Lecture 4.1
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 361 个字 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
先继续上次的浮点数
浮点数
乘法
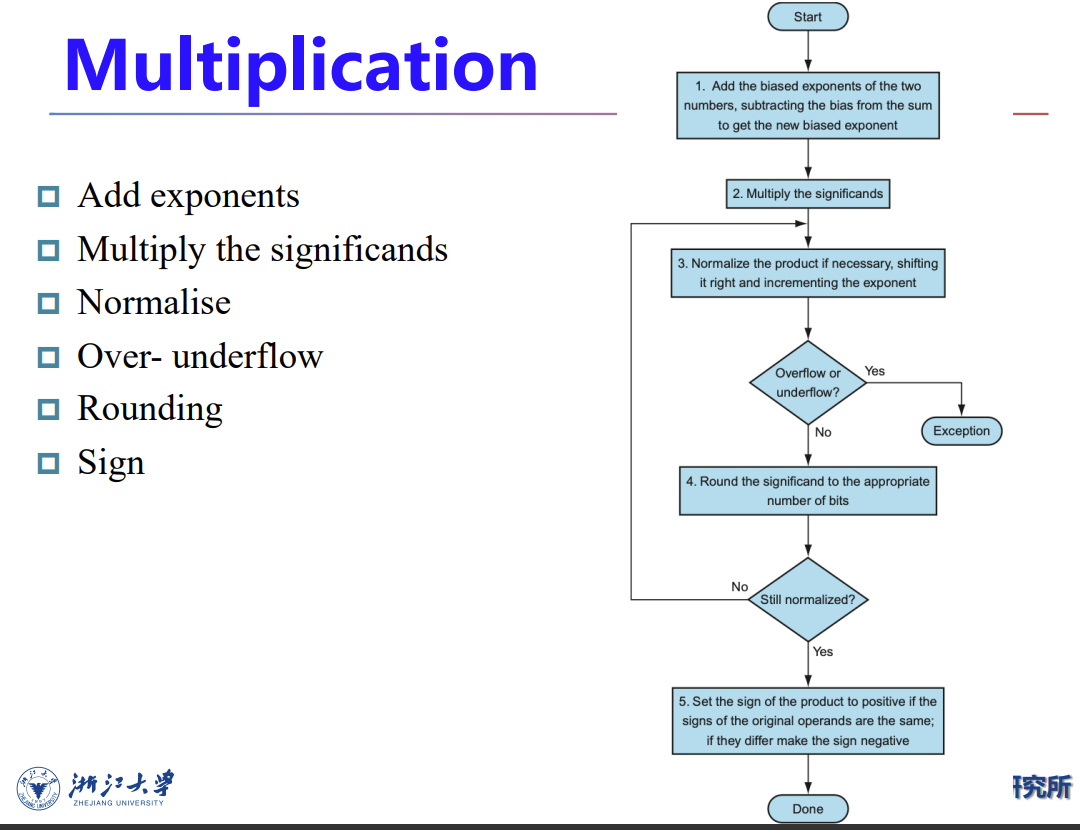
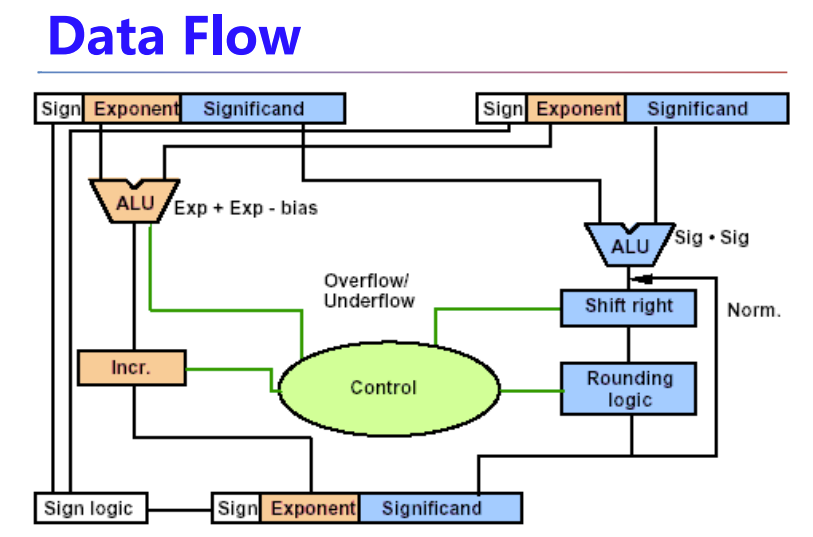
除法

