Lecture 4.2
期末要求
100%!!!!!!!必考
将C代码翻译为机器码
将机器码翻译为C代码
Memory Operand Example
看上面的三行汇编,x开头的都是寄存器,因为double word - 8byte一个最小单元空间,所以矩阵中的第8个空间用8*8=64表示;96同理。
读取的时候以byte为单位。
ld -> load
sd - >store
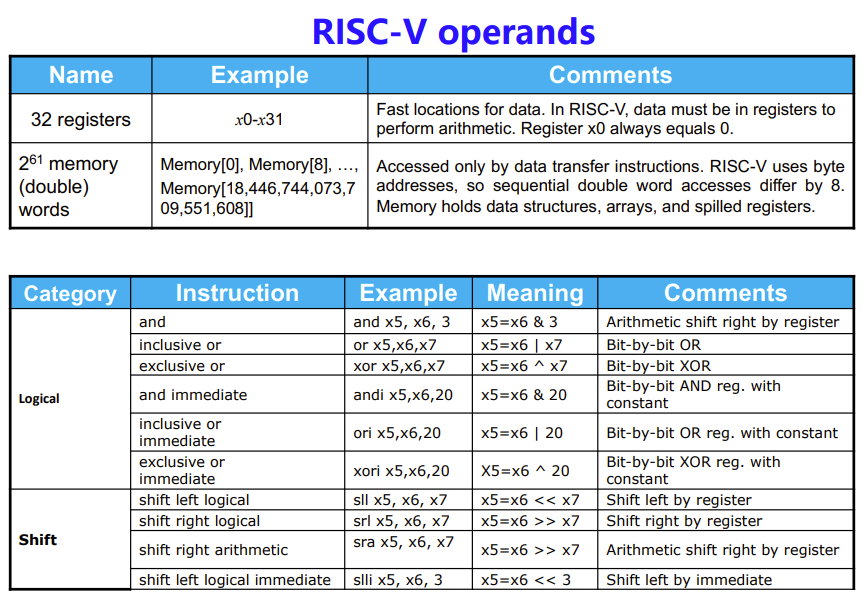
Register vs. Memory
- Operating on memory data requires loads and stores
- More instructions to be executed
- Compiler must use registers for variables as much as possible
- Only spill to memory for less frequently used variables
- Register optimization is important!
Constant or immediate Operands
Immediate
- 立即数
- Avoids the load instruction
- Constant zero: a register x0
- Offer versions of the instruction
- addi x22, x22, 4 // x22= x22+ 4
- 类指令还有 addu 无符号数
- Design Principle 3: Make common case fast
Brief summary
之前学了五条指令
不用死记,用多了就行,还可以查表
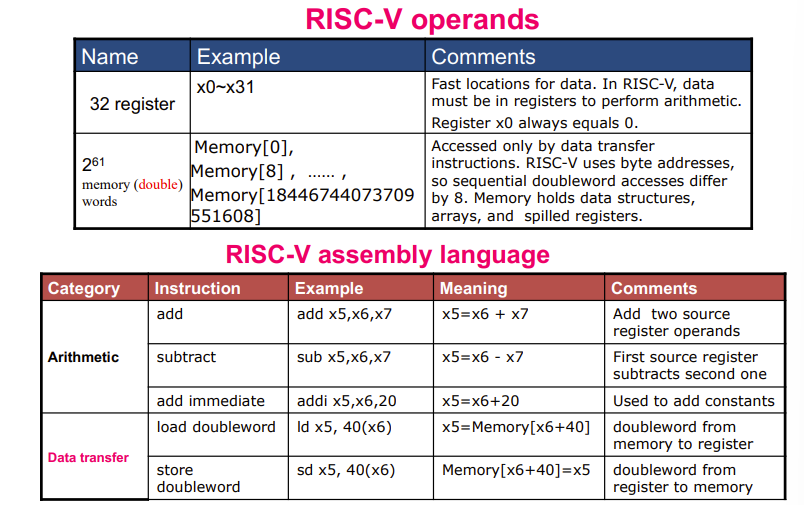
\(2^{61}\)是指可以访问到的空间数量,是因为64位(字长64bit)寄存器多有多\(2^{64}\)个地址,然后因为CPU能访问的最小空间是双子(\(2^3\)),得减去3个bit
2.4 Signed and unsigned numbers
Sign Extension

