Lecture 9 | The Processor-Part2
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 645 个字 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Dynamic Branch Prediction
方法:如果上一次跳了,这次也跳
Use dynamic prediction:
- Branch prediction buffer (aka branch history table)
专门用于储存branch记录
- Indexed by recent branch instruction addresses (lower part)
pc是64bit,太大了,我们只取低的几位n
可能会低几位有正好重复的,导致准确率降低,但是同时减少了reg的s/l开销
- Stores outcome (taken/not taken)
- To execute a branch
- Check table, expect the same outcome
- Start fetching from fall-through or target
- If wrong, flush pipeline and flip prediction
1-Bit Predictor: Shortcoming
1-Bit Predictor 就只记上一次是否有branch
对于loop循环有Shortcoming
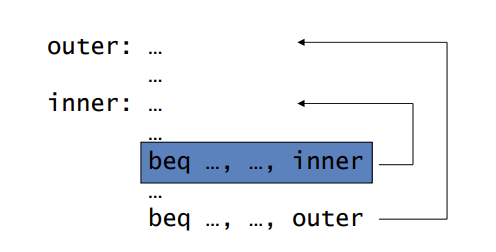
- Inner loop branches mispredicted twice!
- Mispredict as taken on last iteration of inner loop.
- Then mispredict as not taken on first iteration of inner loop next time around
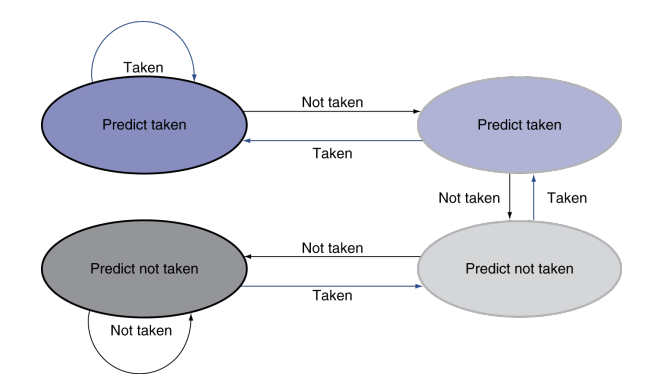
2-Bit Predictor
对于for循环有特效
Only change prediction on two successive mispredictions
Calculating the Branch Target
Even with predictor, still need to calculate the target address
- 1-cycle penalty for a taken branch
Branch target buffer
这个存的下一级要去的的pc地址
Branch prediction buffer 存的是跳转行为,决定是否要跳转
- Cache of target addresses
- Indexed by PC when instruction fetched
- If hit and instruction is branch predicted taken, can fetch target immediately
4.9 Exceptions and Interrupts
“Unexpected” events requiring change in flow of control
- Exception:Arises within the CPU
- 异常
- Interrupt:From an external I/O controller
- 中断
Handling Exceptions
method-1
软件处理
遇到问题,保存当前位置,将相关信息交给专门的程序去统一处理
- Save PC of offending (or interrupted) instruction
- Supervisor Exception Program Counter (SEPC) 用于储存当前PC
- Save indication of the problem
- Supervisor Exception Cause Register (SCAUSE) 一组reg,传递异常时的状态,借给OS去处理
- Jump to handler
- Assume at 0000 0000 1C09 0000hex,异常处理程序的地址
method-2
硬件处理,指用硬件判断异常情况
也是需要专门的程序,但是用硬件先判断是什么异常,根据情况跳到不同程序去分别处理
- Vectored Interrupts
- Handler address determined by the cause
- Exception vector address to be added to a vector table base register
- Undefined opcode 00 0100 0000two
- Hardware malfunction: 01 1000 0000two
- ...
- Instructions either
- Deal with the interrupt, or Jump to real handler
Handler Actions
- Read cause, and transfer to relevant handler
- Determine action required
- If restartable
- Take corrective action,use SEPC to return to program
- Otherwise
- Terminate program,Report error using SEPC, SCAUSE, …
从这开始后面的课可以重新听一下
Exceptions in a Pipeline

