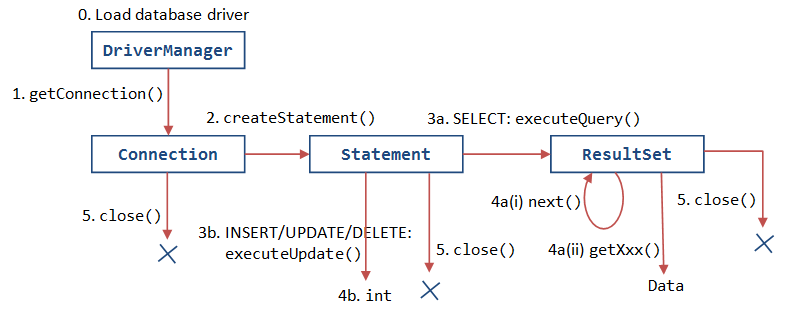
JDBC Intermediate Tutorial
:material-circle-edit-outline: 约 65 个字 :fontawesome-solid-code: 170 行代码 :material-clock-time-two-outline: 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Introduction
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is the Java's Application Programming Interface (API) for interfacing with relational databases.
The API defines how to connect to the database, execute SQL statements, return the results, among others.
JDBC defines the API, while the database vendors develop their specific drivers that meets the JDBC specification.
SQL SELECT
import java.sql.*; // Using 'Connection', 'Statement' and 'ResultSet' classes in java.sql package
public class JdbcSelectTest { // Save as "JdbcSelectTest.java"
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// Step 1: Connect to the database via a 'Connection' object called 'conn'
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ebookshop?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC",
"myuser", "xxxx"); // For MySQL only
// The format is: "jdbc:mysql://hostname:port/databaseName", "username", "password"
// Step 2: Construct a 'Statement' object called 'stmt' inside the Connection created
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
)
{
// Step 3: Write a SQL query string. Execute the SQL query via the 'Statement'.
String strSelect = "select title, price, qty from books";
// The query result is returned in 'ResultSet' object
ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery(strSelect);
// Step 4: Process the 'ResultSet' by scrolling the cursor forward via next().
// For each row, retrieve the contents of the cells with getXxx(columnName).
// Row-cursor initially positioned before the first row of the 'ResultSet'.
// rset.next() inside the whole-loop repeatedly moves the cursor to the next row.
// It returns false if no more rows.
int rowCount = 0;
while(rset.next()) { // Repeatedly process each row
String title = rset.getString("title"); // retrieve a 'String'-cell in the row
double price = rset.getDouble("price"); // retrieve a 'double'-cell in the row
int qty = rset.getInt("qty"); // retrieve a 'int'-cell in the row
System.out.println(title + ", " + price + ", " + qty);
++rowCount;
}
System.out.println("Total number of records = " + rowCount);
} catch(SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// Step 5: Close conn and stmt - Done automatically by try-with-resources (JDK 7)
}
}
SQL UPDATE
import java.sql.*; // Use classes in java.sql package
public class JdbcUpdateTest { // Save as "JdbcUpdateTest.java"
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// Step 1: Allocate a database 'Connection' object
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ebookshop?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC",
"myuser", "xxxx"); // for MySQL only
// Step 2: Allocate a 'Statement' object in the Connection
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
) {
// Step 3 and 4: Execute a SQL UPDATE via executeUpdate()
// which returns an int indicating the number of rows affected.
// Increase the price by 7% and qty by 1 for id=1001
String strUpdate = "update books set price = price*1.07, qty = qty+1 where id = 1001";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + strUpdate + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
int countUpdated = stmt.executeUpdate(strUpdate);
System.out.println(countUpdated + " records affected.\n");
// Step 3 and 4 (again): Issue a SELECT (via executeQuery()) to check the UPDATE.
String strSelect = "select * from books where id = 1001";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + strSelect + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery(strSelect);
while(rset.next()) { // Move the cursor to the next row
System.out.println(rset.getInt("id") + ", "
+ rset.getString("author") + ", "
+ rset.getString("title") + ", "
+ rset.getDouble("price") + ", "
+ rset.getInt("qty"));
}
} catch(SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} // Step 5: Close conn and stmt - Done automatically by try-with-resources
}
}
SQL INSERT and DELETE
import java.sql.*; // Use classes in java.sql package
public class JdbcInsertTest { // Save as "JdbcUpdateTest.java"
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// Step 1: Allocate a database 'Connection' object
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ebookshop?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC",
"myuser", "xxxx"); // for MySQL only
// Step 2: Allocate a 'Statement' object in the Connection
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
) {
// Step 3 and 4: Execute a SQL INSERT|DELETE statement via executeUpdate(),
// which returns an int indicating the number of rows affected.
// DELETE records with id>=3000 and id<4000
String sqlDelete = "delete from books where id >= 3000 and id < 4000";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + sqlDelete + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
int countDeleted = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlDelete);
System.out.println(countDeleted + " records deleted.\n");
// INSERT a record
String sqlInsert = "insert into books values (3001, 'Gone Fishing', 'Kumar', 11.11, 11)";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + sqlInsert + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
int countInserted = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlInsert);
System.out.println(countInserted + " records inserted.\n");
// INSERT multiple records
sqlInsert = "insert into books values "
+ "(3002, 'Gone Fishing 2', 'Kumar', 22.22, 22),"
+ "(3003, 'Gone Fishing 3', 'Kumar', 33.33, 33)";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + sqlInsert + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
countInserted = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlInsert);
System.out.println(countInserted + " records inserted.\n");
// INSERT a partial record
sqlInsert = "insert into books (id, title, author) values (3004, 'Fishing 101', 'Kumar')";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + sqlInsert + "\n"); // Echo for debugging
countInserted = stmt.executeUpdate(sqlInsert);
System.out.println(countInserted + " records inserted.\n");
// Step 3 and 4: Issue a SELECT (via executeQuery()) to check the changes
String strSelect = "select * from books";
System.out.println("The SQL statement is: " + strSelect + "\n"); // Echo For debugging
ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery(strSelect);
while(rset.next()) { // Move the cursor to the next row
System.out.println(rset.getInt("id") + ", "
+ rset.getString("author") + ", "
+ rset.getString("title") + ", "
+ rset.getDouble("price") + ", "
+ rset.getInt("qty"));
}
} catch(SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} // Step 5: Close conn and stmt - Done automatically by try-with-resources
}
}
JDBC Cycle