Lecture 10 | Memory Hierarchy
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 278 个字 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
计算机组成2024-04-30第6-8节 (zju.edu.cn)
5.1 Concepts
前部分都没怎么看,PPT 1~18
主要是看各种概念,各种原理,以及性能比较
我们希望实现的是,在CPU看来,内存的速度和它一样快,大小无穷大
但是这是无法实现的
这部分可以看下前面CSSelf部分晶体管部分
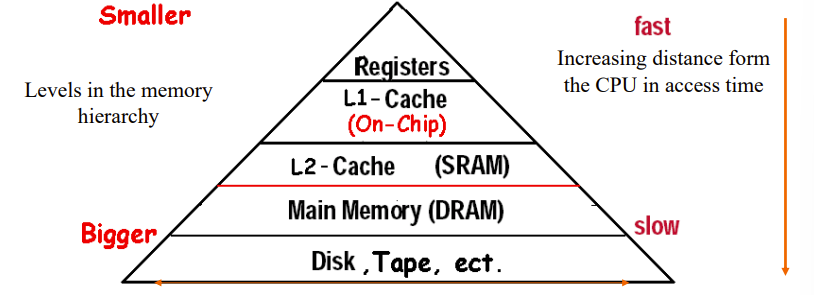
5.2 Memory Hierarchy Introduction
Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time
- Temporal locality: Items accessed recently are likely to be accessed again soon
- Spatial locality: Items near those accessed recently are likely to be accessed soon
Memory Hierarchy Levels
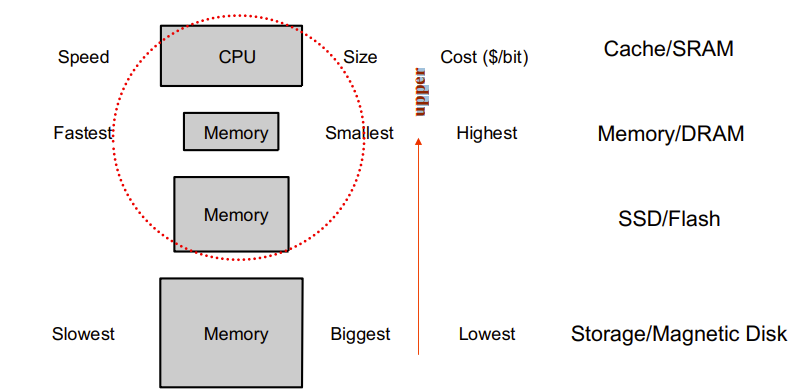
- Block (aka line): unit of copying
If accessed data is present in upper level
- Hit: CPU access satisfied by upper level
- Hit ratio: hits/accesses
- Hit time: The time to access the upper level of the memory hierarchy, which includes the time needed to determine whether the access is a hit or a miss.
If accessed data is absent
- Miss: CPU accesses the upper level and fails. Block copied from lower level
- Time taken: miss penalty
- miss penalty: The time to replace a block in the upper level with the corresponding block from the lower level, plus the time to deliver this block to the processor.
- Miss ratio: misses/accesses = 1 – hit ratio
- Time taken: miss penalty
hit定义是,CPU读取层级最近的mem是否能直接读取到