浮点数有偏差和精度,所以有精度问题

Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Machine
对应wdCO第四章
计算减少,概念增加,不难,但是记的多
2.1 Introduction
Instruction Set
Different computers have different instruction sets
But with many aspects in common
Early computers had very simple instruction sets
Simplified implementation
Many modern computers also have simple instruction sets
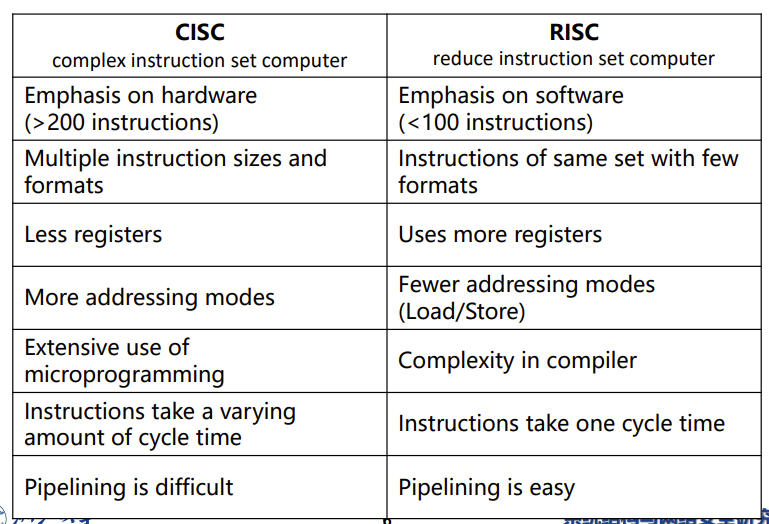
CISC vs RISC
看着玩的
Instruction formats
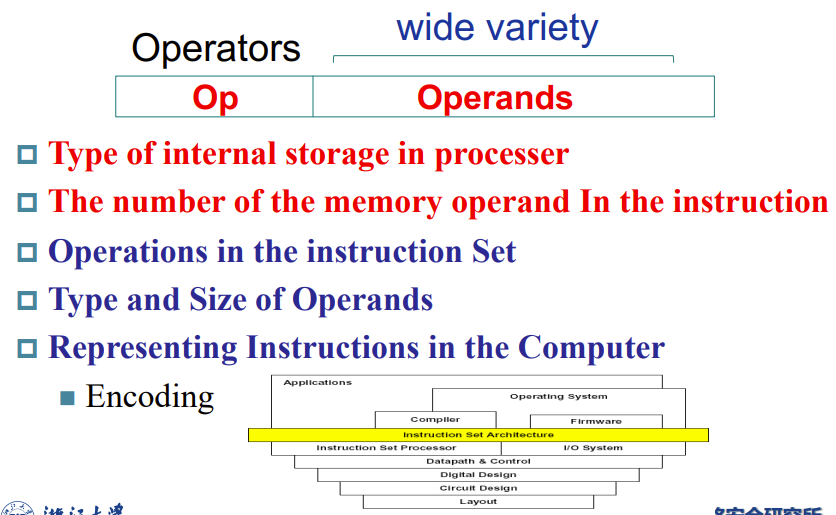
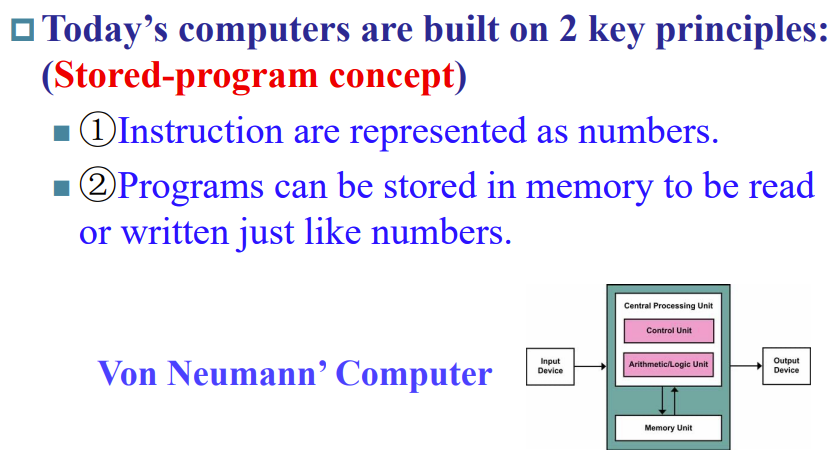
Stored-program concept
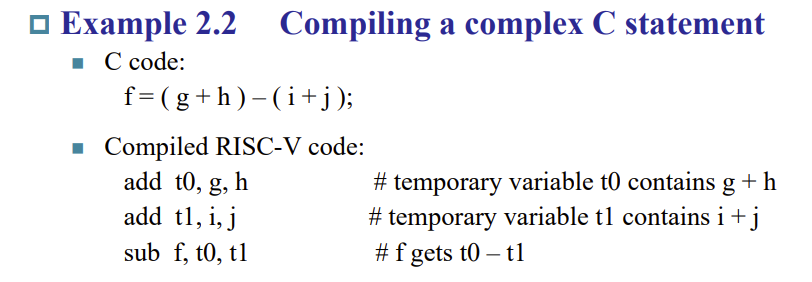
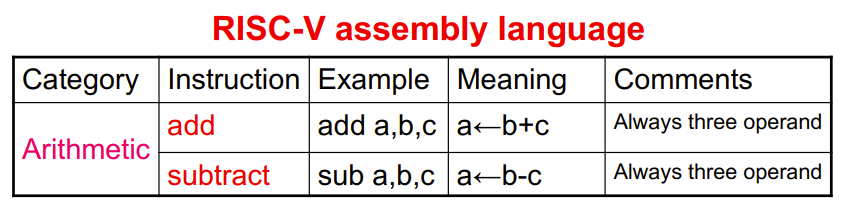
2.2 Arithmetic Operations
- Every computer should perform arithmetic
- Only one operation per instruction
- Add and subtract, three operands
- Two sources and one destination
- add a, b, c // a gets b + c
- a, b, c is address where stores number
- 用地址速度更快
- 数据都存在寄存器里
- All arithmetic operations have this form
- Design Principle 1: Simplicity favors regularity