2.5 Representing Instructions
- Mapping registers into numbers
- map registers x0 to x31 onto registers 0 to 31
- RISC-V instructions
- Encoded as 32-bit instruction words
- All instructions in RISC-V have the same length
- Small number of formats encoding operation code (opcode), register numbers
- Regularity
- Encoded as 32-bit instruction words
接下来介绍RISC-V的几类指令:R型、I型
Signed vs. Unsigned
所有指令后面都可以加个
u

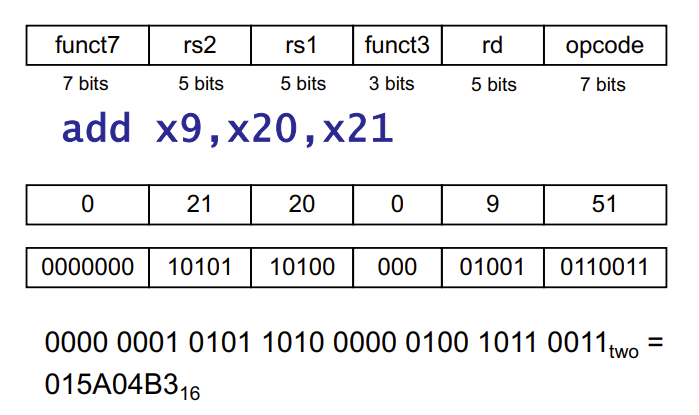
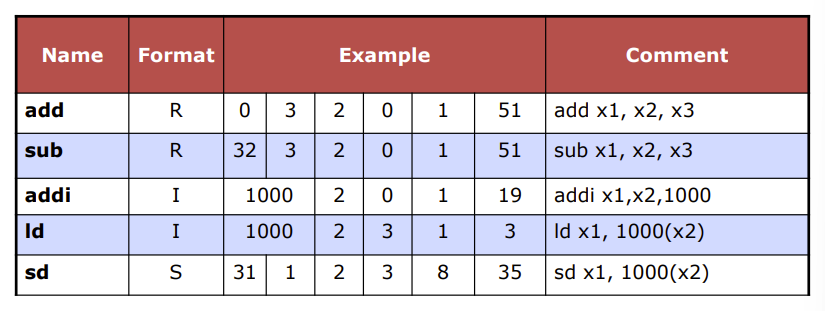
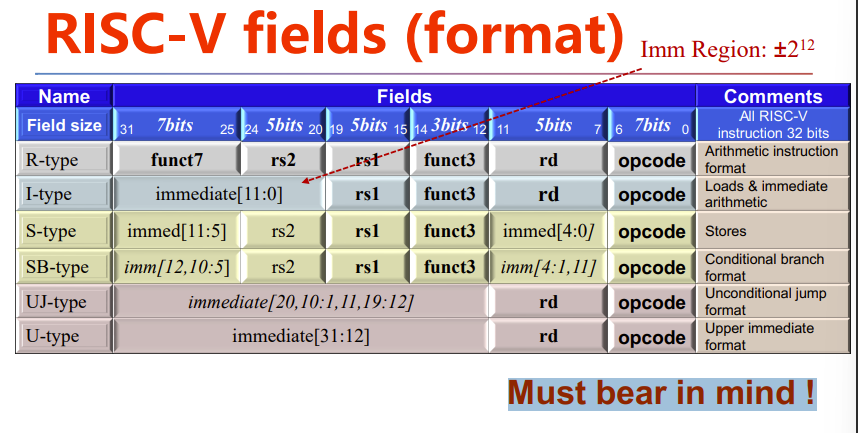
RISC-V R-Format Instructions
R 型指令名称的由来是“Register-to-Register”的缩写,即“寄存器到寄存器”。
I 型指令用于执行立即数到寄存器的操作。

