4.5
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 471 个字 :fontawesome-solid-code: 14 行代码 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP)
指令集并行
- To increase ILP
- Deeper pipeline, as 5 stages in RISCV
- Multiple issue
- 多条流水线组成一个处理器
- Start multiple instructions per clock cycle
多发 - Multiple issue ,同一时间安排多条指令
单周期CPI>1,流水新CPI=1,多发处理器CPI<1
IPC是CPI的倒数,用于描述多发处理器的性能
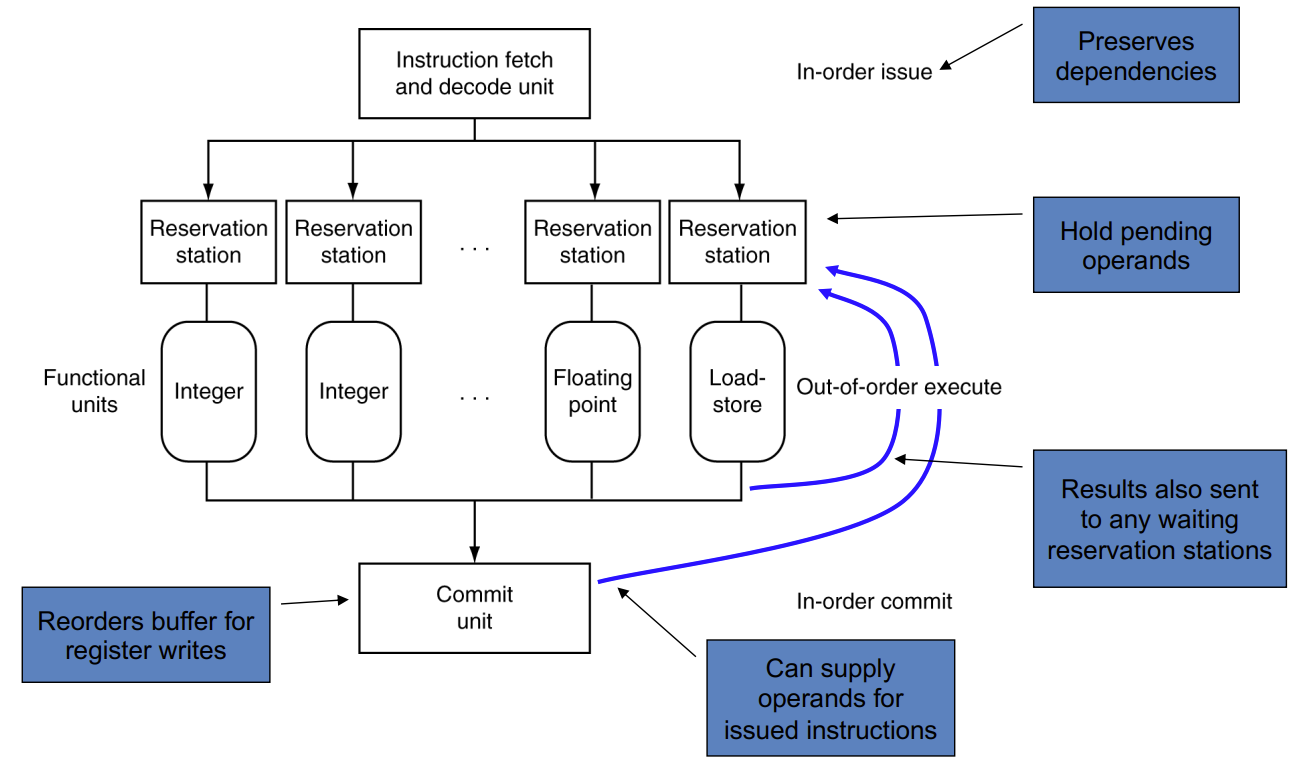
Static Multiple Issue
这一部分重新看PPT Orga_Ch4_Part2_V1.0(2).pdf 80
如何同时安排多条inst开始跑,我们有两种方法
- Static multiple issue
- Compiler groups instructions to be issued together
- Packages them into “issue slots”
- Compiler detects and avoids hazards
- Dynamic multiple issue
- CPU examines instruction stream and chooses instructions to issue each cycle
- CPU resolves hazards
为了实现多路安排,我们需要前瞻——或者说预测—— insts 之间的依赖关系,且需要预测到很远,比prediction远很多。我们称之为Speculation
Speculation and Exceptions
RISCV用的静态双发,而且两条路被加了限制:
- One ALU/branch instruction
- One load/store instruction
即两条只能限制运行自己约定内的指令类型
RISC-V with Static Dual Issue:
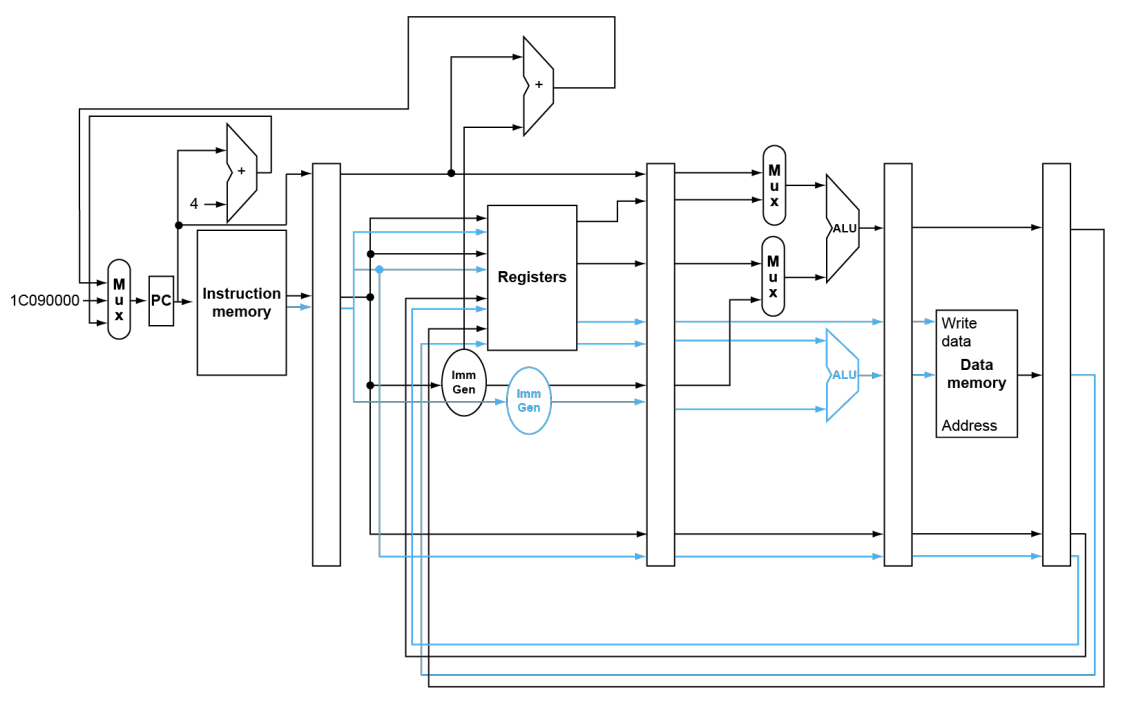