Pipeline with Exceptions
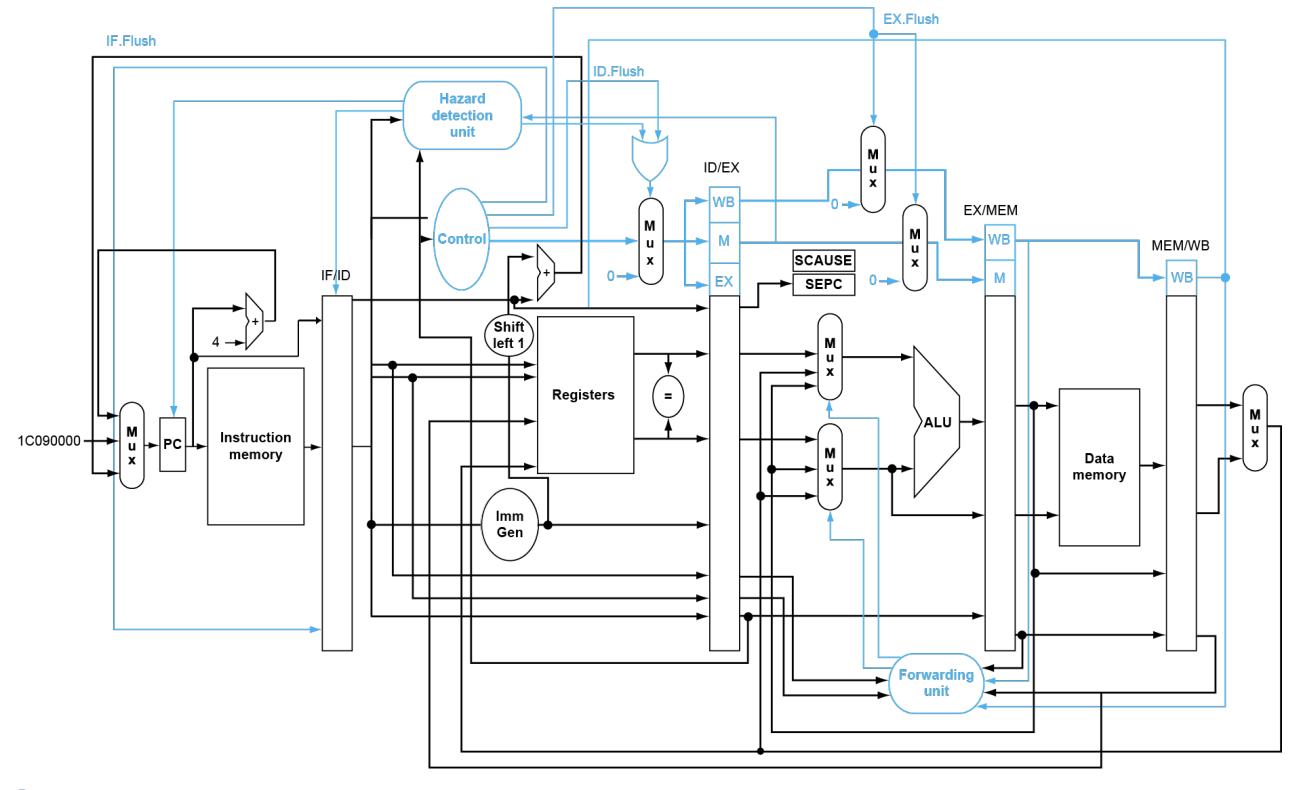
Exception Properties

Exception Example

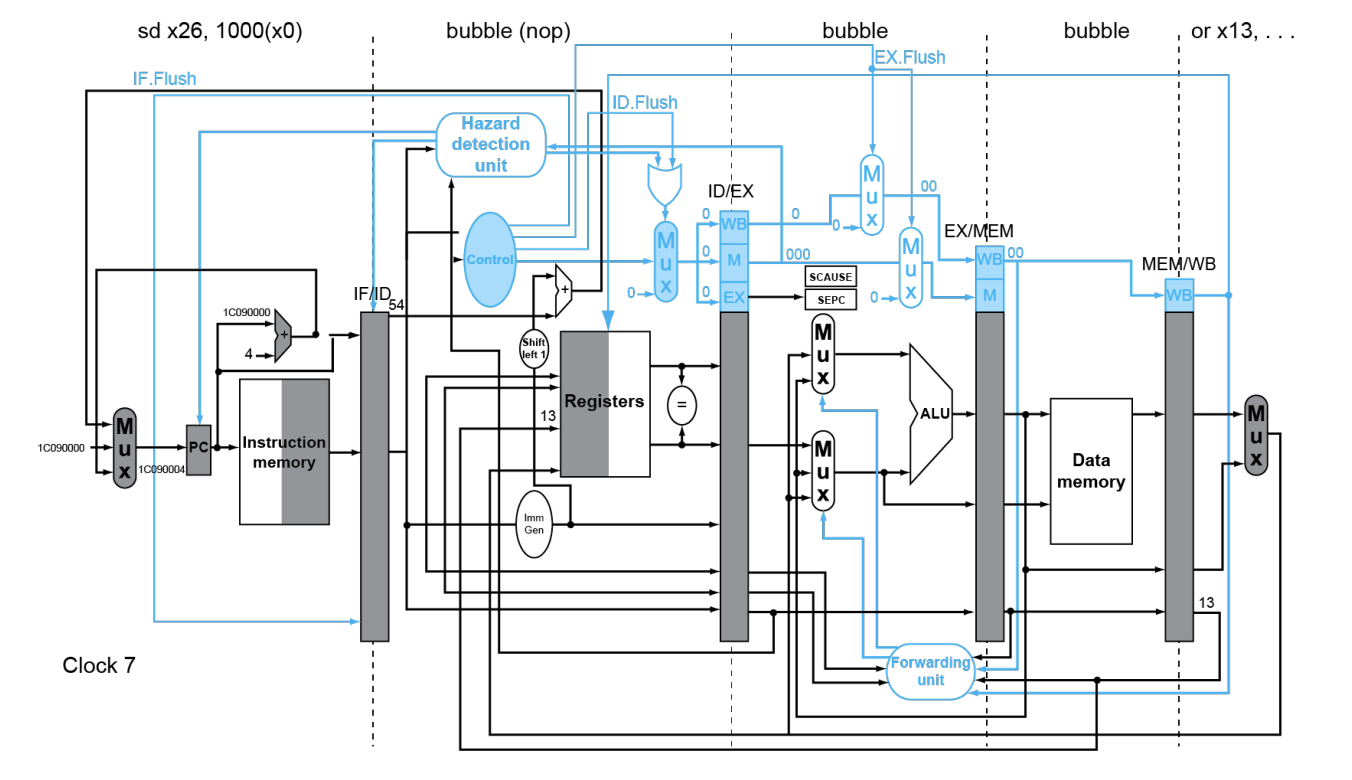
Multiple Exceptions
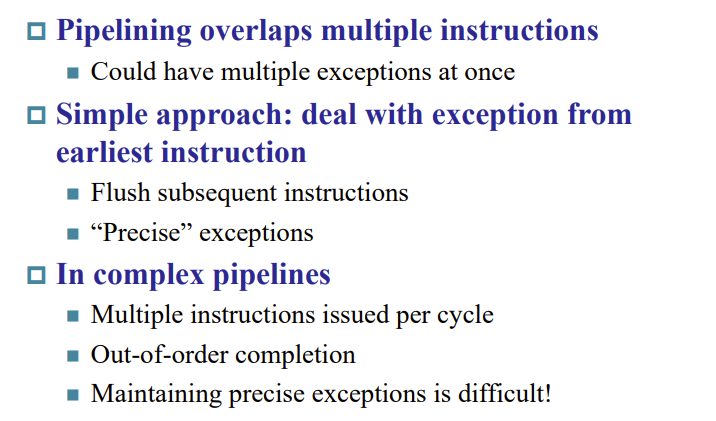
Imprecise Exceptions

