 'r') rose -> ros (remove 'e')
We can use dynamic programming to solve it.Definition:
dp[i][j] represents the minimum edit distance between the substring of word1 ending at index i-1, and the substring of word2 ending at index j-1.
word[i] represents the i-th character of the word
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. The edit distance between "intention" and "execution" is 5.
- B. When word1[i - 1] and word2[j - 1] are not equal, dp[i][j] = min { dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1] } + 1.
- C. When two words have the same suffix, the edit distance remains unchanged after removing the suffix.
- D. When \(i\) is less than the length of word 1, dp[i][0] = i.
Consider the following merge algorithm for skew heaps. A merge is perfomed using a simple routine: merging two skew heaps A and B, if the top of A is less than or equal to the top of B, A becomes the skew heap, its children are swapped and B is merged with the left sub-heap of the root of A. If the left sub-heap is empty, B is assigned to the left sub-heap of A.
A node p is heavy if the number of descendants of p’s right subtree is at least half of the number of descendants of p, and light otherwise.
The potential function is defined to be ** the number of heavy nodes.** Let heap A and heap B be a \(n\)-node tree.
Which of the following is FALSE?
- A. The only nodes whose heavy/light status can change are nodes that are initially on the right path.
- B. The amortized running time of merge is \(O(\log n)\).
- C. All heavy nodes in the right path of A and B will become the light nodes after merging.
- D. There are at most \(O(\log n)\) light nodes in the right path of a \(n\)-node tree.
问题
RBT删除时为什么有儿子可以直接替换????
因为这个结点肯定是红色
B+树偶数阶split砍一刀是往上砍还是往下砍
在问助教ing
B+ 树 all nonleaf nodes have between ⌈M/2⌉ and M children is wrong????
没孩子的根也算非叶
divide into 3 sub-problems of equal complexity \(N/3\) and conquer in \(O(NlogN)\) --》\(O(Nlog^2N)\)???
Which one of the following is the lowest upper bound of \(T(n)\) for the following recursion \(T(n) = 2T(\sqrt{n}) + \log n\)?
- A. \(O(\log n\log \log n)\)
- B. \(O(\log^2 n)\)
- C. \(O(n\log n)\)
- D. \(O(n^2)\)
需要等价替换一下???