- Instruction field
- opcode: operation code
- rd: destination register number
- funct3: 3-bit function code (additional opcode)
- rs1: the first source register number
- rs2: the second source register number
- funct7: 7-bit function code (additional opcode)
- opcode + funct3 + func7 = add
- opcode \(\neq\) add, opcode > add
为什么要拆开为三个部分共同决定操作
因为这样硬件设计更简单,还能归纳电路,让运行速度更快
- Design Principle 3
- Good design demands good compromises
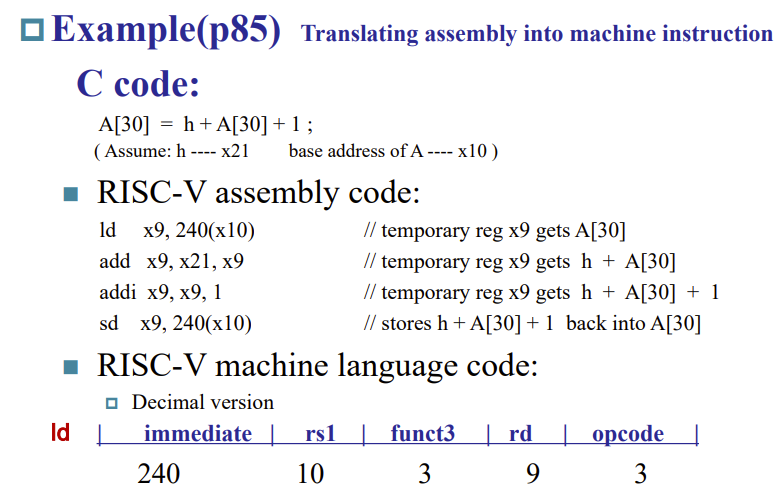
Example: Translating Assembly Code
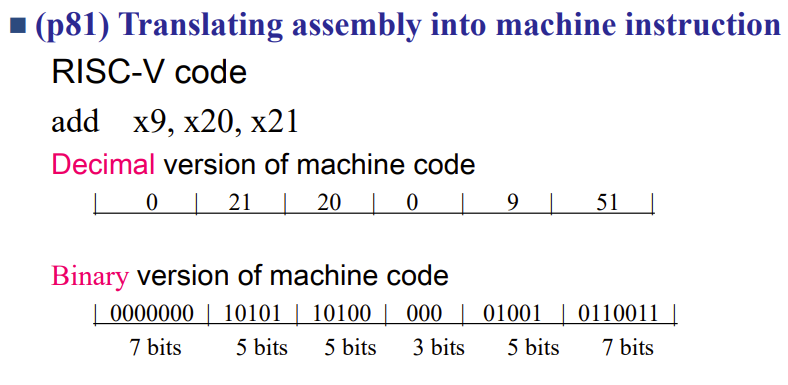
注意register是5bit,因为真的就只有32个
为什么不多几个?因为指令总长度固定为32bit,需要留给其它部分
R-format Example
R型指令,包含add, sub等待
\(opcode=51\)
RISC-V I-Format Instructions
I 型指令名称的由来是“Immediate-to-Register”的缩写,即“立即数到寄存器”。

- rs1: source or base address register number
- immediate: constant operand, or offset added to base address
- 2s-complement, sign extended
- Design Principle 3: Good design demands good compromises
- Different formats complicate decoding, but allow 32-bit instructions uniformly
- Keep formats as similar as possible
可见立即数是\(2^{12}\)的
即I型指令结构上与R型指令十分接近

为什么rs2在rs1左边,因为我们不希望改变rs1,但是rs2可以改变
为什么opcode在右边,因为知识产权的问题,对机器在左边和右边都无所谓
RISC-V S-Format Instructions
S 型指令名称的由来是“Store”的缩写,即“存储”。
S 型指令用于将寄存器中的数据存储到内存中。
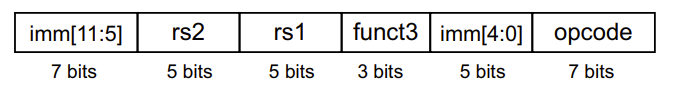
- rs1: base address register number
- rs2: source operand register number
- immediate: offset added to base address
- Split as [15:11] and [4:0] so that rs1 and rs2 fields always in the same place
目标是内存,所以没有rd
imm拆分就是为了保持各类指令结构相似