4.10 Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP)
指令集并行
多发 Multiple issue ,同一时间安排多条指令
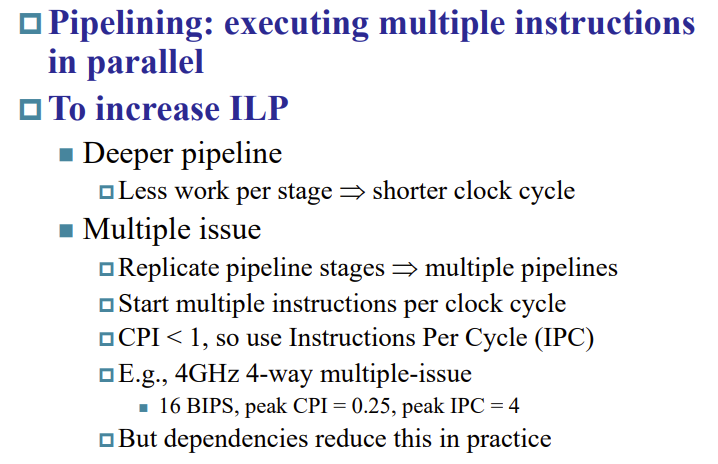
Multiple Issue

Speculation
与prediction不同,这个是调度方面的预测,看怎么排程序出错概率最低

Compiler/Hardware Speculation

Speculation and Exceptions

Static Multiple Issue

