Lecture 14 | APPENDIX | I/O
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 723 个字 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
计算机组成2024-05-28第6-8节 (zju.edu.cn)
Bus Arbitration
总线原则:总线尽可能释放,因为这线路是公用的
设备需要使用总线,需要处理器进行仲裁,决定这个请求是否通过,以避免冲突
Bus masters initiate and control all bus requests
- Four bus arbitration schemes
- daisy chain (not very fair)
- 菊花链,不同的I/O被串成一条,需要顺序访问
- 这导致离处理器近的I/O成功率高,形成了优先级
- centralized, parallel (requires an arbiter), e.g., PCI
- self selection
- e.g., NuBus used in Macintosh
- collision detection
- e.g., Ethernet
- daisy chain (not very fair)
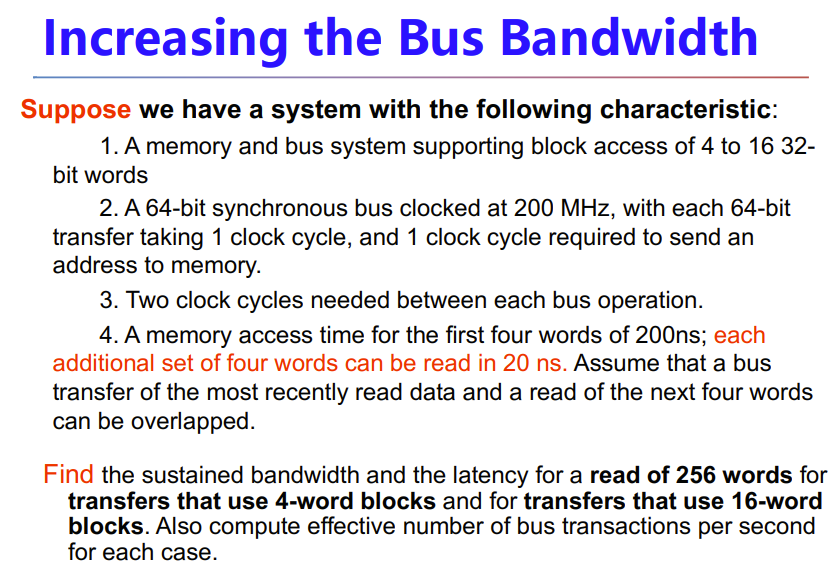
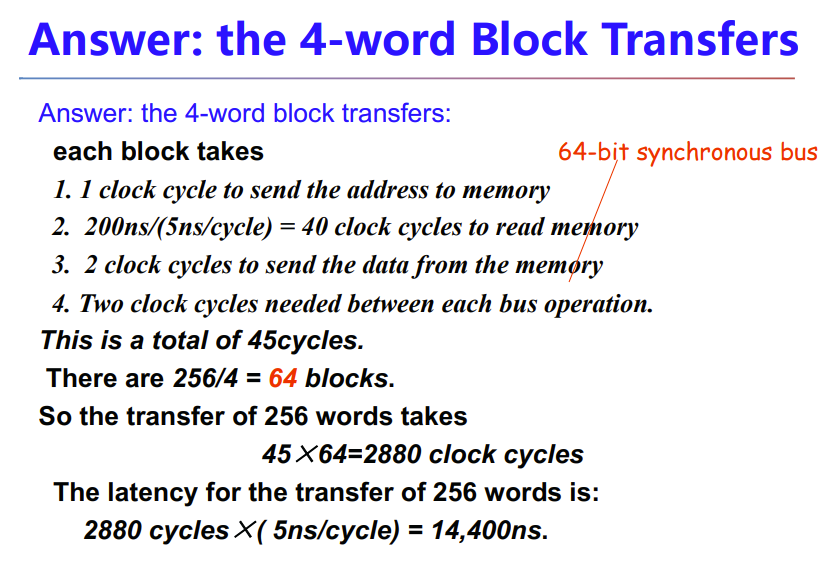
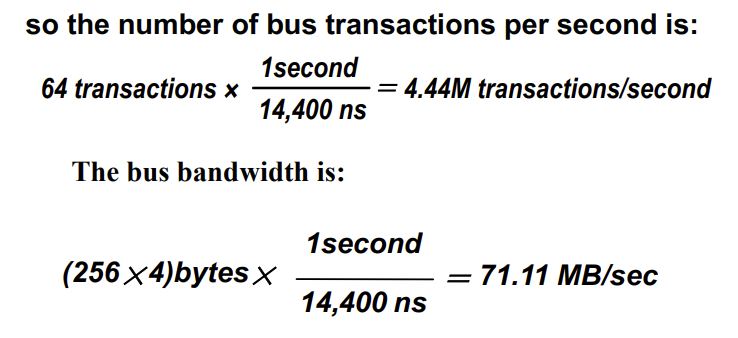

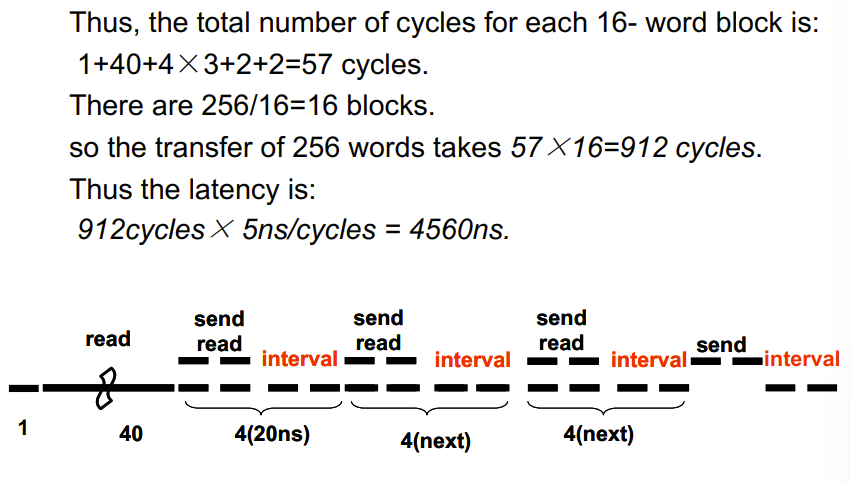
