Lecture 13 | Randomized Algorithms
最后一次课进行答疑
The Hiring Problem
通过面试从n个人招聘一些人,计算n次面试Ci+工资Ch的成本最小值,且保证能找出最优秀的人
最简单的算法就是遍历
int Hiring ( EventType C[ ], int N )
{ /* candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate */
int Best = 0;
int BestQ = the quality of candidate 0;
for ( i=1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i ); /* Ci */
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
BestQ = Qi;
Best = i;
hire( i ); /* Ch */
}
}
return Best;
}
这套算法面试成本固定,我们设招X人,计算X的数学期望\(E[X] = \sum_{j=1}^{N}j\cdot Pr[X=j]\)
但是这太无厘头了,不知道怎么算,我们就换种思路
设 \(X_i\) 记录第 \(i\) 个人是否被录取,就可以用此计算X的期望
我们有一个大前提,因为我们没有提前调查,故这n个人在面试前对于我们是一样优秀的
第 \(i\) 个人被录取的条件只需是他在前 \(i\) 个人里面最优秀,所以是 1/i
?????
得到调和级数,渐进上届为 \(lnN\)

但是我们需要做到的是保证这n个人来面试的顺序是随机的
不能让他们串通,毕竟从弱到强来就会几乎全部录取了
int RandomizedHiring ( EventType C[ ], int N )
{ /* candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate */
int Best = 0;
int BestQ = the quality of candidate 0;
randomly permute the list of candidates;
for ( i=1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i ); /* Ci */
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
BestQ = Qi;
Best = i;
hire( i ); /* Ch */
}
}
}
加入了这一步,这个算法就变成了随机算法
好处是不再要求输入的数据一定是随机的,可以输入有序数据
我们这里讲一种随机的方法,很简单,就是给他们random值,然后从小到大排序,搞定
void PermuteBySorting ( ElemType A[ ], int N )
{
for ( i=1; i<=N; i++ )
A[i].P = 1 + rand()%(N3);
/* makes it more likely that all priorities are unique */
Sort A, using P as the sort keys;
}
PermuteBySortingproduces a uniform random permutation of the input, assuming all priorities are distinct.
Online Hiring Algorithm – hire only once
每面试一个人,不仅决定要不要马上雇佣这个人,而且我们一共只能雇佣一个人
int OnlineHiring ( EventType C[ ], int N, int k )
{
int Best = N;
int BestQ = - ;
for ( i=1; i<=k; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i );
if ( Qi > BestQ ) BestQ = Qi;
}
for ( i=k+1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i );
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
Best = i;
break;
}
}
return Best;
}
这个算法是设置了一个值k,意味着前k个人一定不雇佣,记录其中最高分
剩下的人中,如果分有更高的,就马上录取
相当于前k个人用于建立一个参考来评价剩下的人
我们的问题是,k该怎么取才能让我们获得最优秀的人的概率最高

我们很容易得到其概率
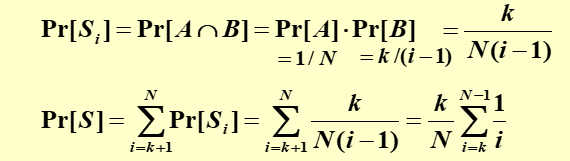
然后试着求一下上下界
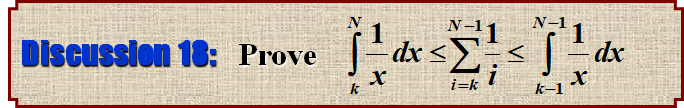
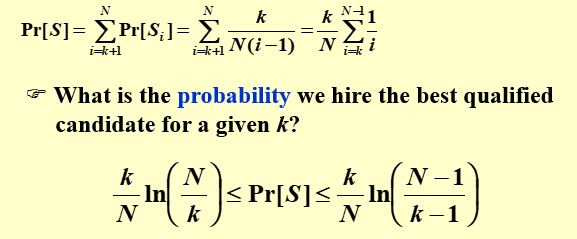
然后试着求一下最大值
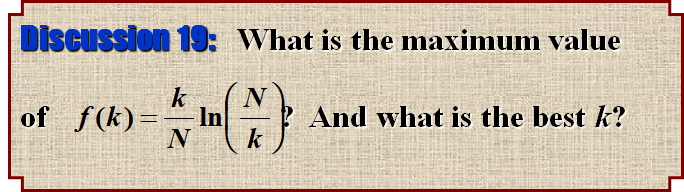
Quicksort
Deterministic Quicksort 就是每次选固定位置的基准,但是会导致最坏的bound,即基准为最大值或最小值
我们尝试改成随机选基准(Central splitter),而且检查比它小和比它大的元素是否均少于n/4,少就重新选
也就是说有一半的元素是我们不能取的,我们每次能有1/2的概率随机正确
由此可以得到 Claim: The expected number of iterations needed until we find a central splitter is at most 2.
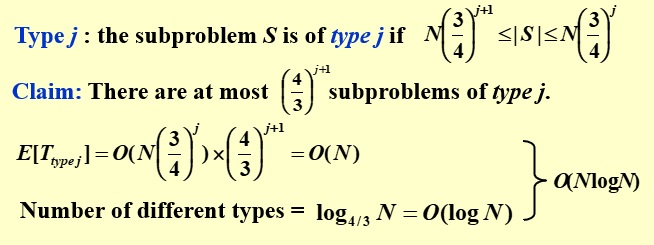
高级数据结构与算法分析2024-05-20第3-5节 (zju.edu.cn)
最后这里还不是特别明白
关于计算机的presentation
- 不讲代码细节就不要放代码
- 不要放无意义的动画(翻页,飘入啥的),会吸引眼球,消耗观众注意力
- 尽可能用英文