RISC-V instruction encoding Example
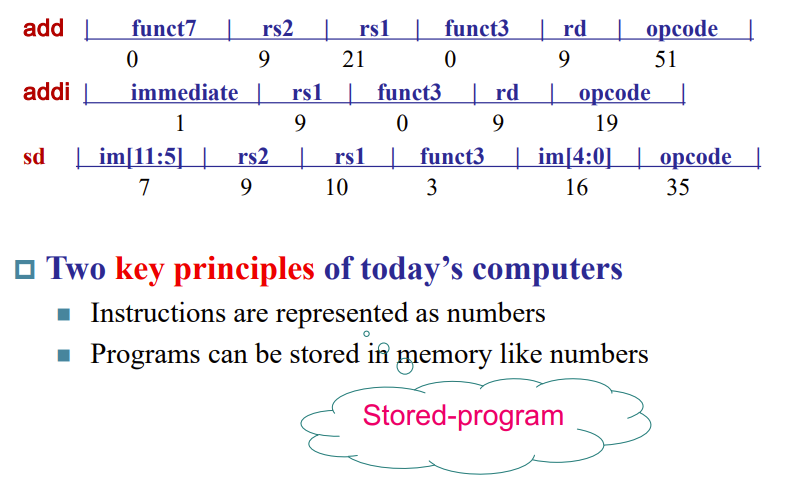
RISC-V fields (format)
总表
Must bear in mind !
2.6 Logical Operations
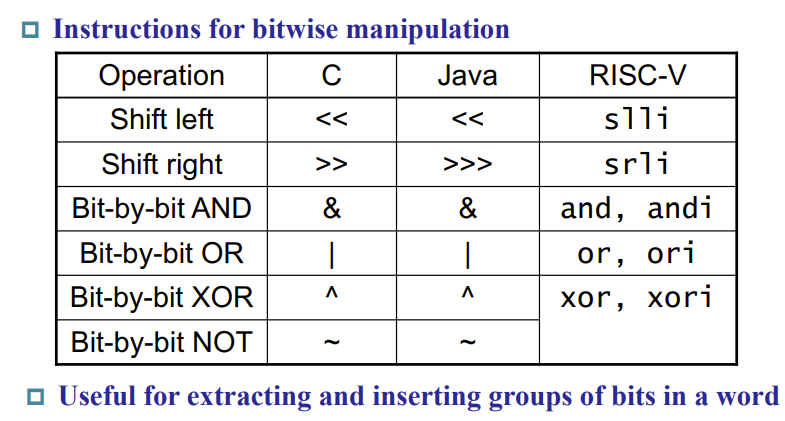
Shift Operations

AND Operations
and 可以用于提取数据,如下面x9通过x11提取了x10的部分数据
Useful to mask bits in a word
Select some bits, clear others to 0

OR Operations
or则可以对一些数据进行修改
Useful to include bits in a word
Set some bits to 1, leave others unchanged

