Lecture 6 | Backtracking
数据结构结束,算法部分开始
上课可能感觉算法简单一些,但由于算法的套路太少了,得靠硬实力/经验,所以实际上难度大大增加
比如,回溯法怎么pruning?
不花时间的话,到期末你做不出题才会发现不就是温水煮青蛙
算法是为了解决问题,问题有解空间。
算法设计者需要从情景中提取出问题,以数据为切入点,找出相应的输入和输出,最终找到解空间。
当然,前提是,问题是可计算问题
定义
回溯法是加上剪枝(pruning)操作的遍历法,即回溯法会遍历每一种可能解,但是会进行预判,通过pruning缩小可能解空间,再进行遍历。
遍历
而遍历的过程不是乱来的,是递进的。
一般一组解由多个元素构成,先找到正确的第一个元素,在此基础上找到匹配的(正确的)第二个元素,以此类推。
如果所有元素都能找到匹配的放进来,就找到了一组解;递进到某一个位置发现找不到,就回到上一个位置,换下一个匹配的元素。以此类推。
其本质是:走不通就回头。
这方法还是比较常见的,不仅仅是在算法里,日常生活中应该也经常使用。
剪枝
根据constrains处理
过程
- 构造空间树;
- 进行遍历;
- 如遇到边界条件,即不再向下搜索,转而搜索另一条链;
- 达到目标条件,输出结果。
建树剪枝时有个问题:
有些剪枝主要剪掉前期的,一开始选择少后面选择多
有些主要剪掉后期的,一开始选择多后面选择少
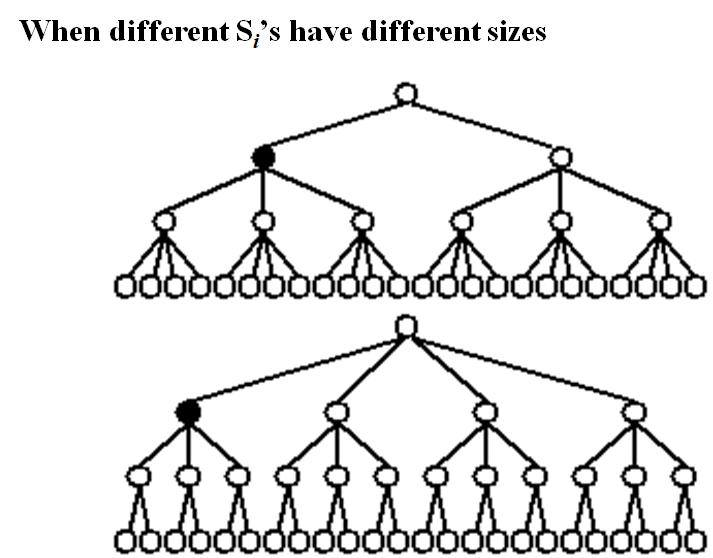
一般选择上面那个,因为一旦在前期排除该路径就可以一下子排除大量分支
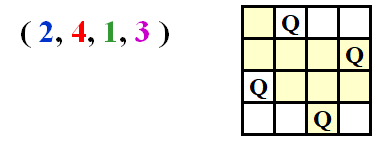
八皇后问题
这是一个十分典型的回溯法使用案例
问题
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
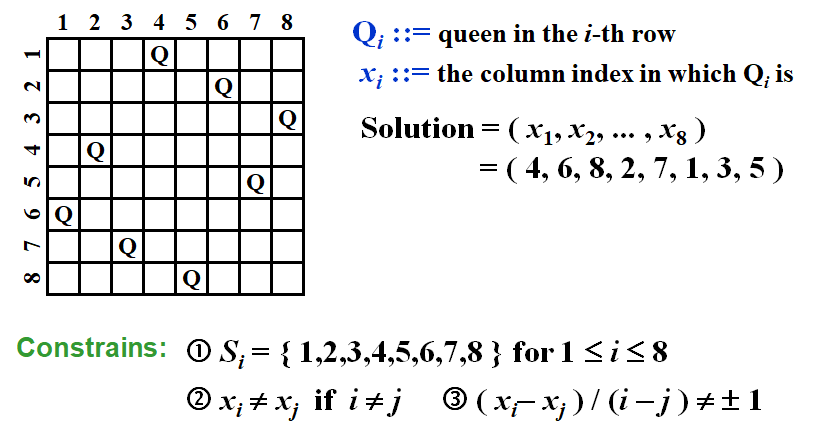
For the problem with n queens, there are n! candidates in the solution space.
