2.6
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 437 个字 :fontawesome-solid-code: 88 行代码 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
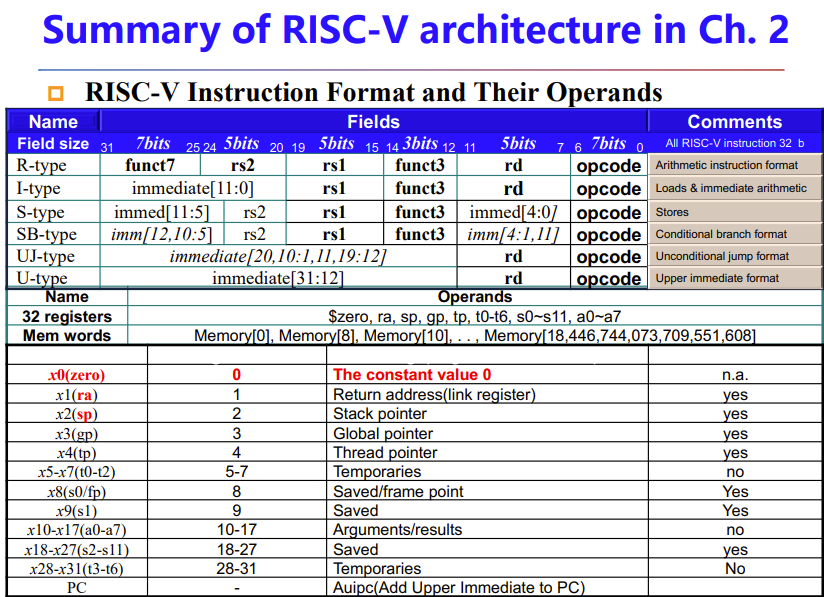
Disassembly
机器码转汇编
这个咩办法,记格式记操作码
下面大部分不用记,看一眼就行,后面37考试会给,当然还是要等通知
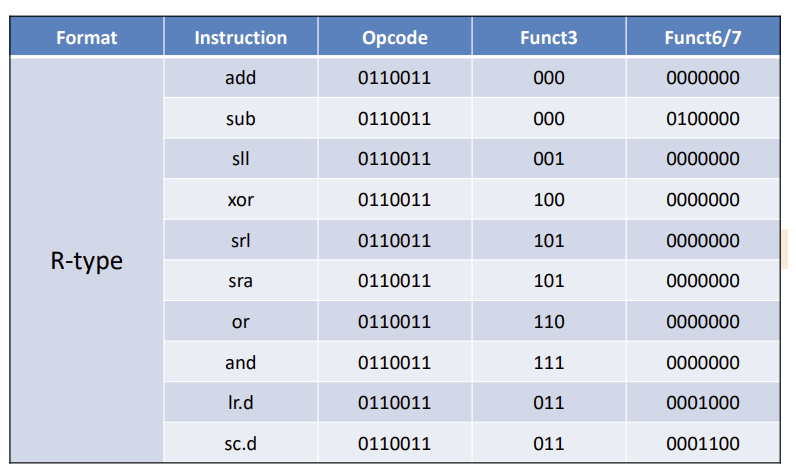
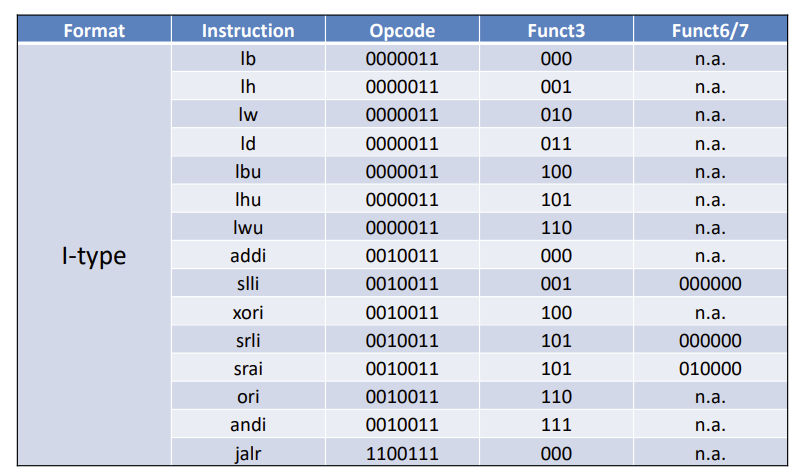
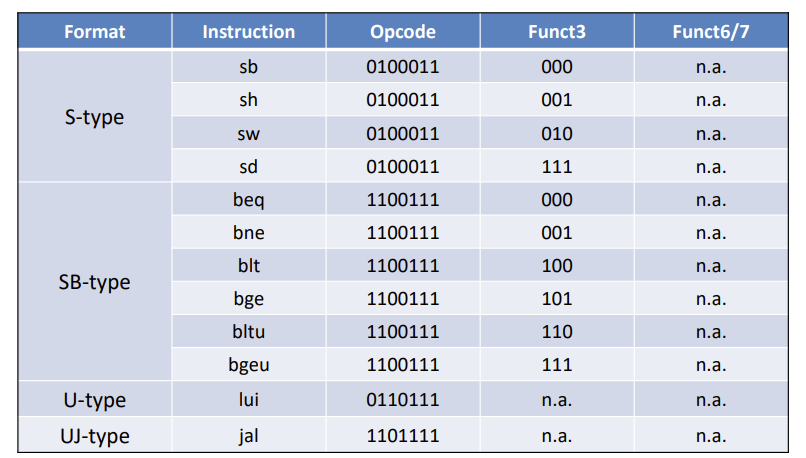
Synchronization
上面是基本,以下是拓展
多核并行使用内存,需要同步,无法单独用软件实现
解决方案:
- 让读写操作原子化
- 一块地址读取后锁住
lr.d,直到发生存储操作sc.d
Example 1: atomic swap (to test/set lock variable)
again:
lr.d x10, (x20)
sc.d x11, (x20), x23 // X11 = status
bne x11, x0, again // branch if store failed
addi x23, x10, 0 // X23 = loaded value
Example 2: lock
addi x12, x0, 1 // copy locked value
again2:
lr.d x10, (x20) // read lock
bne x10, x0, again2 // check if it is 0 yet
sc.d x11, (x20), x12 // attempt to store
bne x11, x0, again2 // branch if fails
Unlock
Translating and starting a program
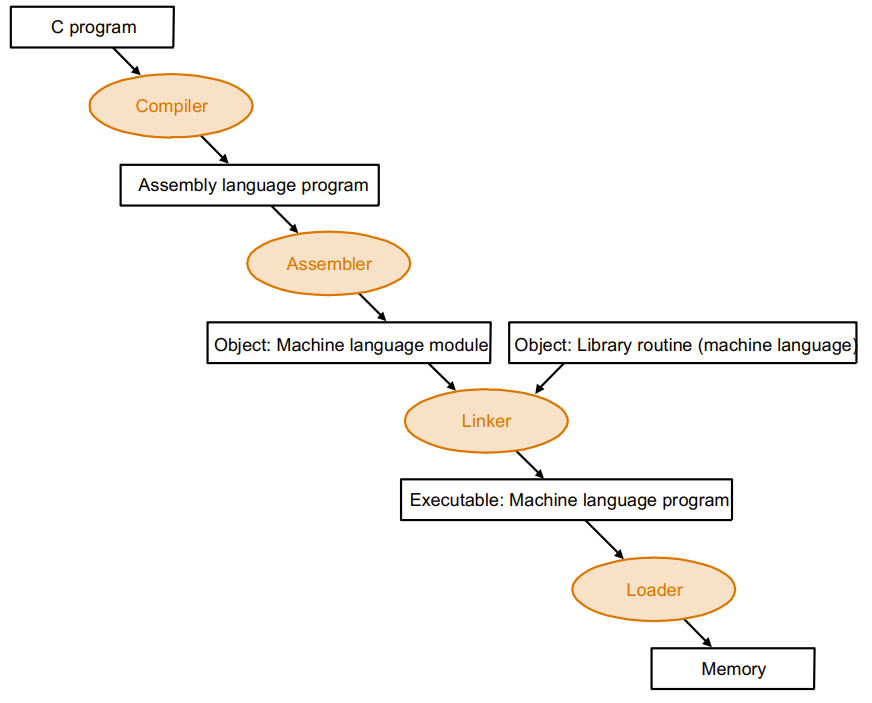
一个程序的结构如下
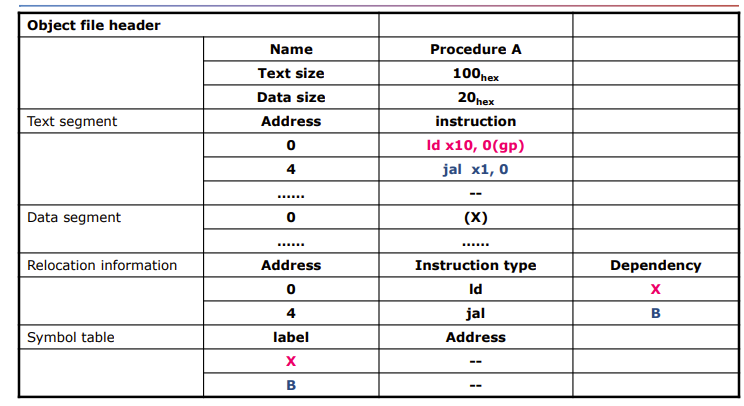
Dynamic Linking
就是只有程序使用时才开始链接
静态是程序已经完成了链接写进了机器码、
还有个Lazy Linkage就是用到这个库才将这个库链接进来
A C Sort Example To Put it All Together
- Three general steps for translating C procedures
- Allocate registers to program variables
- Produce code for the body of the procedures
- Preserve registers across the procedures invocation
Procedure swap