和流水线相比,蓝线是新增的,很多东西都double了
有些小细节,一个是新增的ALU没有ALUSrc的mux
一个是Mem没有mux了
Hazards in the Dual-Issue
- EX data hazard
- Now can’t use ALU result in load/store in same packet
- Split into two packets, effectively a stall
- Load-use hazard
- Still one cycle use latency, but now two instructions
Compiler Schedule Example:
Loop:
ld x31, 0(x20) // x31 = array element
add x31, x31, x21 // add scalar in x21
sd x31, 0(x20) // store result
addi x20, x20, -8 // decrement pointer
blt x22, x20, Loop // branch if x22 < x20
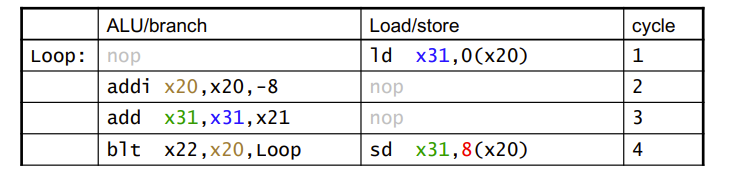
IPC = 5/4 = 1.25 (c.f. peak IPC = 2)
Loop Unrolling
一个场景:循环体展开
对于一个循环,交给两路去跑,最后两路合并
Use different registers per replication
还是上面那个Loop
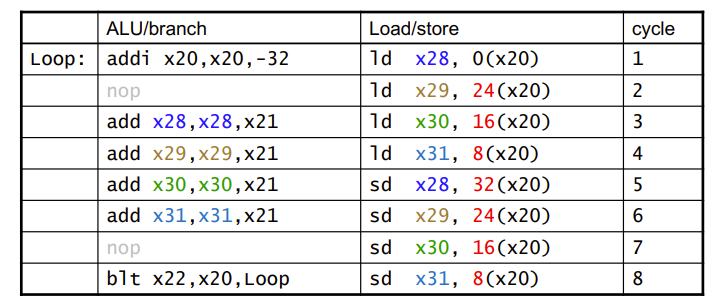
IPC = 14/8 = 1.75
Dynamic Multiple Issue
静态是编译器先处理好程序后再交给硬件跑
动态是直接交给硬件实时判断,所以硬件有大改
我们引入一个概念叫乱序执行
Allow the CPU to execute instructions out of order to avoid stalls
But commit result to registers in order
例如:
ld x31,20(x21)
add x1,x31,x2
sub x23,x23,x3
andi x5,x23,20
#Can start sub while add is waiting for ld
新的硬件设计: