Lecture 12.2 | Memory Hierarchy - Virtual Memory
计算机组成2024-05-16第9-10节 (zju.edu.cn)
5.7 Virtual Memory
Main Memory act as a “Cache” for the secondary storage(disk).
CPU与虚拟内存直接交互,虚拟内存再和物理内存交互
相当于CPU与Mem之间建立新的映射
secondary storage是磁盘之类的,大容量,但不参与计算
我们就假设有一个非常大的Mem,即我们的虚拟内存,其对应的物理内存可能很小,但是我们可以不断进行磁盘与物理内存之间的交互,让CPU看来我们似乎真的有一个很大的物理内存
不仅如此,虚拟内存还可以对大的物理内存进行分块隔离,让CPU看来内存很小,且块与块之间是一定无法交互的,起到安全保护作用
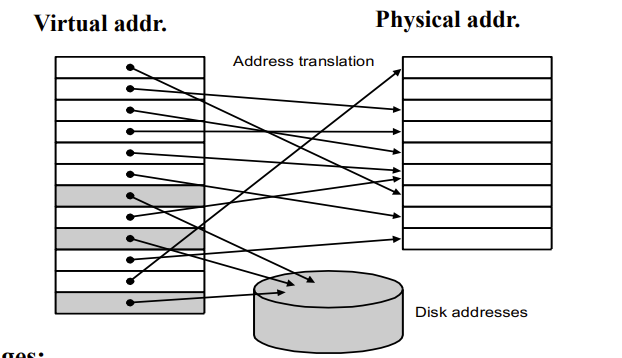
Pages: virtual memory blocks
虚拟内存的block就叫page
faults 即 cache 的 miss
- Page faults: the data is not in memory, retrieve it from disk
- huge miss penalty, thus pages should be fairly large (4KB))
- using write-through is too expensive so we use write back
因为fault的开销太大了,我们用fully associate
Page Tables
fully associate 设计并行检测,但是虚拟内存太大了,所以我们引入一个叫页表的东西
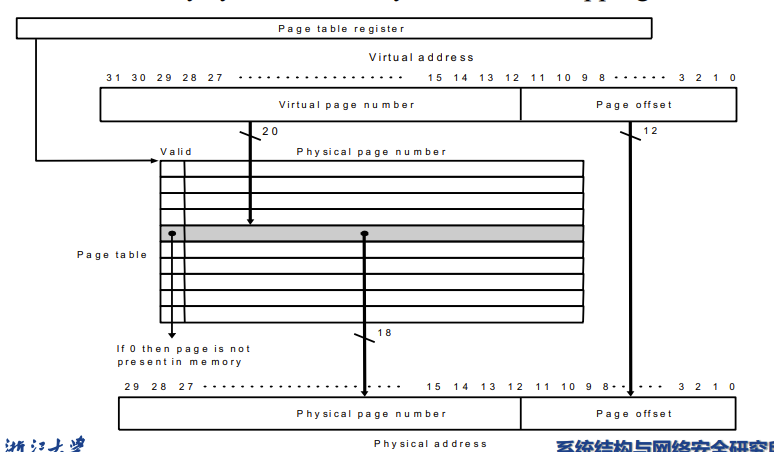
- Page Table : Virtual to physical address
- 保存的就是虚拟内存到物理内存的映射
- Stored into the memory, indexed by the virtual page number
- Each Entry in the table contains the physical page number for that virtual pages if the page is current in memory
- Page table, Program counter and the page table register, specifies the state of the program. Each process has one page table.
- 每个进程有单独的页表,不是操作系统维护
- page table register 存了页表的基地址,用于寻找需要的页表
TLB
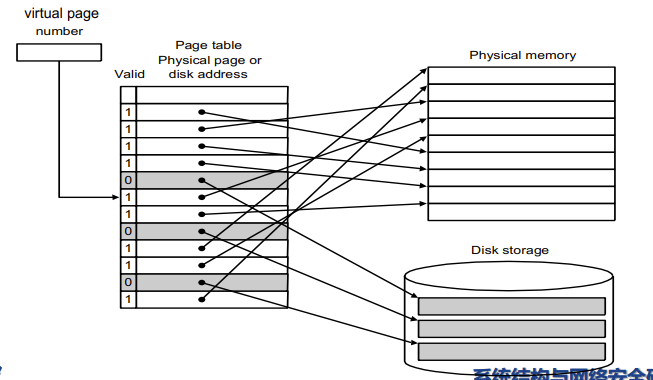
Placing a page and finding it again --Page Tables
Page Faults
这个由操作系统处理
When the OS creates a process, it usually creates the space on disk for all the pages of a process.
The OS will find the page in the disk by the page table.
过程和cache的miss处理类似
How Large Page Table?