void swap ( long long v[ ] , size_t k )
{
long long temp ;
temp = v[ k ] ;
v[ k ] = v[ k + 1 ] ;
v[ k + 1 ] = temp ;
}
- Register allocation for swap
- v ---- x10
- k ---- x11
- temp ---- x5
- swap is a leaf procedure, nothing to preserve
swap:
slli x6, x11, 3 // x6 = k * 8
add x6, x10, x6 // x6 = v + (k * 8)
ld x5, 0(x6) // x5 ← v[k]
ld x7, 8(x6) // x7 ← v[k + 1]
sd x7, 0(x6) // v[k + 1] → v[k]
sd x5, 8(x6) // v[k] → v[k + 1]
jalr x0, 0(x1) // return to calling routine
Procedure bubble sort
void sort (long long v[ ] , size_t n )
{
size_t i , j ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i + = 1 ) {
for ( j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && v[j] > v[j+1] ; j -= 1 )
swap ( v , j ) ;
}
}
- Register allocation for sort
- v ---- x10
- n ---- x11
- i ---- x19
- j ---- x20
- Passing parameters in sort
- Preserving registers in sort
- x1 , x19, x20, x21, x22
这程序有嵌套循环,我们先看外循环
对于循环,我们先不看内容,而是先实现骨架,内容直接跳转即可
The Outer Loop
li x19, 0 // i = 0
for1tst:
bge x19, x11, exit1 // go to exit1 if x19 ≥ x11 (i ≥ n)
...(body of outer for-loop)
addi x19, x19, 1 // i += 1
j for1tst // branch to test of outer loop
exit1:
The Inner Loop
addi x20, x19, -1 // j = i − 1
for2tst:
blt x20, x0, exit2 // go to exit2 if X20 < 0 (j < 0)
slli x5, x20, 3 // reg x5 = j * 8
add x5, x10, x5 // reg x5 = v + (j * 8)
ld x6, 0(x5) // reg x6 = v[j]
ld x7, 8(x5) // reg x7 = v[j + 1]