Scheduling Static Multiple Issue

RISC-V with Static Dual Issue
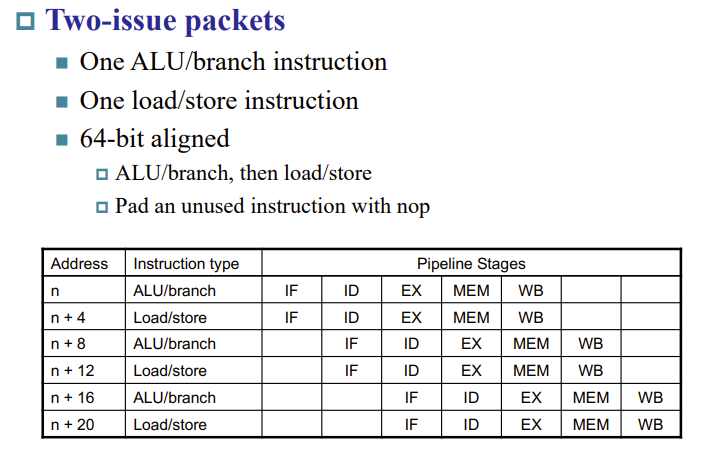
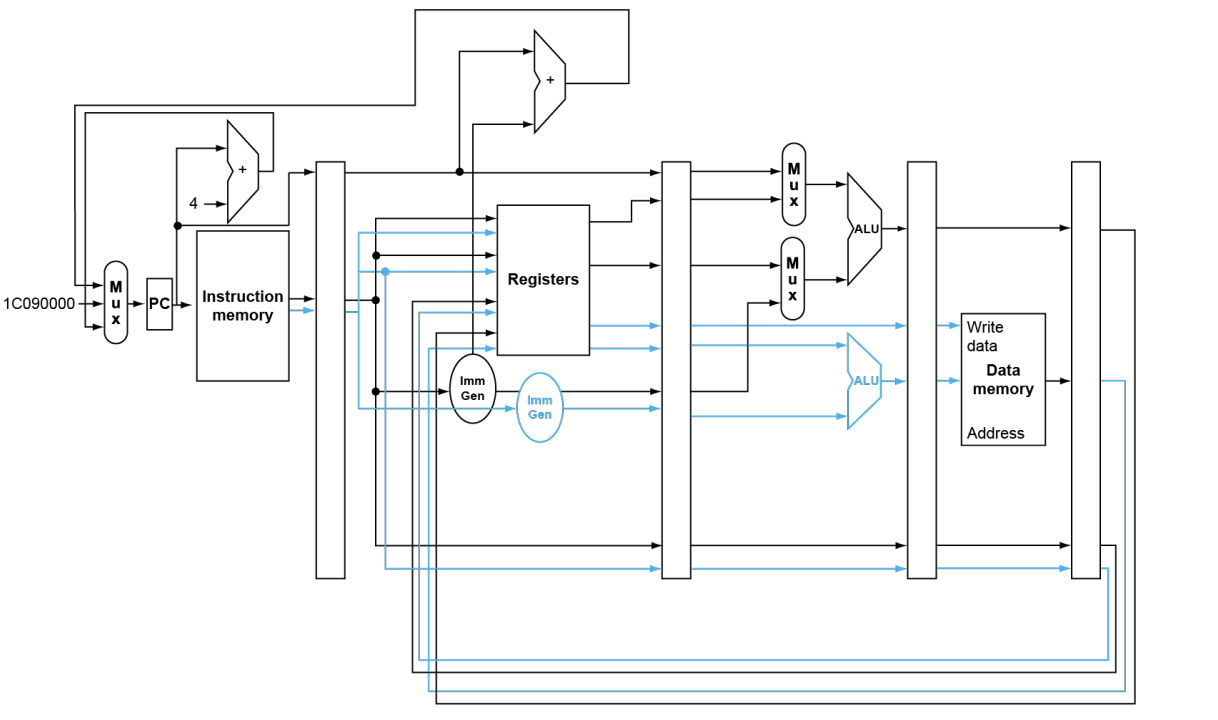
Hazards in the Dual-Issue RISC-V

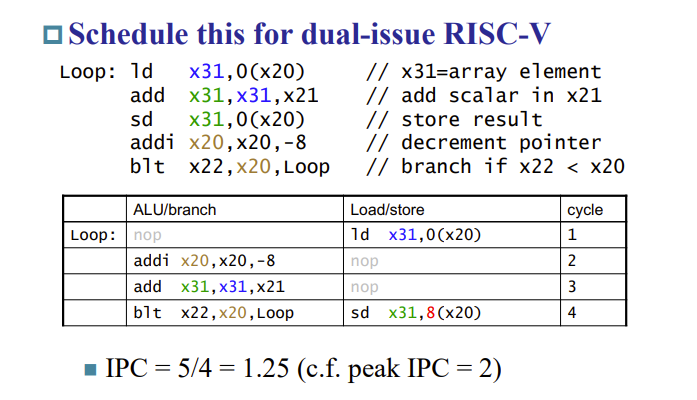
Scheduling Example
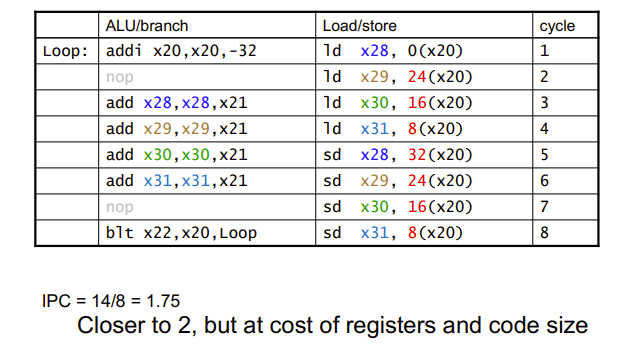
Loop Unrolling