To approximate a maximum spanning tree \(T\) of an undirected graph \(G=(V,E)\) with distinct edge weights \(w(u,v)\) on each edge \((u,v)\in E\), let's denote the set of maximum-weight edges incident on each vertex by \(S\). Also let \(w(E')=\sum_{(u,v)\in E'} w(u,v)\) for any edge set \(E'\). Which of the following statements is TRUE?
- A. \(S=T\) for any graph \(G\)
- B. \(S\ne T\) for any graph \(G\)
- C. \(w(T) \ge w(S)/2\) for any graph \(G\)
- D. None of the above
不会
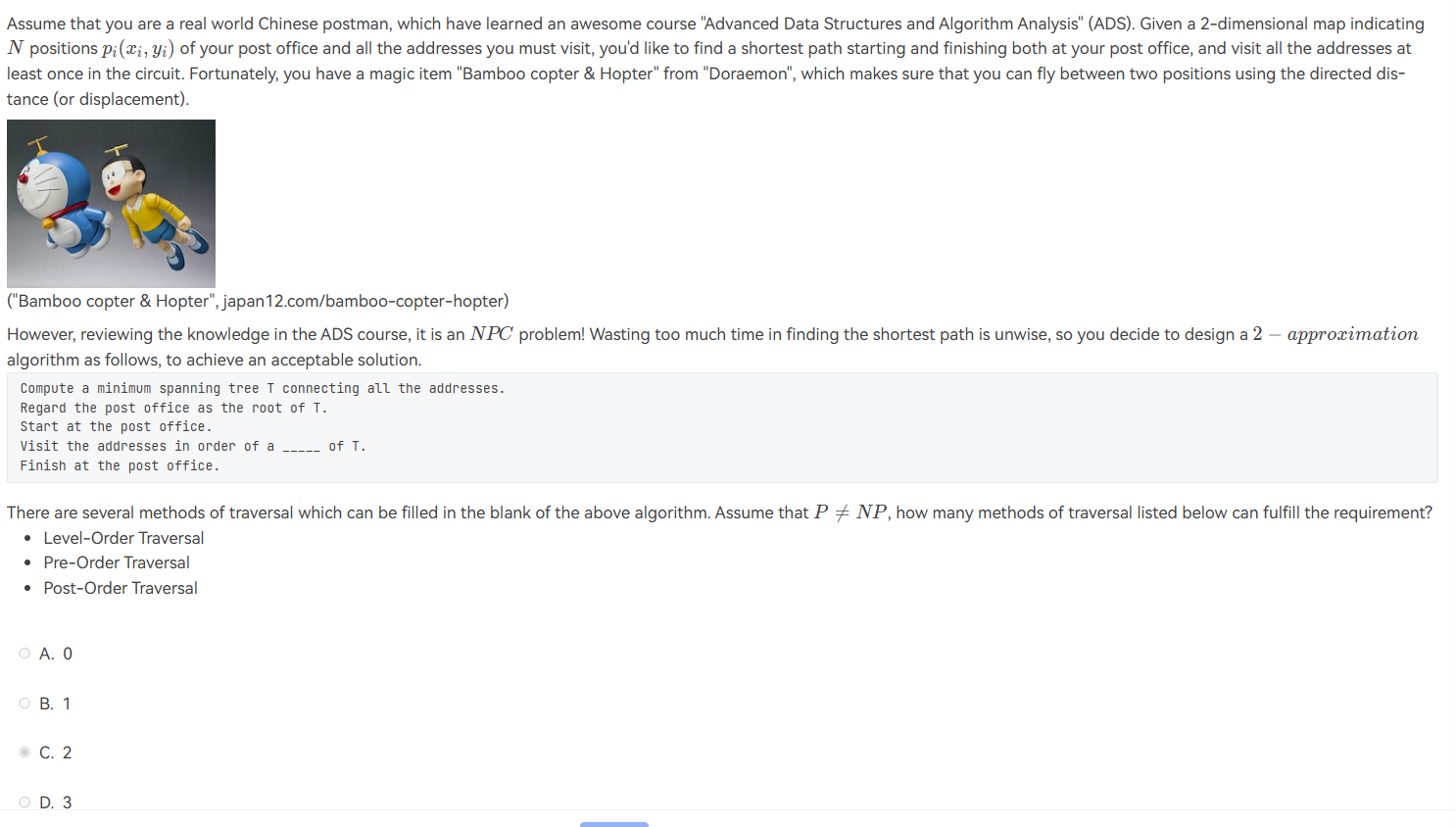
Given a 3-SAT formula with \(k\) clauses, in which each clause has three variables, the MAX-3SAT problem is to find a truth assignment that satisfies as many clauses as possible. A simple randomized algorithm is to flip a coin, and to set each variable true with probability \(1/2\), independently for each variable. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. The expected number of clauses satisfied by this random assignment is \(7k/8\).
- B. For every instance of 3-SAT, there is a truth assignment that satisfies at least a \(7/8\) fraction of all clauses.
- C. If we repeatedly generate random truth assignments until one of them satisfies \(\ge 7k/8\) clauses, then this algorithm is a \(8/7\)-approximation algorithm.
- D. The probability that a random assignment satisfies at least \(7k/8\) clauses is at most \(1/(8k)\).
不知道答案
HW1 AVL/SPLAY/均摊

换个角度思考
AVL代码
typedef struct AVLNode *Position;
typedef Position AVLTree;
struct AVLNode{
int data;
AVLTree left;
AVLTree right;
int height;
};
int getBalance(AVLTree T){
if(!T) return 0;
return height(T->left) - height(T->right);
}
AVL旋转代码
AVLTree rRotate(AVLTree T){
AVLTree Tp = T->left;
AVLTree r = Tp->right;
Tp->right = T;
T->left = r;
T->height = max(height(T->left), height(T->right)) + 1;
Tp->height = max(height(Tp->left), height(Tp->right)) + 1;
return Tp;
}
AVLTree lrRotate(AVLTree T){
T->left = lRotate(T->left);
return rRotate(T);
}
AVL插入代码
AVLTree insert(AVLTree T, int x){
if(!T){
T = newNode(x);
}else if(x<T->data){
T->left = insert(T->left, x);
if(getBalance(T)==2){
if(x<T->left->data)
T = rRotate(T); //note: not T->left
else
T = lrRotate(T);
}
}else if(x>T->data){
T->right = insert(T->right, x);
if(getBalance(T)==-2){
if(x>T->right->data)
T = lRotate(T);
else
T = rlRotate(T);
}
}
T->height = max(height(T->left), height(T->right)) + 1;
return T;
}
以上代码中,只有 insert 函数是接入口
In the context of Divide and Conquer algorithms, which of the following statements is true regarding the "Merge Sort" algorithm?
- A. Merge Sort performs sorting by repeatedly partitioning the array into subarrays and selecting pivot elements for comparison.
- B. Merge Sort has a average-case time complexity of \(O(n \log n)\) and uses a divide-and-conquer approach to sort a list of elements.
- C. Merge Sort has a worst-case time complexity of \(O(n^2)\) and employs a greedy strategy to sort elements efficiently.
- D. Merge Sort is not suitable for sorting large datasets due to its inefficient memory usage.
A 的 pivot 是快排的,C 的贪心算法和归并没屁关系,D 的话,归并的空间复杂度是 O(N)
HW2 BST
删除时为什么有儿子可以直接替换????
In the red-black tree that results after successively inserting the keys 41; 38; 31; 12; 19; 8 into an initially empty red-black tree, which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. 38 is the root
- B. 19 and 41 are siblings, and they are both red
- C. 12 and 31 are siblings, and they are both black
- D. 8 is red
红黑树多练插入和删除
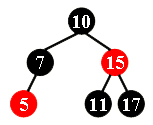
After deleting 15 from the red-black tree given in the figure, which one of the following statements must be FALSE?
- A. 11 is the parent of 17, and 11 is black
- B. 17 is the parent of 11, and 11 is red
- C. 11 is the parent of 17, and 11 is red
- D. 17 is the parent of 11, and 17 is black
下图的红黑树是否合法?
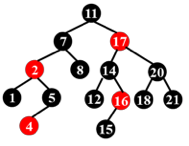
合法红黑树不存在只有一个非叶子节点的红色节点