解法
先拿四皇后作为分析的例子
Step 1
Construct a game tree according to constrains
这里就已经进行了剪枝
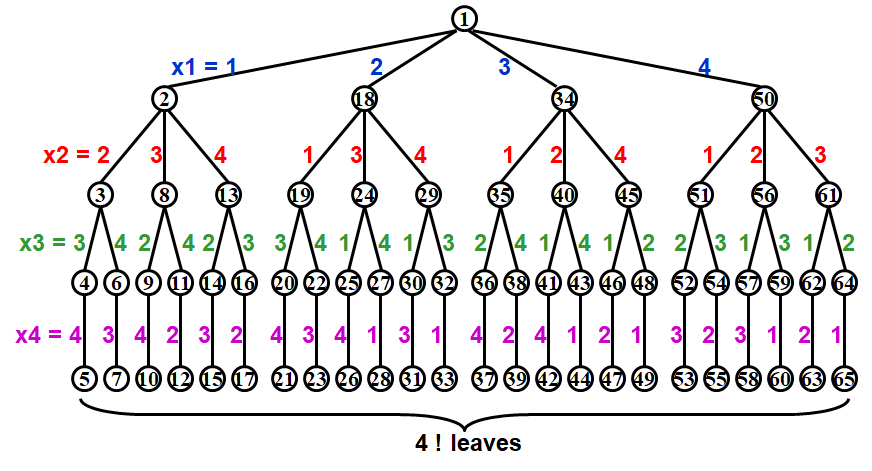
Step 2
Perform a depth-first search ( post-order traversal ) to examine the paths
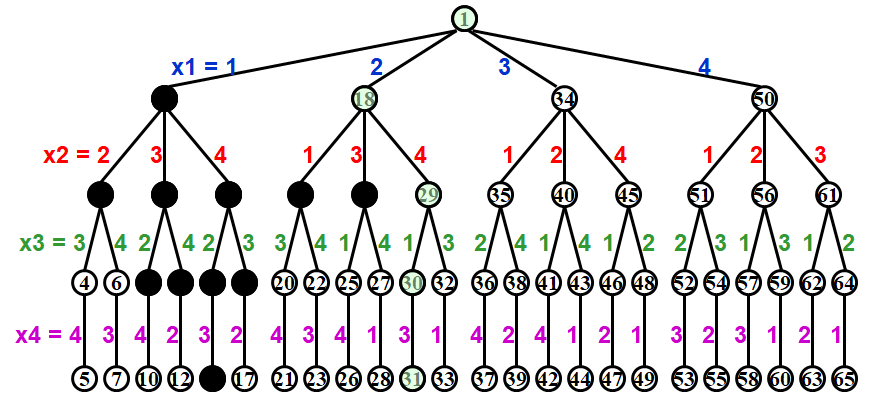
Each path from the root to a leaf defines an element of the solution space.
Note: No tree is actually constructed. The game tree is just an abstract concept.
