4.4
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 388 个字 :fontawesome-solid-code: 13 行代码 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
Exceptions and Interrupts
“Unexpected” events requiring change in flow of control
- Exception: Arises within the CPU
- 异常是CPU内部引起的
- Interrupt: From an external I/O controller
- 中断是外部IO引起的
Handling Exceptions
method-1
纯软件处理
遇到问题,保存当前位置,将相关信息交给专门的程序去统一处理
- Save PC of offending (or interrupted) instruction
- Supervisor Exception Program Counter (SEPC)
- 用于储存当前PC,保证在异常后能跳回来继续执行,以及告诉控制器哪里出错了
- Save indication of the problem
- Supervisor Exception Cause Register (SCAUSE)
- 一组reg,传递异常时的状态,交给OS去处理
- Jump to handler
- Assume at 0000 0000 1C09 0000hex
- 异常处理程序的入口地址
method-2
硬件处理,指用硬件判断异常情况
依旧需要专门的处理软件,但是用硬件先判断是什么异常,根据情况跳到不同程序去处理
Handler Actions
- Read cause, and transfer to relevant handler
- Determine action required
- If restartable
- Take corrective action,use SEPC to return to program
- Otherwise
- Terminate program,Report error using SEPC, SCAUSE, …
举个异常处理的例子:
Consider malfunction on add in EX stage
- Prevent
x1from being clobbered - Complete previous instructions
- Flush add and subsequent instructions
- Set SEPC and SCAUSE register values
- Transfer control to handler
Similar to mispredicted branch. Use much of the same hardware