Insert 3, 1, 4, 5, 9, 2, 6, 8, 7, 0 into an initially empty 2-3 tree (with splitting). Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. 7 and 8 are in the same node
- B. the parent of the node containing 5 has 3 children
- C. the first key stored in the root is 6
- D. there are 5 leaf nodes
他吗的乱七八糟的定义
可以确认的是,ADS的B+树规则如下:
- m 阶B+树的叶结点可以有 m 个key,内部结点只能 m-1 个key,只有根时当成叶子
- m 阶B+树内部结点最少得有 [m/2] 个 key,[m/2]+1个child,除了 root
- m 阶B+树叶子结点最少得有 [m/2]+1 个 key,除了 root
- key满了就中间砍一刀,取切割出右边第一个 key 复制到上面的索引结点,注意是复制
- 索引(内部)结点 split 之后是移动 key 往上走,而不是复制
After deleting 9 from the 2-3 tree given in the figure, which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. the root is full
- B. the second key stored in the root is 6
- C. 6 and 8 are in the same node
- D. 6 and 5 are in the same node
找兄弟借,借不到就拆家,与邻居重组为新家,把根拉下来

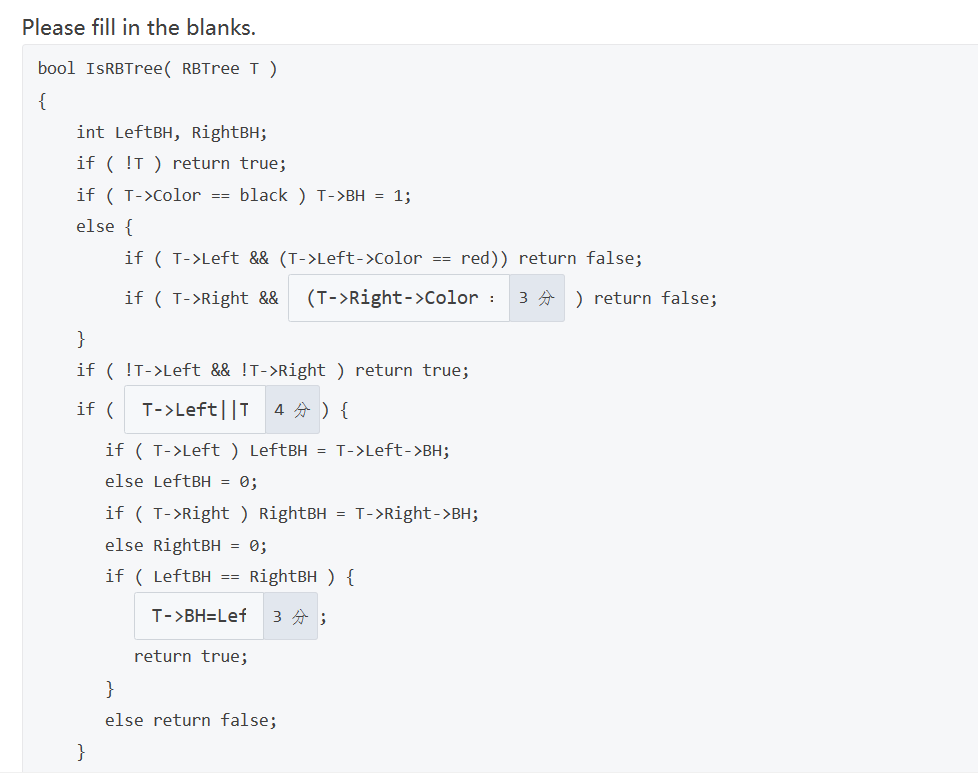
HW3 倒排索引
While accessing a term, hashing is faster than search trees.
- T
In distributed indexing, document-partitioned strategy is to store on each node all the documents that contain the terms in a certain range.
- F
数据库太大了,我们尝试讲数据存放在多台服务器,这就是 distributed indexing
term-partitioned 策略即一个服务器存放所有包含某些单词的文档
document-partitioned 根据文档的 id 决定该放哪个服务器
倒排索引(inverted file index)通过将单词或短语作为关键字,并将它们出现在文档中的位置记录在一个索引中,从而支持快速的文本检索。
对于每一个单词,我们记录它出现在哪些文档的哪个位置,以及记录他们出现的次数(频率)
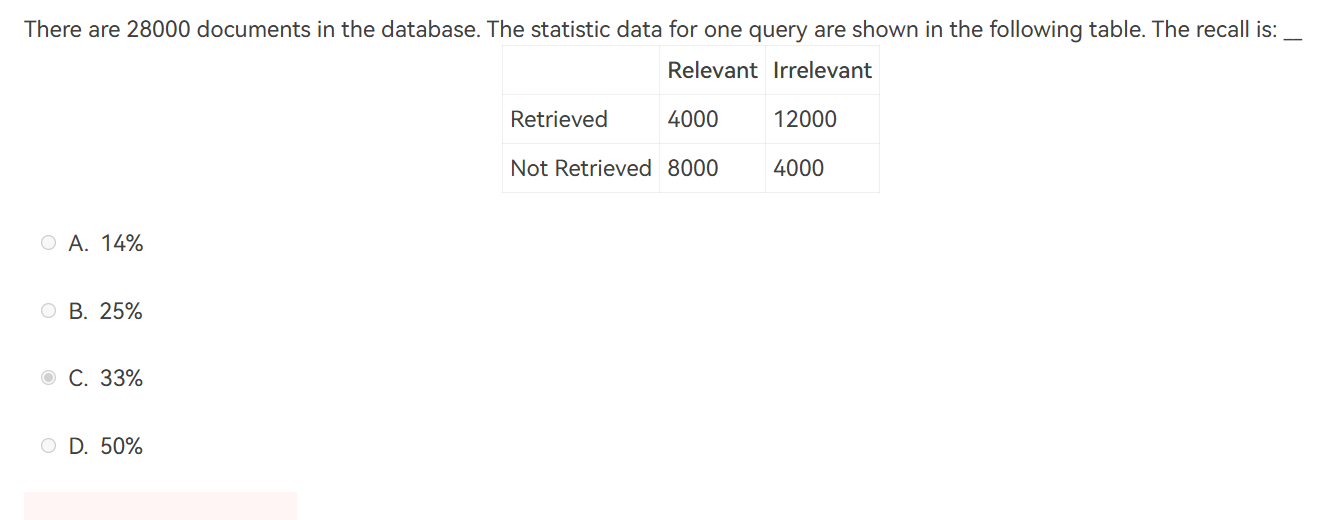
When evaluating the performance of data retrieval, it is important to measure the relevancy of the answer set.