在key=31我们得到了第一组解↓
The Turnpike Reconstruction Problem
在一条直线公路上准备修N个收费站
给出两两加油站之间所有的距离,求这N个加油站的位置
注意给距离集合是可重集,即可存在相同元素。
很明显,他会给我们 N ( N – 1 ) / 2 个距离,由此可计算出收费站数量 N
思路
最大的距离代表最左边和最右边的收费站的距离,由此确定了搜索区间就是这个距离内,还需要放N-2个加油站
然后第二大距离是跟最左边或最右边组成的
出现了二选一选择,就可以建树了
之后就依次递进,将第n大的距离当成是与最边上的加油站产生的进行构造
例子
\(x_i 是指数轴上从左到右第几个收费站的位置,设x_1=0\)
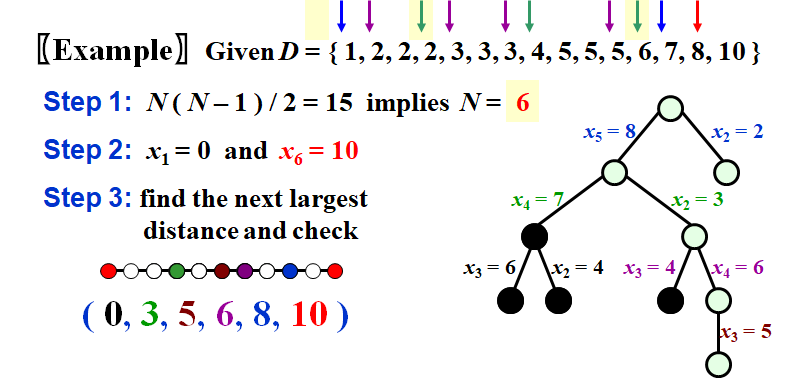
显然这个逻辑树是的高度是N-2,因为每一层都在确定一个收费站的位置,我们需要确定N-2个
Note: No tree is actually constructed. The game tree is just an abstract concept.
It is a logical tree.
代码
bool Reconstruct ( DistType X[ ], DistSet D, int N, int left, int right )
{ /* X[1]...X[left-1] and X[right+1]...X[N] are solved */
bool Found = false; //final output
if ( Is_Empty( D ) )
return true; /* solved */
D_max = Find_Max( D );/* option 1:X[right] = D_max */
/* check if |D_max-X[i]|属于D is true for all X[i]’s that have been solved */
OK = Check( D_max, N, left, right ); /* pruning,即看下 */
if ( OK ) { /* add X[right] and update D */
X[right] = D_max;
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ ) Delete( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ ) Delete( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
Found = Reconstruct ( X, D, N, left, right-1 );
if ( !Found ) { /* if does not work, undo */
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ ) Insert( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ ) Insert( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
}
}
/* finish checking option 1 */
/* if option 1 does not work */
/* option 2: X[left] = X[N]-D_max */
if ( !Found ) {
OK = Check( X[N]-D_max, N, left, right );
if ( OK ) {
X[left] = X[N] – D_max;
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ ) Delete( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ ) Delete( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
Found = Reconstruct (X, D, N, left+1, right );
if ( !Found ) {
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ ) Insert( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ ) Insert( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
}
}
/* finish checking option 2 */
}
/* finish checking all the options */
return Found;
}
回溯法代码的套路就是,每一层递归先将待测试的元素放进去试一下,看下行不行,不行就撤回
表现在这里就是将目前最大的dist先当成正确的,更新X和D,然后check一下,不行就恢复X和D的内容
Backtracking Template
bool Backtracking ( int i )
{ Found = false;
if ( i > N )
return true; /* solved with (x1, …, xN) */
for ( each xi Si ) {
/* check if satisfies the restriction R */
OK = Check((x1, …, xi) , R ); /* pruning */
if ( OK ) {
Count xi in;
Found = Backtracking( i+1 );
if ( !Found )
Undo( i ); /* recover to (x1, …, xi-1) */
}
if ( Found ) break;
}
return Found;
}
Minimax Strategy
好绕
α-β pruning
alpha-beta剪枝建立在两个假设上:
- 整个博弈过程属于零和博弈
- 博弈双方足够聪明
在满足这样的假设的情况下,整个α-β剪枝的核心思想就是,当你知道你有一个选择A时,此时你知道了B选择不如A选择好,那么你就不需要知道B选择有多坏。