XOR Operations
比较不同

summary
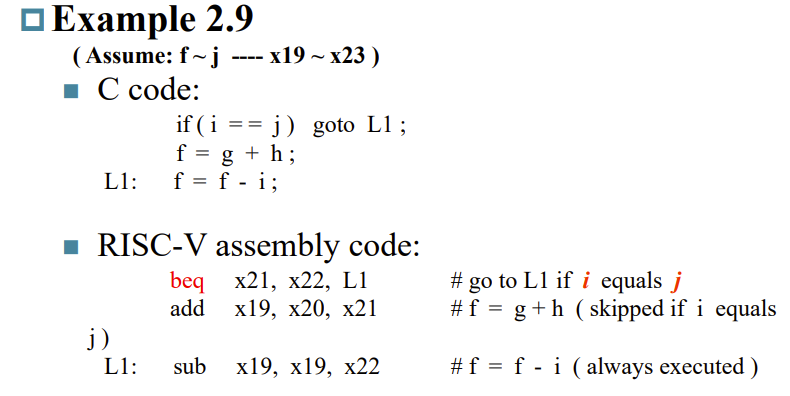
2.7 Instructions for making decisions
- Branch instructions
- Branch to a labeled instruction if a condition is true
- Otherwise, continue sequentially
- exp
beq rs1, rs2, L1: if (rs1 == rs2) branch to instruction labeled L1bne rs1, rs2, L1: if (rs1 != rs2) branch to instruction labeled L1
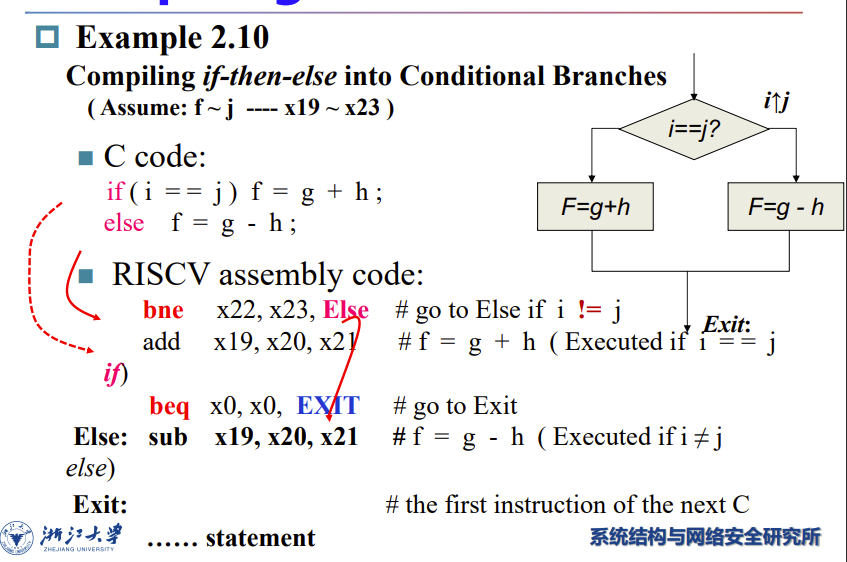
Compiling an if statement
Compiling if-then-else
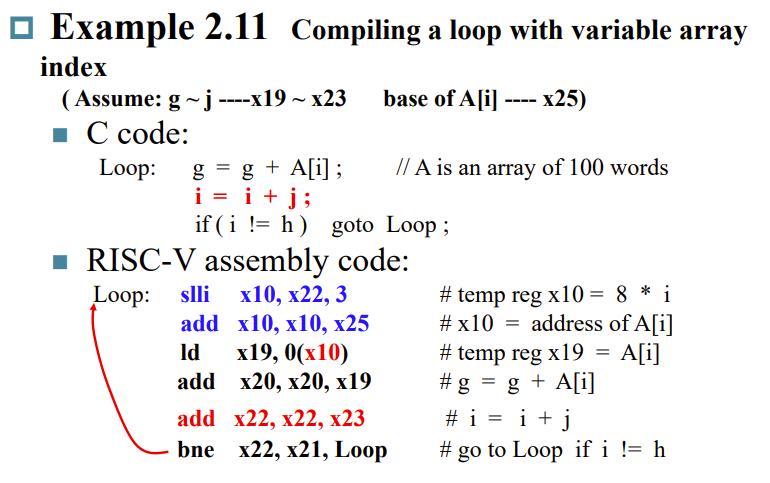
Compiling LOOPs
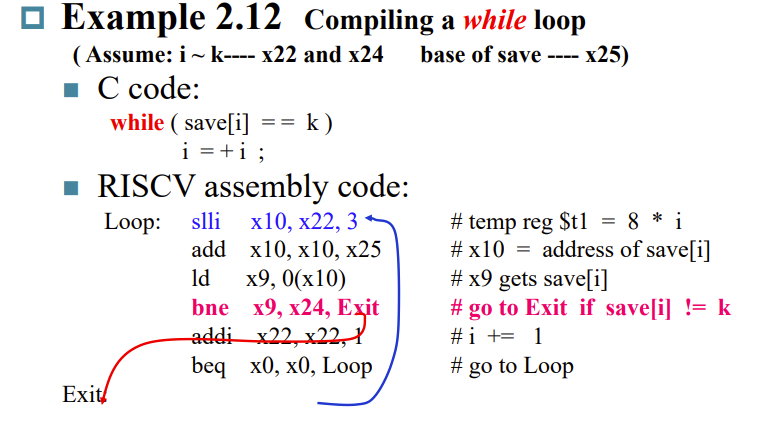
Compiling while
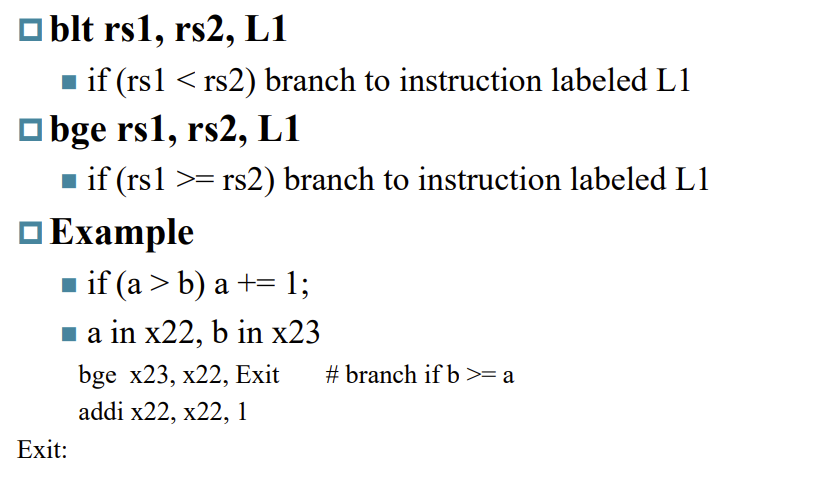
More Conditional Operations
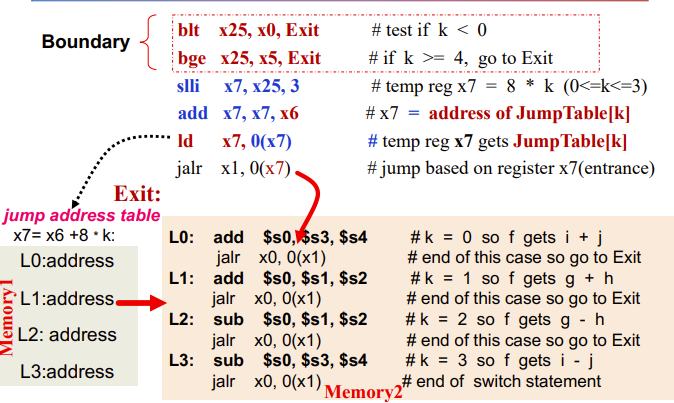
Hold out Case/Switch