- F
data retrieval:数据检索/召回,relevancy:相关性
HW4 左偏堆/斜堆
左偏堆(leftist heap)和斜堆(skew heap),与npl有关,null的npl为-1,叶子节点为0,内部节点取左右儿子中小的npl+1
左偏堆就是让结点左儿子npl永远大于右儿子,可知左偏堆结点npl为右儿子npl+1
npl=n的结点对应的子树至少是一个n+1层的满二叉树,由此推断结点数
左偏树右路径长度为r,则左偏树至少有 \(2^r-1\) 个结点
反之,左偏树节点数为n,则右路径最多只有 \([log(N+1)]\)
左偏堆的核心操作就是合并,其它操作都可以看作是合并特殊情况。
都在右路径操作,插入就放在最右下角
思路就是先维护堆的性质,在回溯时维护左偏性质,是一个先自上而下再自下而上的过程
插入分为递归式和迭代式两种
The result of inserting keys 1 to \(2^k -1\) for any \(k>4\) in order into an initially empty skew heap is always a full binary tree.
- T
The right path of a skew heap can be arbitrarily long.
- T
Merge the two leftist heaps in the following figure. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. 2 is the root with 11 being its right child
- B. the depths of 9 and 12 are the same
- C. 21 is the deepest node with 11 being its parent
- D. the null path length of 4 is less than that of 2
递归法
左偏堆先不要管左偏性质,在右路径上找到插入位置,然后将这个位置下面的结点及其子树拆离,接上待插入树;被拆离的子树作为新的待插入树,递归
插入结束后,往回递归检查,即从下往上看左偏性质是否被破坏,破坏了就左右交换,直至根节点
迭代法
也是先不要管左偏性质,在右路径上找到插入位置。
但是迭代法需要将两棵树都拆成一个个样本,然后对这些样本按照根节点大小顺序进行合并
注意,左子树里面的右子树不要拆,左子树是一个整体
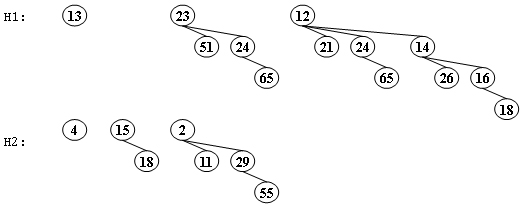
We can perform BuildHeap for leftist heaps by considering each element as a one-node leftist heap, placing all these heaps on a queue, and performing the following step: Until only one heap is on the queue, dequeue two heaps, merge them, and enqueue the result. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. in the \(k\)-th run, \(\lceil N/2^k \rceil\) leftist heaps are formed, each contains \(2^k\) nodes
- B. the worst case is when \(N=2^K\) for some integer \(K\)
- C. the time complexity \(T(N) = O(\frac{N}{2}log 2^0 + \frac{N}{2^2}log 2^1 + \frac{N}{2^3}log 2^2 + \cdots + \frac{N}{2^K}log 2^{K-1})\) for some integer \(K\) so that \(N=2^K\)
- D. the worst case time complexity of this algorithm is \(\Theta (NlogN)\)
这题不会啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊
D。根据 C,可得 𝑇=𝑂(𝑁)T=O(N)。
Insert keys 1 to 15 in order into an initially empty skew heap. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. the resulting tree is a complete binary tree
- B. there are 6 leaf nodes
- C. 6 is the left child of 2
- D. 11 is the right child of 7
熟能生巧了已经,没必要做了,忘了当我没说
The function is to merge two leftist heaps H1 and H2.
PriorityQueue Merge( PriorityQueue H1, PriorityQueue H2 )
{
if (H1==NULL) return H2;
if (H2==NULL) return H1;
if (H1->Element>H2->Element) //blank
swap(H1, H2); //swap H1 and H2
if ( H1->Left == NULL )
H1->Left = H2 ; //blank
else {
H1->Right = Merge( H1->Right, H2 );
if ( H1->Left->Npl < H1->Right->Npl )
SwapChildren( H1 ); //swap the left child and right child of H1
H1->Npl = H1->Right->Npl+1; //blank
}
return H1;
}
A leftist heap with the null path length of the root being \(r\) must have at least \(2^{r+1}-1\) nodes.
