REVIEW 2 Language of the Machine
对应wdCO第四章,还没看过
Concepts
Instruction formats

RISC-V Registers
-
RISC-V has a 32 × 64-bit register file
- 64-bit data is called a “doubleword”
- 32-bit data is called a “word”
- 32 x 64-bit general purpose registers x0 to x31
- 64-bit data is called a “doubleword”
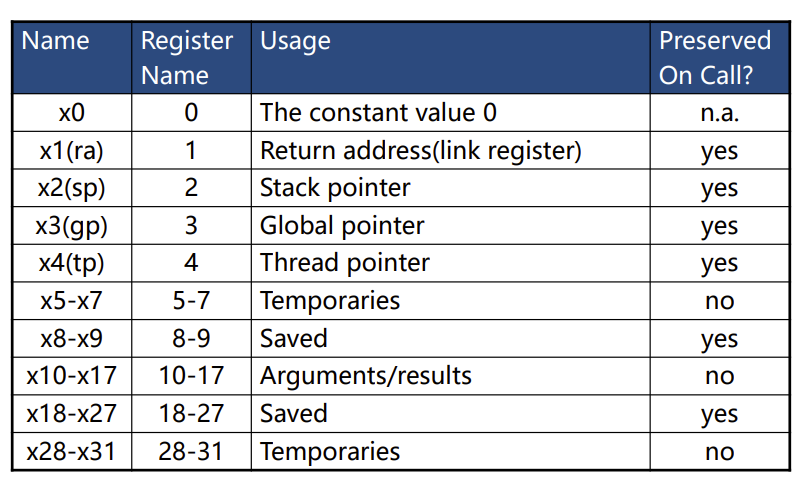
- x0可以用于运算,但不会改变,永远是0
Operations
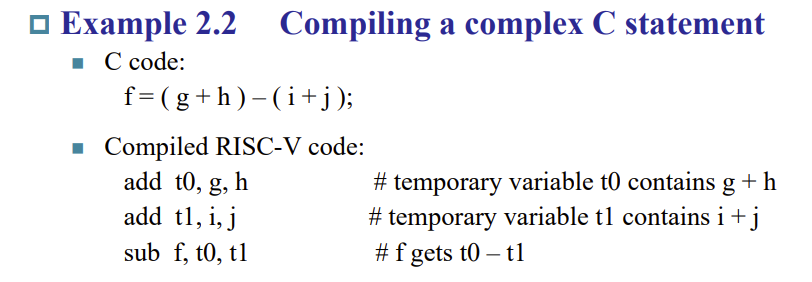
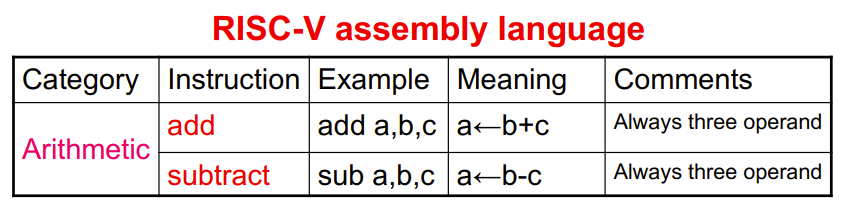
Arithmetic Operations
- Only one operation per instruction
- Add and subtract, three operands
- Two sources and one destination
- add a, b, c // a gets b + c
- a, b, c is address where stores number
- 用地址速度更快
- 数据都存在寄存器里
- All arithmetic operations have this form
- a, b, c is address where stores number
Memory Operands
-
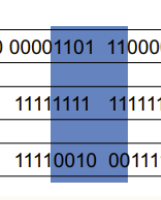
Memory is byte addressed
- Each address identifies an 8-bit byte
- 64位 = 8byte,占8个地址为一组
RISC-V does not require words to be aligned in memory
即一个地址一定指向8byte的空间,这是最小单元,不可分割
- RISC-V is Little Endian
- 小端模式
- 如果一个数需要存储于多个byte,那么我们将小的位存放在小的地址指向的byte
- Least-significant byte at least address of a word
- 小端模式
Big Endian: most-significant byte at least address
地址编号小的是小地址,大的是大地址。也成为高低地址
数据地位就是小的位,略
注意,一个储存单位是1byte,有8bit
每个byte里面位的顺序不受大端/小段模式的影响
是byte的顺序受影响
读取一定是从小地址开始读取,区别是从低往高放,还是从高往低放
Memory Operand Example
ld和sd是内存操作指令