Jump register & jump address table
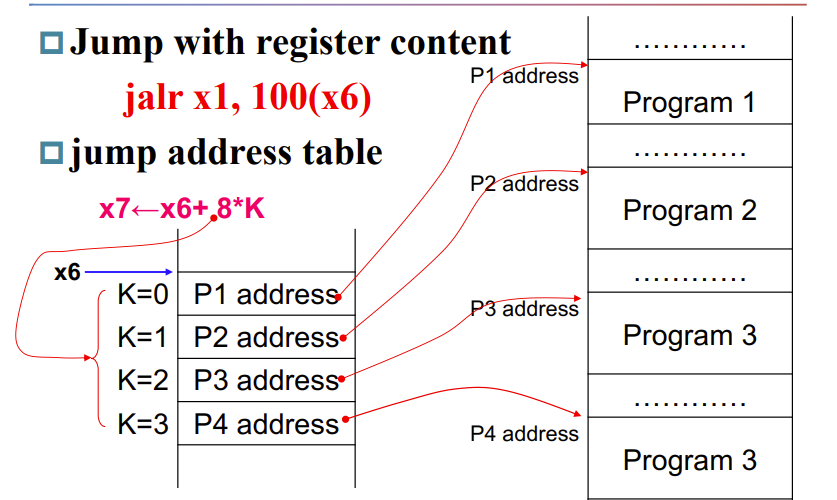
jalr即无判断直接跳转到寄存器
对于jalr x1, 100(x6),x1是返回地址,因为循环完还得出来,这个地址就是告诉程序回到哪;100(x6)表示要跳到哪
RISC-V assembly code