- T
我真的服了这都能错
Which one of the following statements is FALSE about skew heaps?
- A. Comparing to leftist heaps, skew heaps are always more efficient in space
- B. Skew heaps have \(O(log N)\) amortized cost per operation
- C. Skew heaps have \(O(log N)\) worst-case cost for merging
- D. Skew heaps do not need to maintain the null path length of any node
A 是因为斜堆没了npl以及相关的计算,需要储存的东西少了
HW5 二项队列
二项队列,so easy
For a binomial queue, __ takes a constant time on average.
- A. merging
- B. find-max
- C. delete-min
- D. insertion
insertion 均摊就是常数时间
find-min 也是常数时间,find-max 比较难操作
merge 和 delete-min 都是 O(logN)。
Merge the two binomial queues in the following figure. Which one of the following statements must be FALSE?
- A. there are two binomial trees after merging, which are \(B_2\) and \(B_4\)
- B. 13 and 15 are the children of 4
- C. if 23 is a child of 2, then 12 must be another child of 2
- D. if 4 is a child of 2, then 23 must be another child of 2
考前做一下,恢复记忆
The functions BinQueue_Find and Recur_Find are to find X in a binomial queue H. Return the node pointer if found, otherwise return NULL.
BinTree BinQueue_Find( BinQueue H, ElementType X )
{
BinTree T, result = NULL;
int i, j;
for( i=0, j=1; j<=H->CurrentSize; i++, j*=2) { /* for each tree in H */
T= H->TheTrees[i];
//blank
if ( X >= T->Element ){ /* if need to search inside this tree */
result = Recur_Find(T, X);
if ( result != NULL ) return result;
}
}
return result;
}
BinTree Recur_Find( BinTree T, ElementType X )
{
BinTree result = NULL;
if ( X==T->Element ) return T;
if ( T->LeftChild!=NULL ){
result = Recur_Find(T->LeftChild, X);
if ( result!=NULL ) return result;
}
if ( > T->NextSibling != NULL) //blank
result = Recur_Find(T->NextSibling, X);
return result;
}
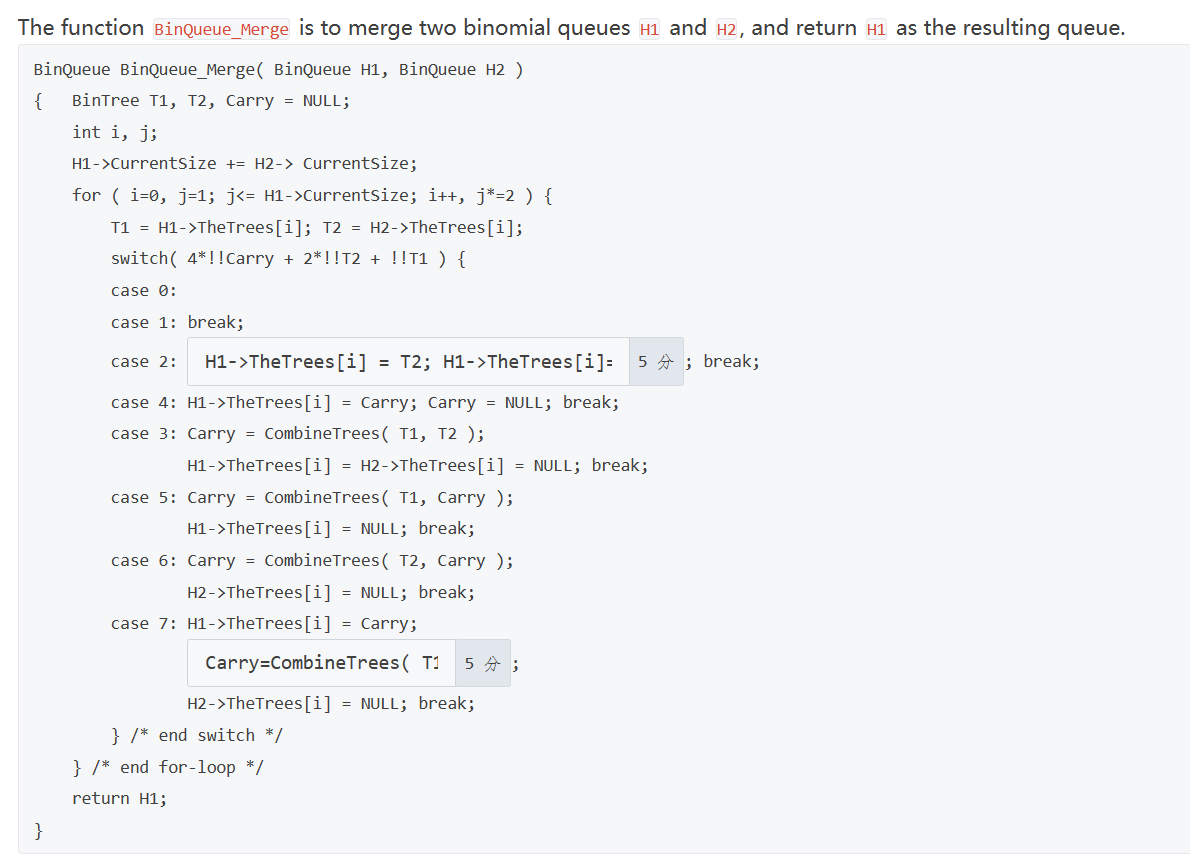
程序填空题:Merge two binomial queues H1 and H2 - 题库 - HYLUZ
[程序填空题:BinQueue_Merge 3] - 题库 - HYLUZ
HW6 回溯法
Given the following game tree, the red node will be pruned with α-β pruning algorithm if and only if __.