- 精简有利于规律化
2.3 Operands
- Arithmetic instructions use register operands
- RISC-V has a 32 × 64-bit register file
- Use for frequently accessed data
- 64-bit data is called a “doubleword”
- 32 x 64-bit general purpose registers x0 to x31
- 32-bit data is called a “word”
- Design Principle 2: Smaller is faster
RISC-V Registers
需要记忆,实验用
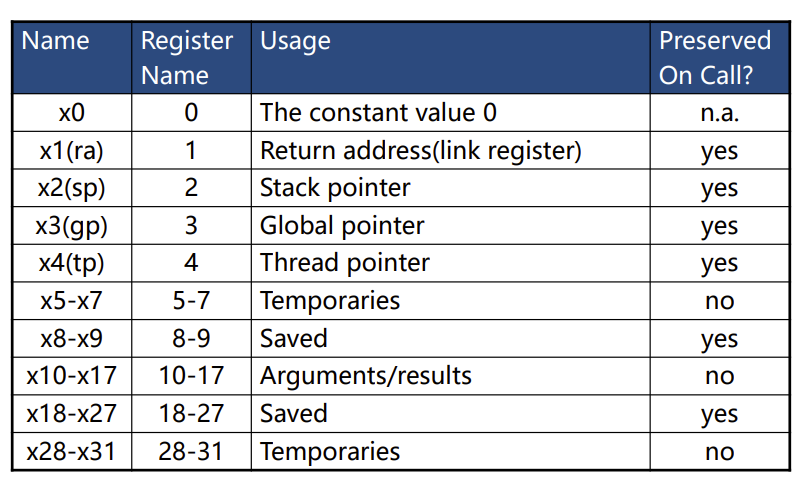
- x0可以用于运算,但不会改变,永远是0

Memory Operands
- Main memory used for composite data‘
- e.g. Arrays, structures, dynamic data
- To apply arithmetic operations:
- Load values from memory into registers
- Store result from register to memory
- Memory is byte addressed
- Each address identifies an 8-bit byte
- 64位8byte占8个地址
- RISC-V is Little Endian
- 小端模式
- 一个数存储于多个byte,约定最小位放在最小地址指向byte
- Least-significant byte at least address of a word
- Big Endian: most-significant byte at least address
- 小端模式

- RISC-V does not require words to be aligned in memory
- Unlike some other ISAs

Endianness/byte order