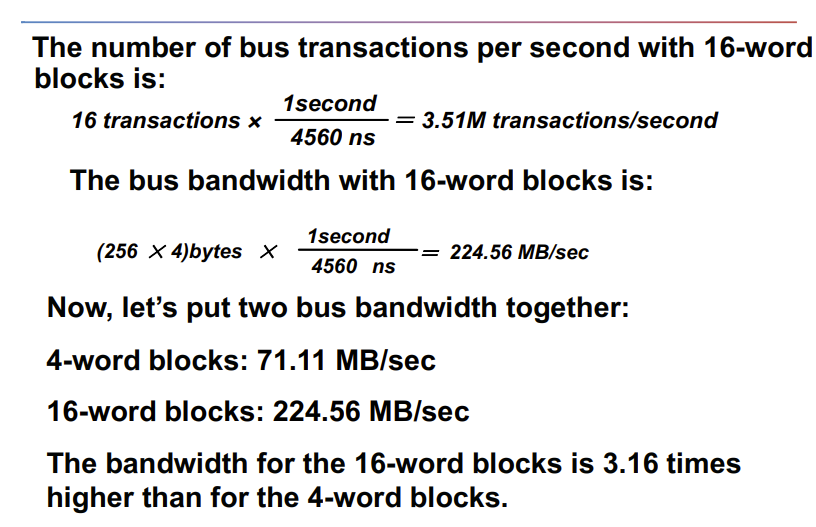
- Increasing the Bus Bandwidth
- p Increasing data bus width
- p Use separate address and data lines
- p Transfer multiple words
A.5 Interfacing I/O Devices to the Memory, Processor, and Operating System
- Three characteristics of I/O systems
- shared by multiple programs using the processor
- I/O被多个程序共享
- often use interrupts to communicate information about I/O operations
- 使用中断来交换信息
- The low-level control of an I/O devices is complex
- 低级控制很复杂
- shared by multiple programs using the processor
- Three types of communication are required
- The OS must be able to give commands to the I/O devices.
- The device must be able to notify the OS, when I/O device completed an operation or has encountered an error.
- Data must be transferred between memory and an I/O device
Giving Commands to I/O Devices
- Two methods used to address the device
- memory-mapped I/O
- 把一部分内存地址划出来专门给一个IO设备使用
- 这样可以通过内存地址区分是哪个IO设备在工作,以及可以通过内存寻址去访问对应的IO
- special I/O instructions
- memory-mapped I/O
Communication with the Processor
大部分设备有事情找处理器都是通过中断的方式进行,当然还有其它的选择:
- Polling
- CPU每隔一段时间检查有没有新的IO操作
- 和同步一样的问题,像鼠标一秒几百次操作,CPU都看的话太浪费了
- Interrupt
- IO有事情就让处理器中断
- When an I/O device wants to notify processor that it has completed some operation or needs attentions, it causes processor to be interrupted
- DMA(direct memory access)
- 单独设计一个控制器叫DMA,磁盘和内存的数据传输交给DMA专门负责,不需要CPU
Interrupt-Driven I/O Mode
这个模式好处是可以并行操作
下面的例子是打印机进行操作
Idle是空闲的意思
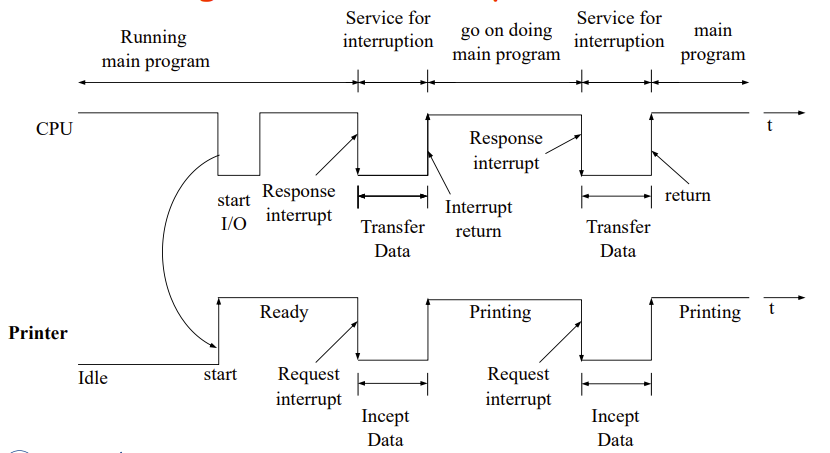
CPU低的部分表示在处理Printer的事情,高的部分表示在处理其他事情
DMA Transfer Mode
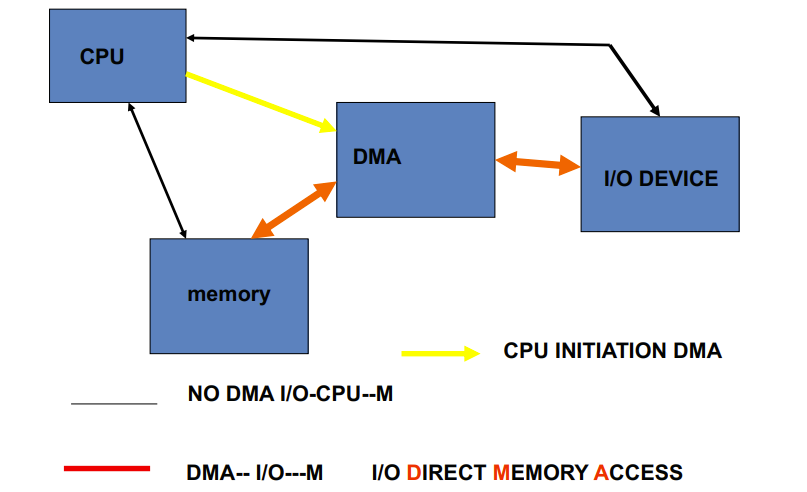
黑色的线不用走了