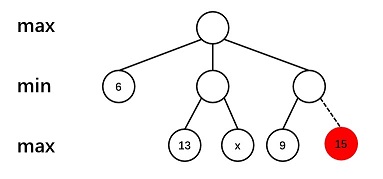
- A. \(6 \leq x\leq13\)
- B. \(x\geq13\)
- C. \(6 \leq x\leq9\)
- D. \(x\geq9\) √
这篇文章神中神
很难理解为什么这么简单的操作在课上会被讲的那么复杂,搞得我之前和同学在这吵了半天
HW7 分治法
解递归方程看手写笔记
When solving a problem with input size \(N\) by divide and conquer, if at each stage the problem is divided into 8 sub-problems of equal size \(N/3\), and the conquer step takes \(O(N^2 logN)\) to form the solution from the sub-solutions, then the overall time complexity is __.
- A. \(O(N^2 logN)\) √
- B. \(O(N^2 log^2 N)\)
- C. \(O(N^3 logN)\)
- D. \(O(N^{log8/log3})\)
复习主方法,其实是考验你的高中数学比大小技能
To solve a problem with input size \(N\) by divide and conquer algorithm, among the following methods, __ is the worst.
- A. divide into 2 sub-problems of equal complexity \(N/3\) and conquer in \(O(N)\)
- B. divide into 2 sub-problems of equal complexity \(N/3\) and conquer in \(O(NlogN)\)
- C. divide into 3 sub-problems of equal complexity \(N/2\) and conquer in \(O(N)\)
- D. divide into 3 sub-problems of equal complexity \(N/3\) and conquer in \(O(NlogN)\)
还是考验你的高中数学比大小技能
HW8 动态规划

D就是C后面单独拿出来
Given a recurrence equation \(f_{i,j,k} =f_{i,j+1,k}+\min_{0 \le l \le k}\{f_{i-1,j,l}+w_{j,l}\}\). To solve this equation in an iterative way, we cannot fill up a table as follows:
- A. for k in 0 to n: for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0
- B. for i in 0 to n: for j in 0 to n: for k in 0 to n
- C. for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0: for k in n to 0
- D. for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0: for k in 0 to n
注意各个变量各自可增序可降序,不需要统一顺序
这里 j 的依赖关系要求 j 必须降序
动态规划的编程题:
6-1 Programming Contest - ZJUADS_杨洋2024_HW8 (pintia.cn)
HW9 贪心算法
到贪心算法了
Greedy algorithm works only if the local optimum is equal to the global optimum.
- T
Let S be the set of activities in Activity Selection Problem. Then the earliest finish activity \(a_m\) must be included in all the maximum-size subset of mutually compatible activities of S.