Loop Unrolling Example
Dynamic Multiple Issue
Dynamic Pipeline Scheduling

Dynamically Scheduled CPU
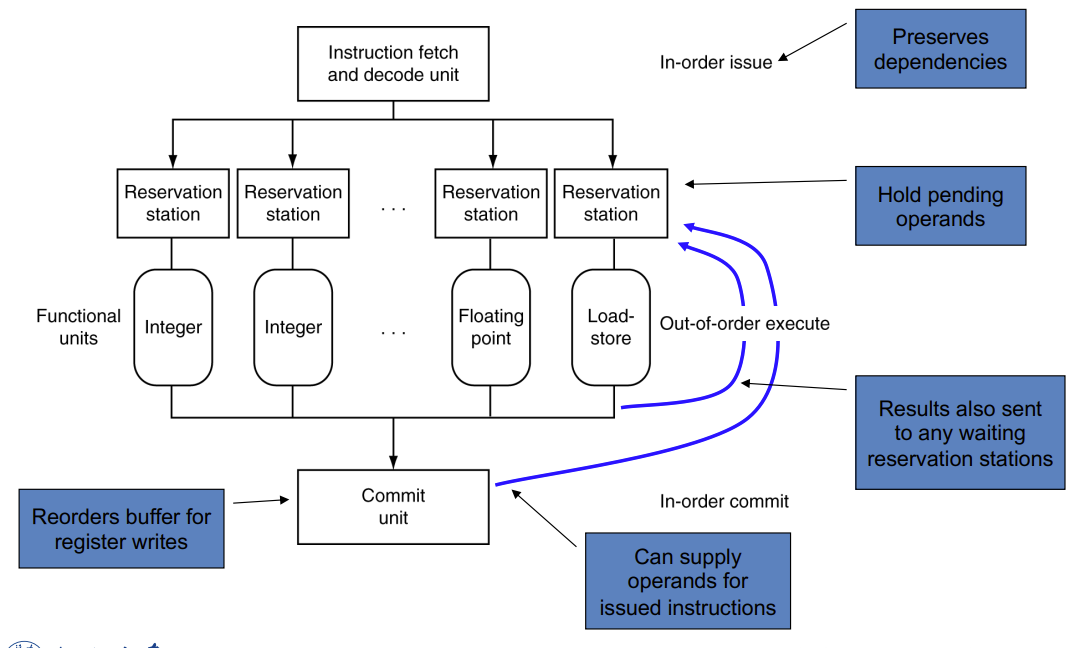
Register Renaming

Speculation

Why Do Dynamic Scheduling?

Does Multiple Issue Work?

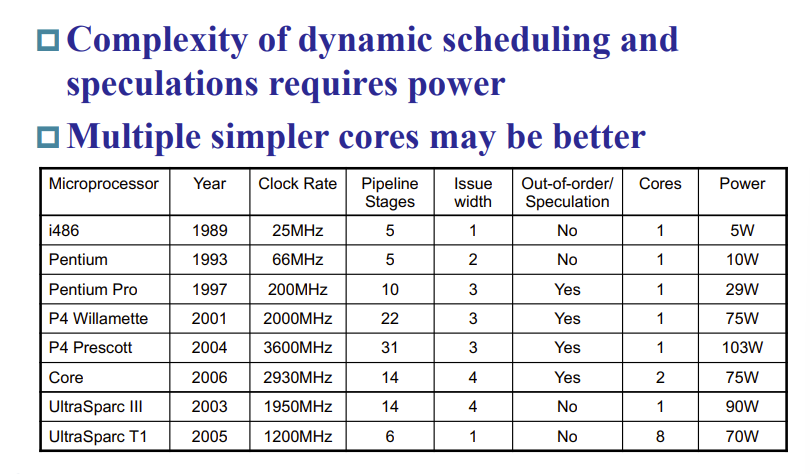
Power Efficiency