ble x6, x7, exit2 // go to exit2 if x6 ≤ x7
mv x21, x10 // copy parameter x10 into x21
mv x22, x11 // copy parameter x11 into x22
mv x10, x21 // first swap parameter is v
mv x11, x20 // second swap parameter is j
jal x1, swap // call swap
addi x20, x20, -1 // j –= 1
j for2tst // branch to test of inner loop
exit2:
然后是整个程序的框架
//Saving registers
sort:
addi sp, sp, -40 // make room on stack for 5 registers
sd x1, 32(sp) // save return address on stack
sd x22, 24(sp) // save x22 on stack
sd x21, 16(sp) // save x21 on stack
sd x20, 8(sp) // save x20 on stack
sd x19, 0(sp) // save x19 on stack
......Procedure body{Outer loop {Inner loop} }
//Restoring registers
exit1:
ld x19, 0(sp) // restore x19 from stack
ld x20, 8(sp) // restore x20 from stack
ld x21, 16(sp) // restore x21 from stack
ld x22, 24(sp) // restore x22 from stack
ld x1, 32(sp) // restore return address from stack
addi sp, sp, 40 // restore stack pointer
jalr x0, 0(x0) // return to calling routine
Arrays vs. Pointers
指针比array更高效
- Array indexing involves
- Multiplying index by element size
- Adding to array base address
- Pointers correspond directly to memory addresses
指针可以直接操作物理地址,而数组需要计算出地址偏移量
Compiler can achieve same effect as manual use of pointers
编译器会优化数组的操作
*2.16 Real Stuff: MIPS Instructions
精简指令集架构
MIPS: commercial predecessor to RISC-V
2.17 Real Stuff: The Intel x86 ISA
复杂指令集架构