三行汇编,x开头的都是寄存器。
因为double word - 8byte一个最小单元空间,所以矩阵中的第8个空间用8*8=64表示;96同理。
偏移量单位是byte。读取的时候也是以byte为单位。
Constant or immediate Operands
- 立即数 Immediate
- Avoids the load instruction
- Constant zero: a register x0
- 需要再指令后面加个
i- addi
- 类似的有无符号数 addu
Signed and unsigned numbers
所有指令后面都可以加个
u,表示无符号运算
Sign Extension
因为最小储存单元为byte,如果要拓展储存空间,就会有大量空闲bit
- 无符号数就填充0
- 有符号数正0负1
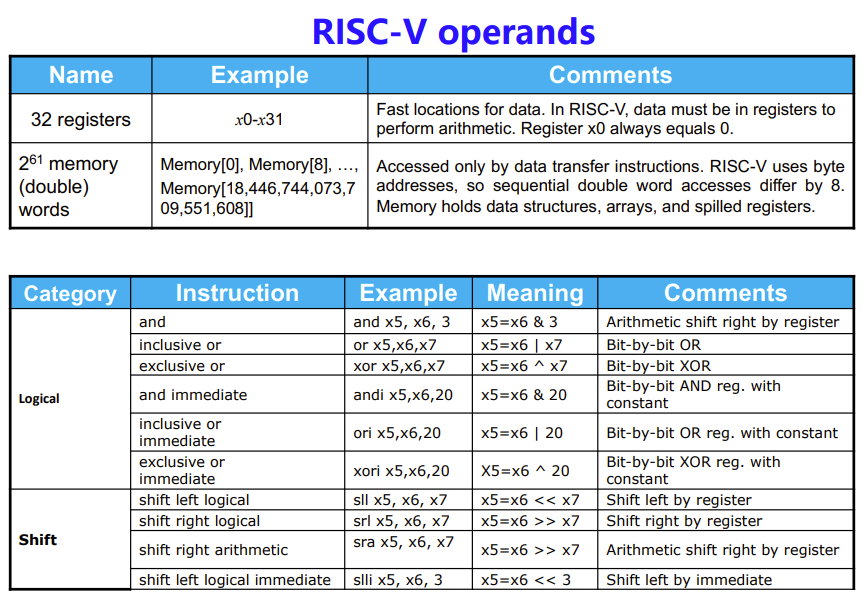
下表汇总了上面的内容,包括32个reg,双字下可用的的内存,五个指令
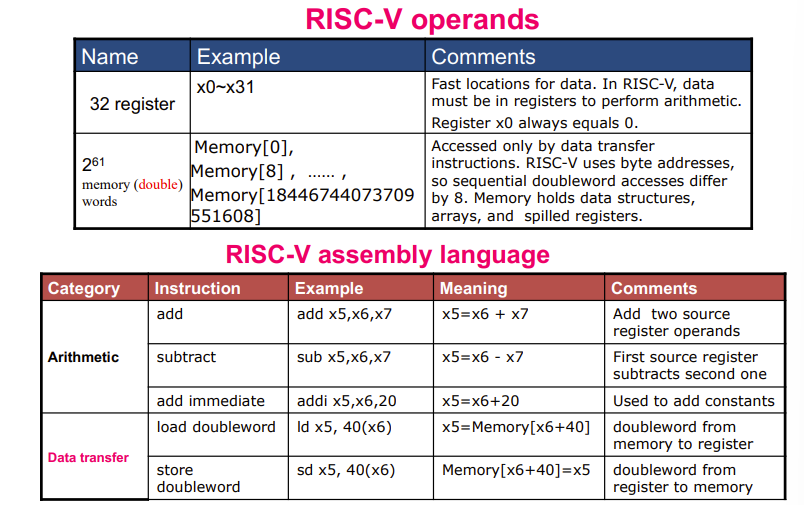
\(2^{61}\)是指可以访问到的空间数量,是因为64位(字长64bit)寄存器多有多\(2^{64}\)个地址,然后因为CPU能访问的最小空间是双子(\(2^3\),1byte),得减去3个bit
Signed and unsigned numbers
所有指令后面都可以加个
u,表示无符号运算