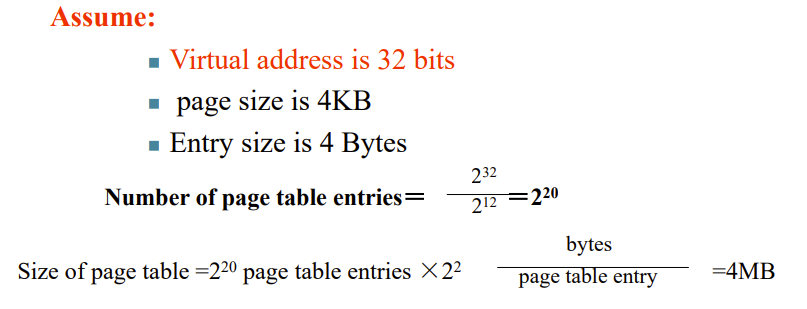
Making Address Translation Fast--TLB
The TLB (Translation-lookaside Buffer) acts as Cache on the page table
TLB 即页表的cache
- 我们讲了内存的cache
- 虚拟内存有个cache
- 页表有个cache
A cache for address translations: translation look aside buffer
TLB用的全关联,fully associate
因为TLB很小
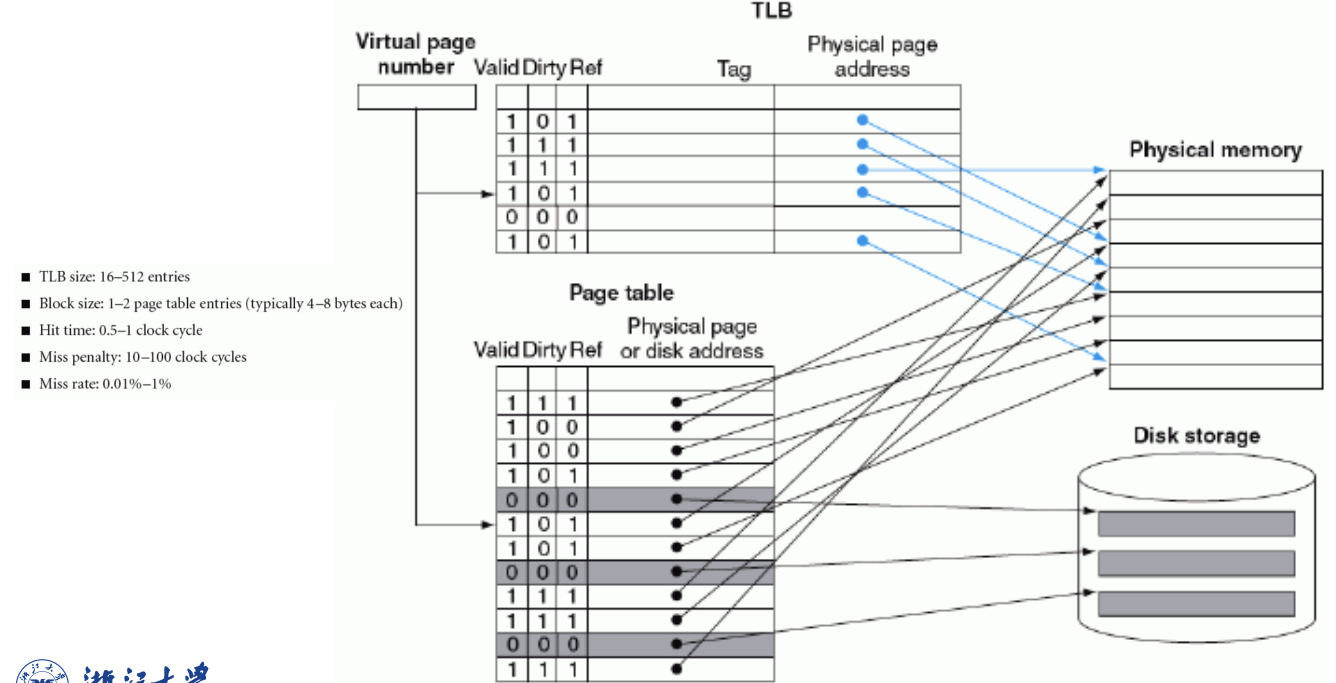
LRU真正实现比较麻烦
我们可以定期对valid清零,表示很久没用了
FastMATH Memory Hierarchy
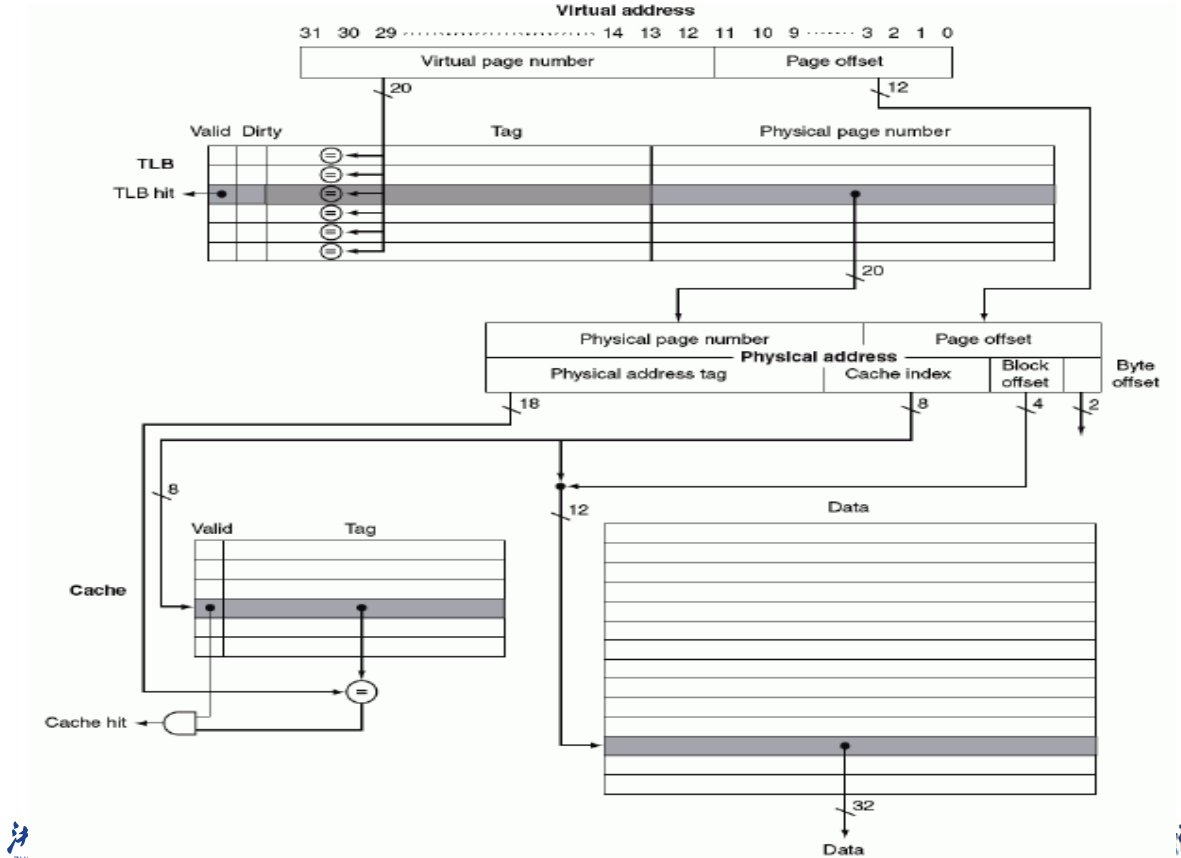
TLBs and Caches
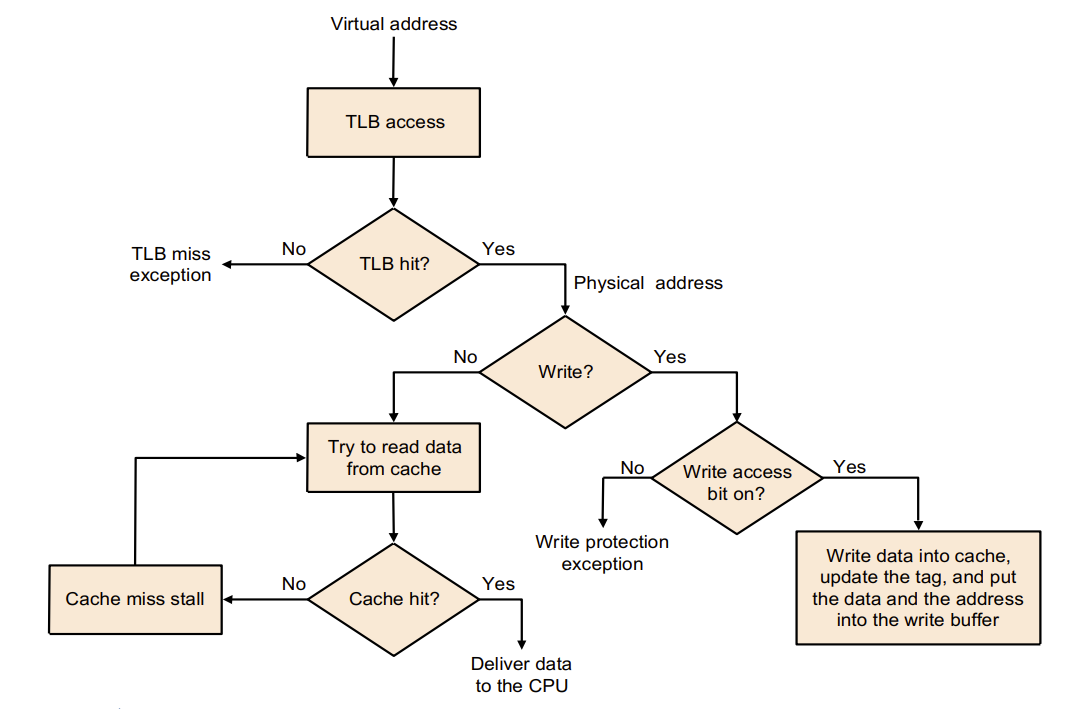
Possible Combinations of Event
Three different types of misses: TLB miss, page Fault, cache miss