DMA一开始通过黄色的线中断以被CPU配置,然后剩下的事情都是红
- A DMA transfer need three steps
- The processor sets up the DMA by supplying some information, including the identity of the device, the operation, the memory address that is the source or destination of the data to be transferred, and the number of bytes to transfer
- The DMA starts the operation on the device and arbitrates for the bus. If the request requires more than one transfer on the bus, the DMA unit generates the next memory address and initiates the next transfer
- Once the DMA transfer is complete, the controller interrupts the processor, which then examines whether errors occur.

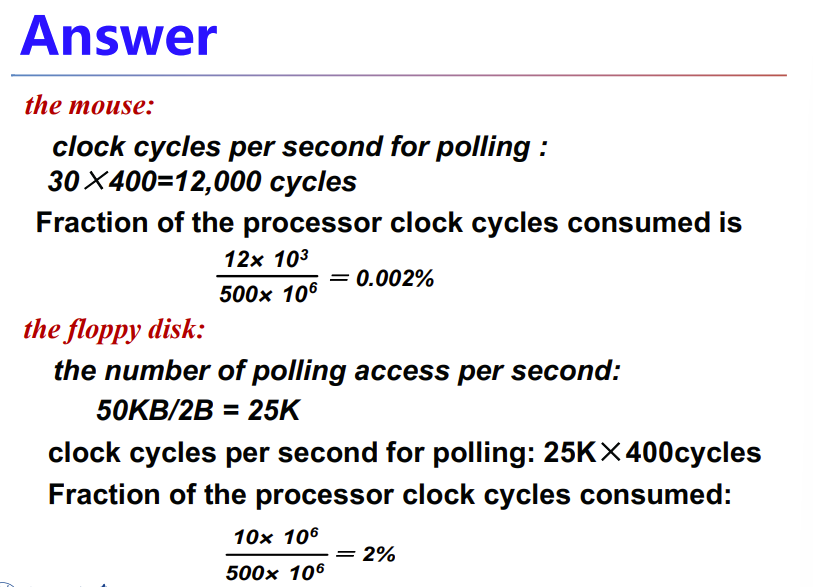

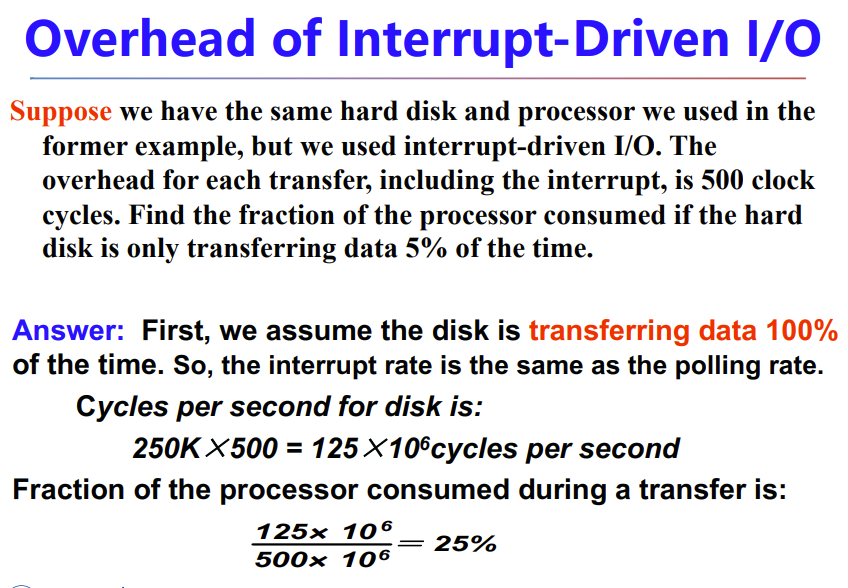

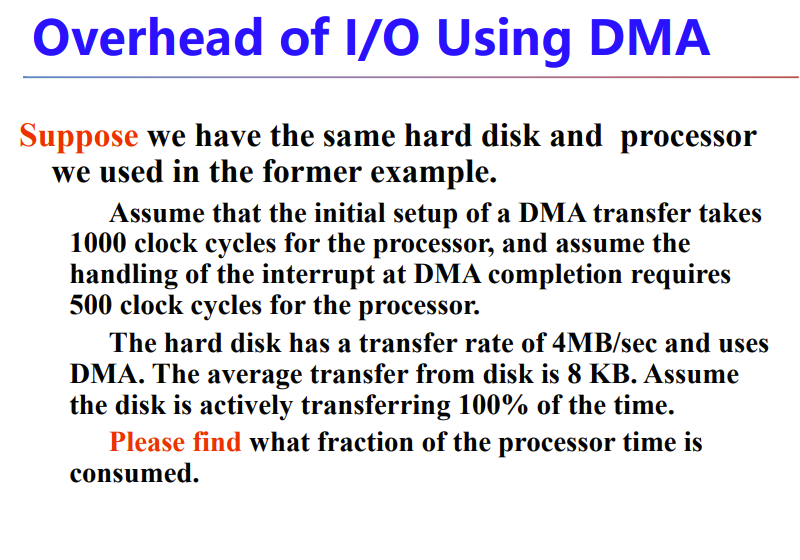
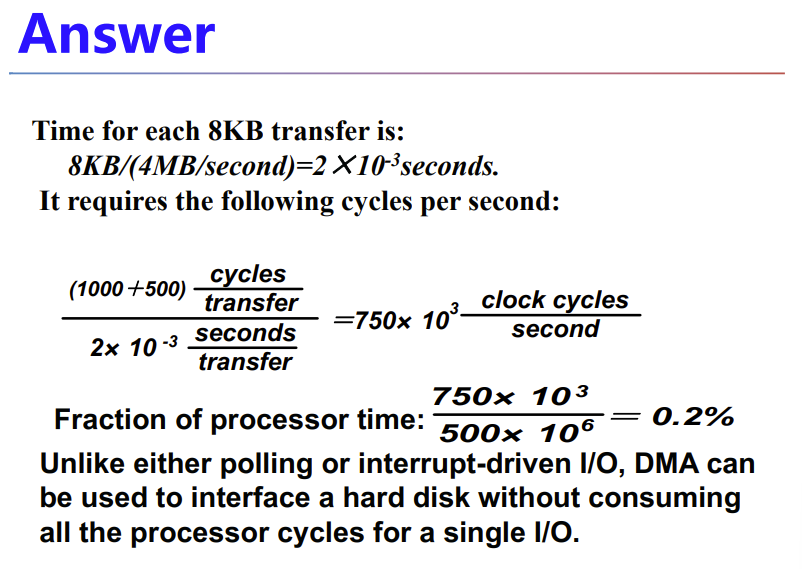
A.6 I/O Performance Measures: Examples from Disk and File Systems