Sign Extension
因为最小储存单元为byte,如果要拓展储存空间,就会有大量空闲bit
- 无符号数就填充0
- 有符号数就填充1


Representing Instructions
注意我们学的都是RISC-V
- All instructions in RISC-V have the same length 32-bit
- RISC-V指令可分为以下几类
- R 型:Reg与Reg的交互
- I 型:Imm到Reg的交互
- S 型:Store,内存交互
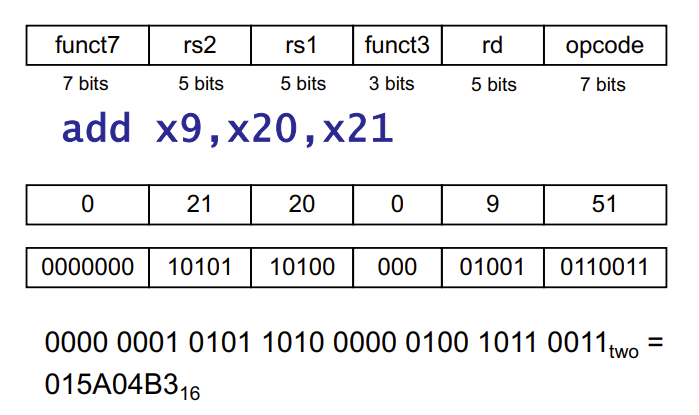
R-Format Instructions
R 型指令名称的由来是“Register-to-Register”的缩写,即“寄存器到寄存器”。

- opcode: operation code
- rd: destination register number
- funct3: 3-bit function code (additional opcode)
- rs1: the first source register number
- rs2: the second source register number
- funct7: 7-bit function code (additional opcode)
- opcode + funct3 + func7 = add
- opcode \(\neq\) add, opcode > add
- opcode $= $ add, sub, ...
R-format Example
包含add, sub等
\(opcode=51\)
I-Format Instructions
I 型指令名称的由来是“Immediate-to-Register”的缩写,即“立即数到寄存器”。

与R型的区别就是
funcy7,rs2被合并为了immediate作为新的二号操作对象可见立即数容量是\(2^{12}\)
- rs1: source or base address register number
- immediate: constant operand, or offset added to base address
- 2s-complement, sign extended

RISC-V S-Format Instructions
S 型指令名称的由来是“Store”的缩写,即“存储”,用于将寄存器中的数据存储到内存中。
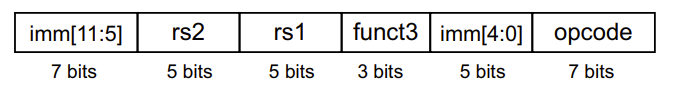
- rs1: base address register number
- rs2: source operand register number
- immediate: offset added to base address
- Split as [15:11] and [4:0] so that rs1 and rs2 fields always in the same place
与下图的R型对比,可见是
funct7,rd被替换为了imm
目标是内存,所以没有rd(reg)

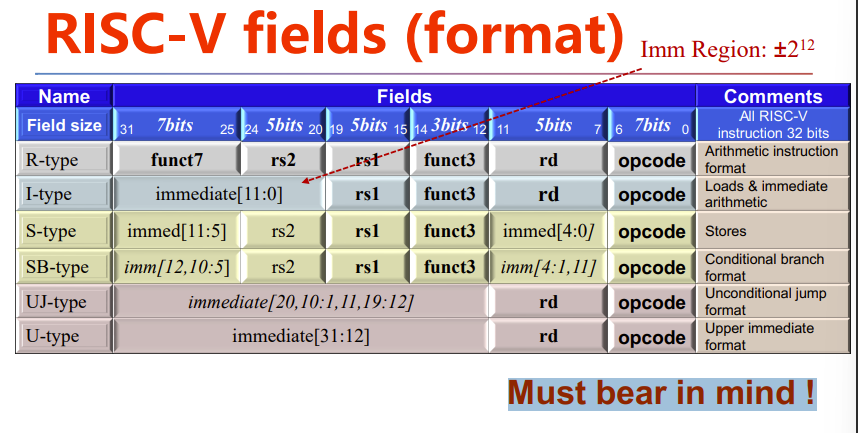
RISC-V fields (format)
总表
Logical Operations
Shift

