Lecture 1
yy第二节课不下课,交discussion被罚站
AVL树
基本概念
二叉查找树查询某个元素的复杂度 = 高度
高度平衡:任意左右子树高度差小于等于1
- 本课堂约定空树高度为-1,故一个节点高度为0
平衡因子 即左右子树高度差,左子树 - 右子树,有负数情况
discussion1
一个LL右旋
插入修复
AVL插入节点后需要进行修复,从插入的结点往上找到 第一个 出问题的结点,对它和它的子树进行旋转,或提起他的孙子。
LL和RR是对异常节点的儿子操作,LR和RL则是对孙子操作,不一定是对刚插入的节点
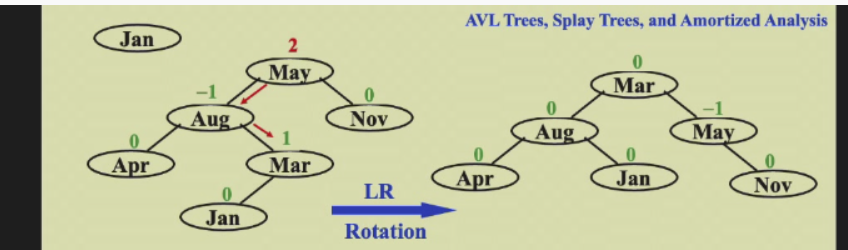
如上图,LR、RL实际是旋转2次:第一次是aug和mar左旋,提起mar;第二次是mar和may右旋,提起mar

特殊性质
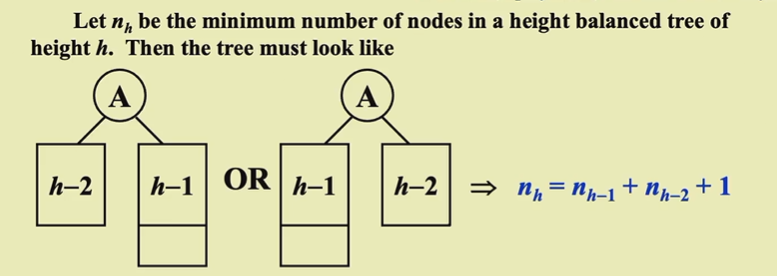

数学归纳法证明
Bug
什么鬼,三个参数,不会证啊,不知道哪里想错了
Splay Tree
splay不是高度平衡树,不是AVL树,没要求高度平衡,也算一种平衡树,能保证时间复杂度为logN
AVL代码比较难写,这个代码巨好写
Splay 树,即伸展树,想要解决的问题和 AVL 树类似,只不过 Splay 树希望达到的目标是在摊还(Amortized)复杂度O(logN*)的情况下完成大部分对点操作
splay tree很适合用于这种情况:从一个空树开始工作,工作包含输入、查询等,且操作有很多
AVL树每次查询一个元素,就将其提到根节点。
不过有bug,存在最坏情况:
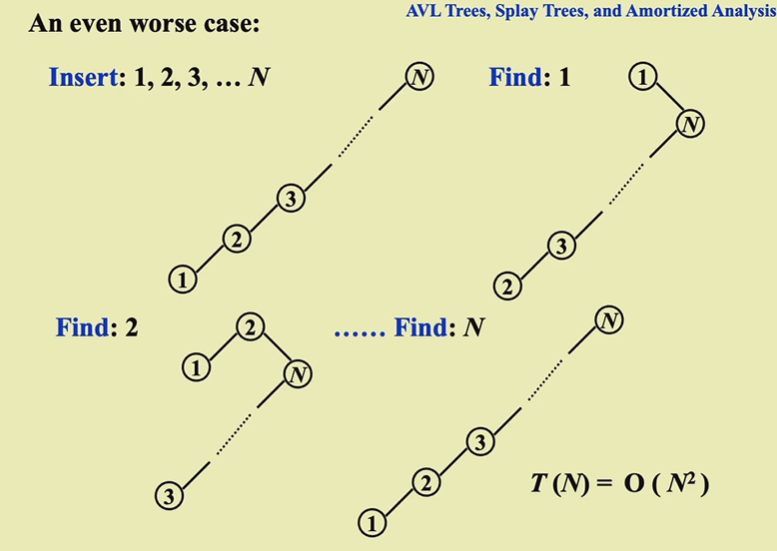
那我们就改一下旋转方式(splay树的精髓):
分三种情况,设要旋转的节点为X,其父节点为P,祖父节点为G,则,
- P是根节点 --> 旋转X和P
- P不是根节点(即存在祖父节点G),分两种情况:
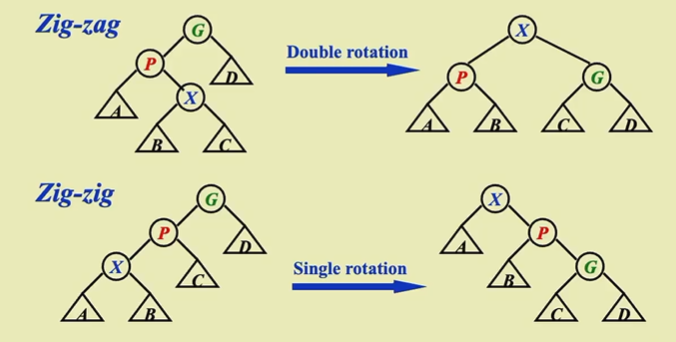
- zig-zag:和AVL树的LR、RL旋转一样,只转X,旋转两次
- zig-zig:P,G,X在同一条直线上,先提P,再提X
转完之后还需要检查X上面有没有新的P和G,有的话递归一下,继续判断和旋转
splay树几乎每次提完高度就少了一半,节点越多越明显
splay树在整个过程中不要求高度平衡,不是高度平衡树,但是平衡树,能保证时间复杂度在O(MlogN)