带有异常处理机制的线路,多了很多 flush:
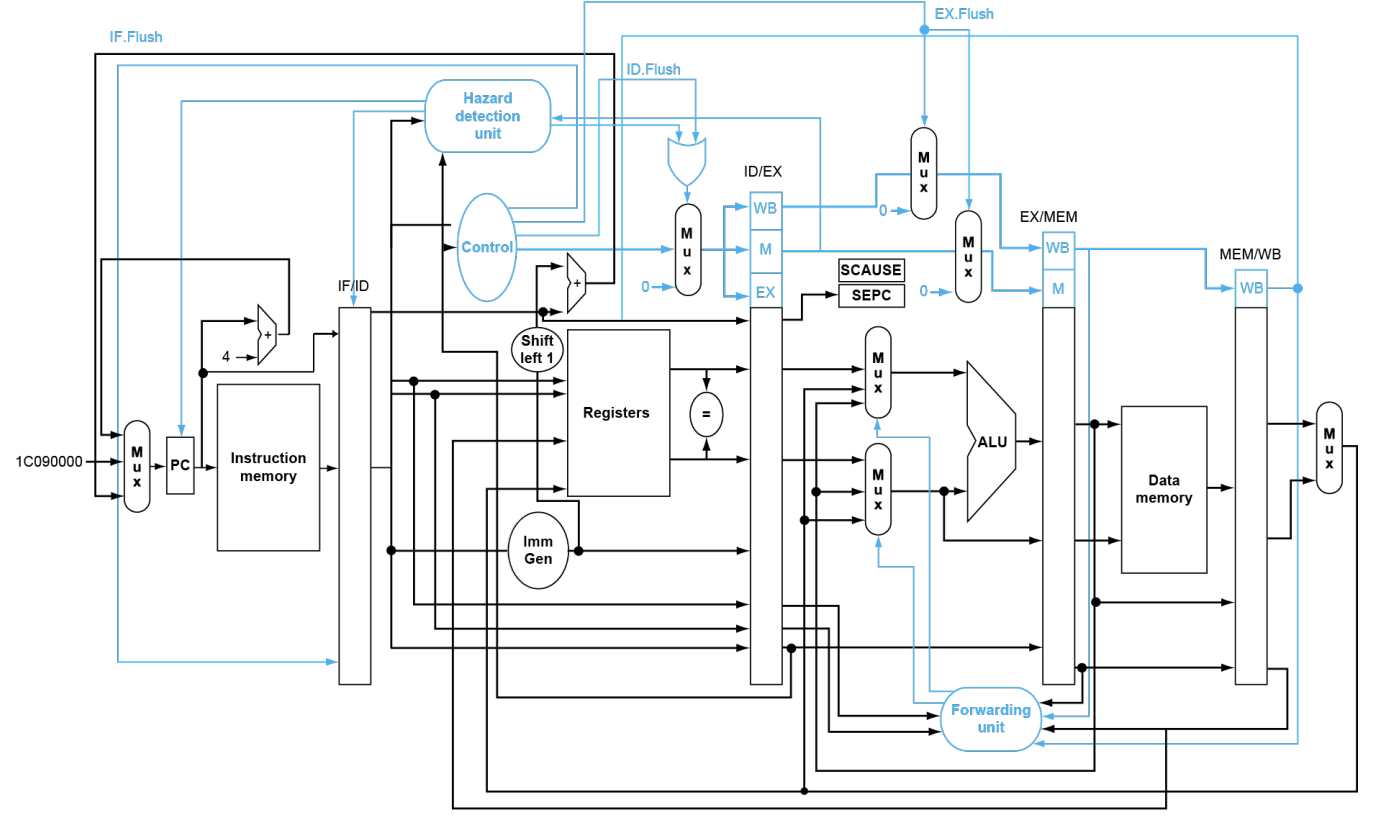
注意SCAUSE和SEPC从ID/EX出来的,实际上不是一点从这出来,这里只是
add出错的情况,其它情况可能从其它reg出来
下面看个例子
40 sub x11, x2, x4
44 and x12, x2, x5
48 orr x13, x2, x6
4c add x1, x2, x1
50 sub x15, x6, x7
54 ld x16, 100(x7)
…
#Handler
1C090000 sd x26, 1000(x10)
1c090004 sd x27, 1008(x10)
…
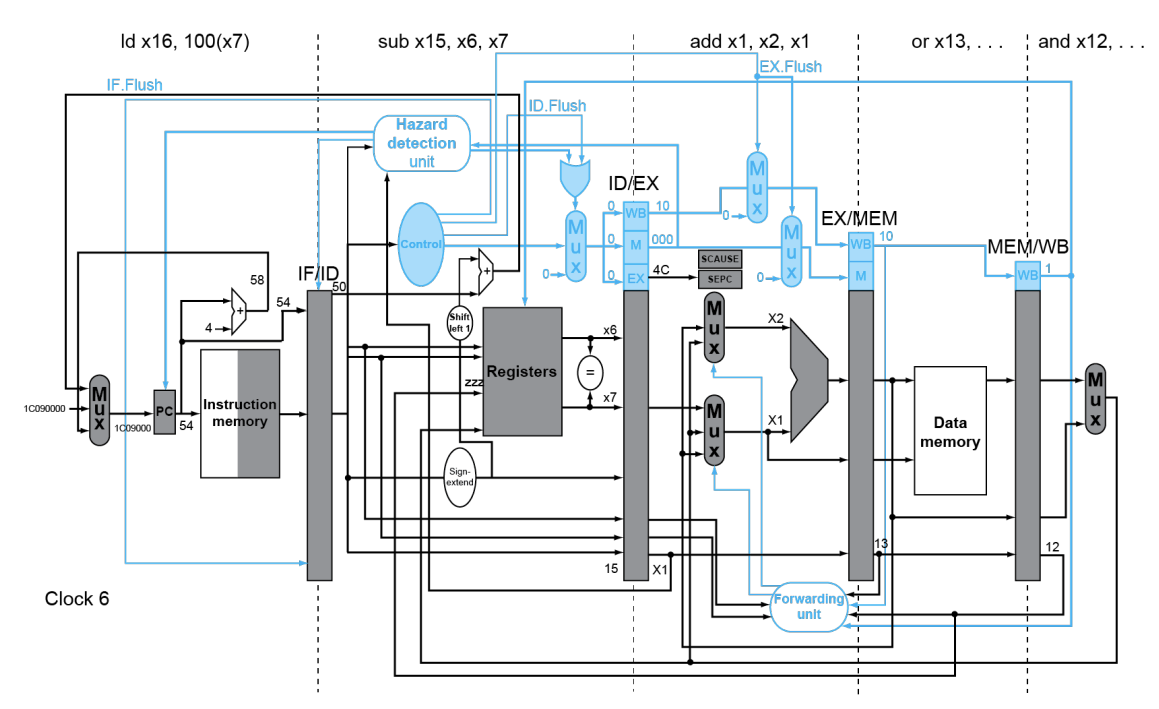
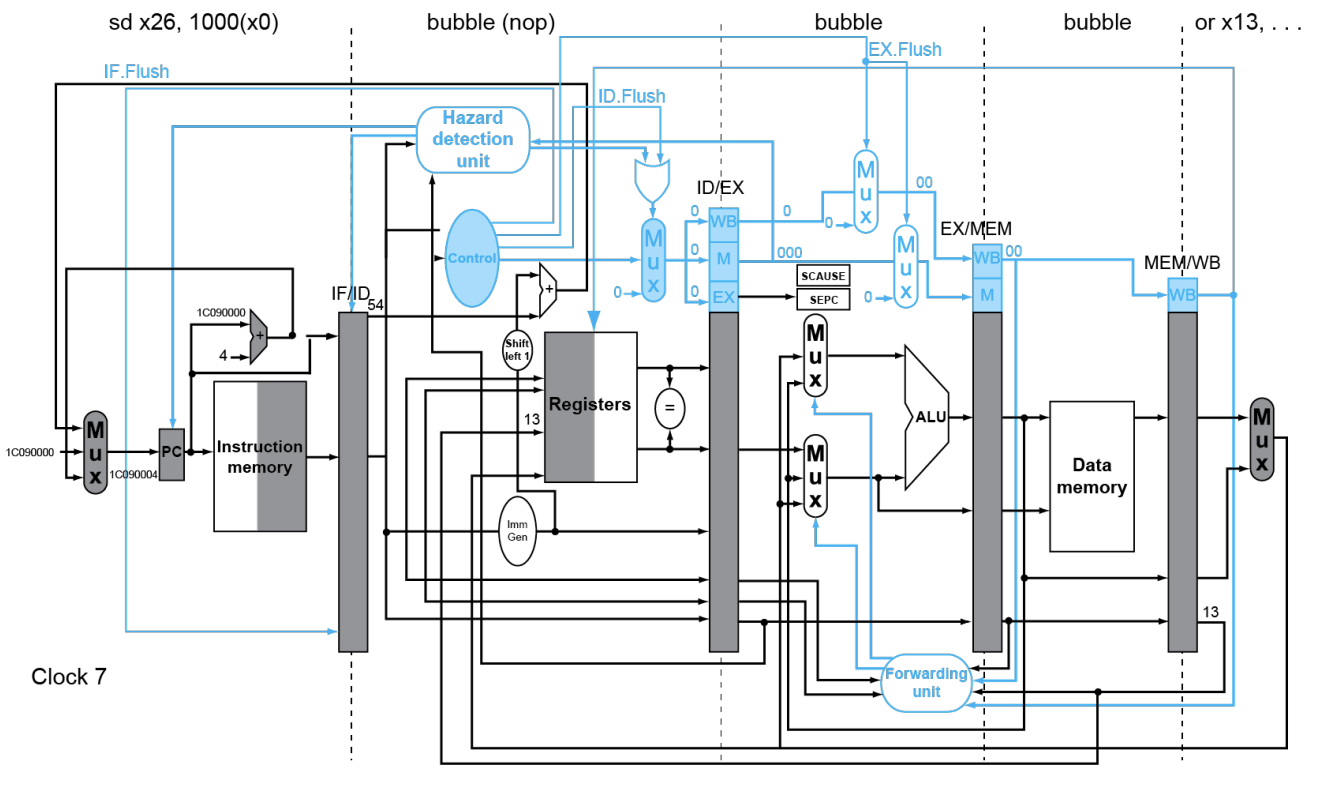
Multiple Exceptions
Pipelining could have multiple exceptions at once
Simple approach: deal with exception from earliest instruction
- Flush subsequent instructions
“Precise” exceptions&Imprecise Exceptions