imm: how many positions to shift
不管左移右移都是用0填充
用来进行乘法与除法
slli- shift left
- multiplies by \(2^i\)
srli- shift right
- devides by \(2^i\)
AND
and 可以用于 提取/选取 数据
Select some bits, clear others to 0
OR
or则可以对一些0数据进行修改
Set some bits to 1, leave others unchanged
XOR
用于比较两段数据的不同
Instructions for making decisions
- Branch instructions
- Branch to a labeled instruction if a condition is true
- Otherwise, continue sequentially
- Example
beq rs1, rs2, L1if (rs1 == rs2) branch to instruction labeled L1bne rs1, rs2, L1if (rs1 != rs2) branch to instruction labeled L1
beq, bnq可以实现以下逻辑
各类逻辑的实现
if

if-then-else

关键点是
beq x0, x0, EXIT
LOOPs

while

More Conditional Operations
blt rs1, rs2, L1if(rs1<rs2) L1- 大于需要用EXIT实现

bge rs1, rs2, L1if(rs1\(\ge\) rs2) L1- 同上
Jump
jalr即无判断直接跳转到寄存器
对于jalr x1, 100(x6),x1是返回地址,因为循环完还得出来,这个地址就是告诉程序回到哪;100(x6)表示要跳到哪
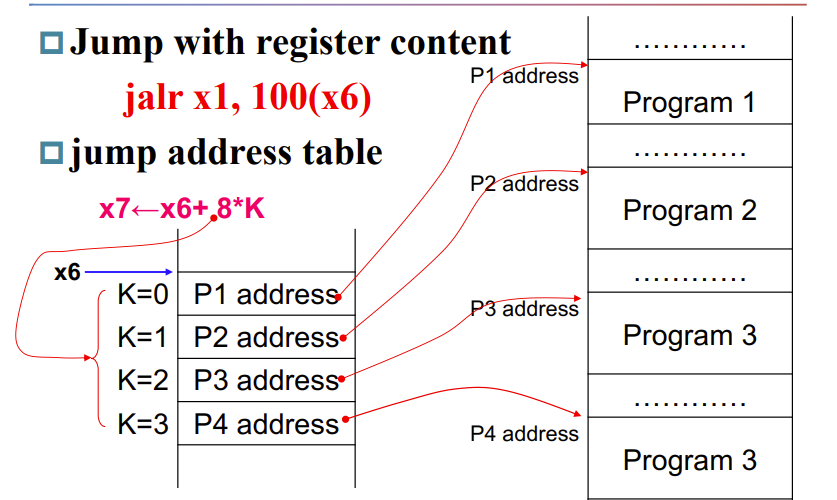
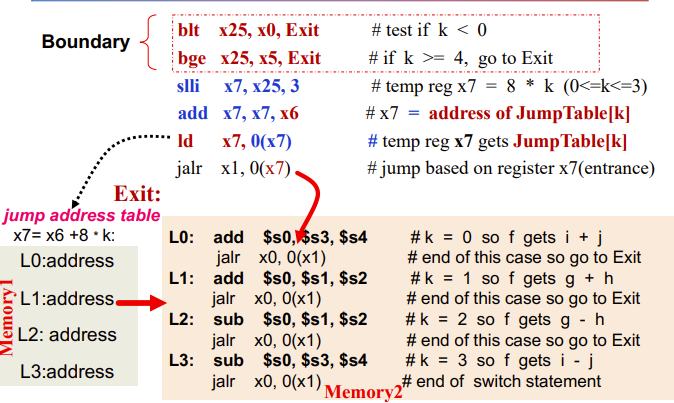
switch/case 逻辑就用 jump address table
EXAMPLE
Basic Blocks
跳转让优化变得很困难,因为跳转是未知的、不确定的。
为了方便预测并优化,将指令集合分为多个basic block
- 每个block里面不会进行jump,还有一些其它的性质:
A basic block is a sequence of instructions with
- No embedded branches (except at end)
- No branch targets (except at beginning)

Supporting Procedures
lecture 5