大作业1

Amortized Analysis
三种bound

M是调用次数
以前都是分析worst bound,现在要考试分析均摊的bond了。
- worst-case bound
- 最紧的界,不仅仅是总的,还要保证每一次的,都找不到一个case超过bound
- amortized bound
- 保证不管怎么样,M次操作后,总的不超过bound,但可能设计出超过的数据
- average-case bound
- 如果给的数据是均匀分布的,但可以构造最坏数据,让每一次都是最坏的,超过这个bound
前两个与数据分布无关,最后一个与数据分布有关
三种分析方法
下面是amortized bound的三种方法:
- aggregate analysis
- 聚合法
- 保证总时间开销一定,分析总开销是多少。直接
Show that for all n, a sequence of n operations takes worst-case time T(n) in total. In the worst case, the average cost, or amortized cost, per operation is therefore T(n)/n.
还不太懂聚合法
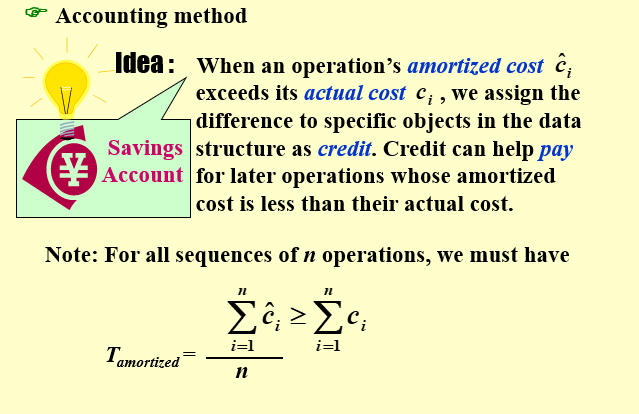
- accounting method
- 核算方法
- 保证任意时刻的 均摊代价(amortized cost) 都要大于等于 实际代价(actual cost) ,即保证不赊账。大于的时候多的部分就是 积分(credit),积分可以在少的时候 支付(pay) 少的部分。
- 由此均摊代价就是实际代价的均摊界。
- potential method
- 势能法
An Introduction to Amortized Analysis
An Introduction to Amortized Analysis | Baeldung on Computer Science
Overview
Amortized analysis is a technique for estimating run-time cost over a sequence of operations.
Amortized Analysis
When we use data structures, we typically execute operations in a sequence rather than individually.
Simply adding up the worst-case cost of individual operations may grossly over-estimate our actual runtime cost.
Amortization analysis attempts to solve this problem by averaging out the cost of more “expensive” operations across an entire sequence.
More formally, amortized analysis finds the average cost of each operation in a sequence, when the sequence experiences its worst-case.
The Aggregate Method

必看的举例:An Introduction to Amortized Analysis | Baeldung on Computer Science
Limitations
this method is very straight forward. However, it only works when we have a concrete definition of how much our sequence will cost.
Also, if our sequence contains multiple types of operations, then they will all be treated the same. We can’t obtain different amortized costs for different types of operations in the sequence. This might not be ideal!
The Accounting Method
For this method, we think about amortized cost as being a “charge” that we assign to each operation.
Each time we encounter an operation, we try to pay for it using this “charge”.
If the operation actually costs less than our “charge”, we stash the change in a bank account. If the operation actually costs more than our “charge”, we can dip into our bank account to cover the cost.
但是不能赊账!!
必看的举例:An Introduction to Amortized Analysis | Baeldung on Computer Science
Different Operation Types
The Aggregate Method will always treat every operation the same way, and cannot deduce different amortized costs for multiple types of operations in a sequence.
On the other hand, the Accounting Method can be easily applied to multiple operation types to deduce the amortized cost of each.
To achieve this goal, we can simply assign a different charge to each operation type to reveal a unique amortized cost.
鱼肆周报 002 - 势能分析法
势能分析英文 Amortized Analysis 也翻译作摊还分析,这个翻译其实更直观一些。它所做的事情其实就是把消耗大的操作给消耗小的操作“匀”一点,这就是摊还/平摊。

想要理解势能的意义,我们只需要一个口诀即可:让消耗大的那一步操作势能大大的降!
我们把每一步的代码看成了:原本的代价+势能的变化。
所以如果原本的代价很大我们让势能大下降,这样就把原本的代价抵消了,也就是所谓的摊还。
当然这样做当然不是无止境的,不能每一步都让势能下降,毕竟最终我们要求终点的势能是要大于起点的势能的。
所以到时候让代价小的操作的势能上升就可以实现把代价大的操作的代价摊到代价小的操作上了。
那么这样的正确性是很显然的啦,我们不要去想每一步亏了多少赚了多少,我们只需要知道我们最开始的那个式子:最终势能相较于一开始是上升的,所以我们这样做只会让总体的代价变大,对于分析上界不会带来问题。
4一些例子
还没看↓
作业
强推重做