- F
最优解不一定是贪婪最优解。
7-1 To Fill or Not to Fill - ZJUADS_杨洋2024_HW9 (pintia.cn)
编程题不一定要看
HW10 NP
NP
还没看,可以看下大佬的笔记
Homework - Jianjun Zhou's Notebook (zhoutimemachine.github.io)
All decidable problems are NP problems.
- F
All NP problems are decidable.
- T
All NP-complete problems are NP problems.
- T
All NP problems can be solved in polynomial time in a non-deterministic machine.
- T
If a problem can be solved by dynamic programming, it must be solved in polynomial time.
- F
Among the following problems, __ is NOT an NP-complete problem.
- A. Vertex cover problem
- B. Hamiltonian cycle problem
- C. Halting problem
- D. Satisfiability problem
Suppose Q is a problem in NP, but not necessarily NP-complete. Which of the following is FALSE?
- A. A polynomial-time algorithm for SAT would sufficiently imply a polynomial-time algorithm for Q.
- B. A polynomial-time algorithm for Q would sufficiently imply a polynomial-time algorithm for SAT.
- C. If Q \(\notin P\), then \(P \neq NP\).
- D. If Q is NP-hard, then Q is NP-complete.
HW11 近似算法
An approximation scheme that runs in \(O(n^2/\epsilon)\) for any fixed \(\epsilon >0\) is a fully polynomial-time approximation scheme.
- T
如果算法的复杂度与\(\epsilon\)有关系就是一个PTAS
既与\(\epsilon\)有关系还与规模有关系就是 fully polynomial-time approximation scheme (FPTAS)
An approximation scheme that runs in \(O(n^2 3^\epsilon)\) for any fixed \(\epsilon >0\) is a polynomial-time approximation scheme.
- T
For the bin-packing problem: let \(S=\sum S_i\). Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. The number of bins used by the next-fit heuristic is never more than \(\lceil 2S\rceil\)
- B. The number of bins used by the first-fit heuristic is never more than \(\lceil 2S\rceil\)
- C. The next-fit heuristic leaves at most one bin less than half full
- D. The first-fit heuristic leaves at most one bin less than half full
过一次即可,挺简单的
HW12 本地搜索
Greedy method is a special case of local search.
- F
Greedy是不断前进,最后达到解
local search是从一个随机解出发,不断微调,调向一个最佳的解,每一步的结果都是一个解
For the graph given in the following figure, if we start from deleting the black vertex, then local search can always find the minimum vertex cover.
- T
初始解就是全部点加进来,每次的邻居就是删去一个点的解
这题要你自己先找出最优解
Since finding a locally optimal solution is presumably easier than finding an optimal solution, we can claim that for any local search algorithm, one step of searching in neighborhoods can always be done in polynomial time.
- F
HW13 随机算法
The worst-case running time is equal to the expected running time within constant factors for any randomized algorithm.
- F
If we repeatedly perform independent trials of an experiment, each of which succeeds with probability \(p>0\), then the expected number of trials we need to perform until the first success is:
- A. \(p/(1-p)\)
- B. \(1/(1-p)\)
- C. \(1/p\)
- D. None of the above
HW14 并行算法
EREW does not allow simultaneous access by more than one processor to the same memory location for read or write purposes.
- T
Exclusive-Read Exclusive-Write (EREW)
Concurrent-Read Exclusive-Write (CREW)
Concurrent-Read Concurrent-Write (CRCW)
The prefix-min problem is to find for each \(i\), \(1 \le i \le n\), the smallest element among \(A(1)\), \(A(2)\), \(\cdots\), \(A(i)\). What is the run time and work load for the following algorithm?
for i, 1≤i≤n pardo
B(0, i) = A(i)
for h=1 to log(n)
for i, 1≤i≤n/2^h pardo
B(h, i) = min {B(h-1, 2i-1), B(h-1, 2i)}
for h=log(n) to 0
for i even, 1≤i≤n/2^h pardo
C(h, i) = C(h+1, i/2)
for i=1 pardo
C(h, 1) = B(h, 1)
for i odd, 3≤i≤n/2^h pardo
C(h, i) = min {C(h + 1, (i - 1)/2), B(h, i)}
for i, 1≤i≤n pardo
Output C(0, i)
- A. \(O(n)\), \(O(n)\)
- B. \(O(log n)\), \(O(log n)\)
- C. \(O(log n)\), \(O(n)\)
- D. \(O(n)\), \(O(lof n)\)