Review 6 | Physical Storage Systems & Data Storage Structures
Lecture 9
Storage Hierarchy(存储级别)
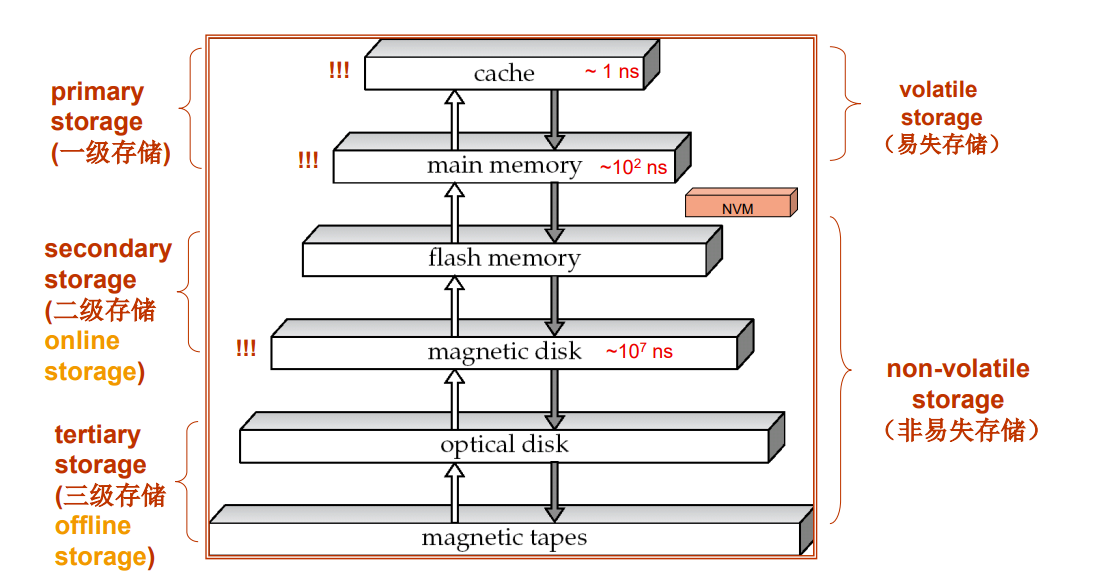
硬盘和内存之间的数据传输是以 块 为单位的,即便只要1bit也会传输一块数据
Magnetic Hard Disk
Mechanism
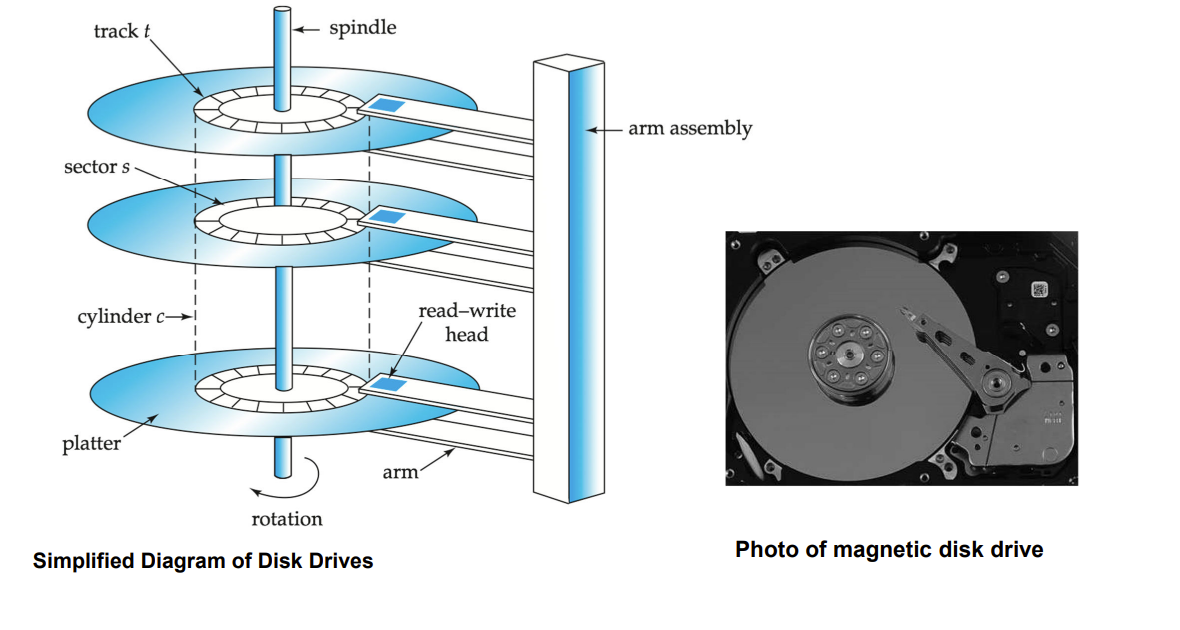
磁盘有以下几部分
- Read-write head (读写头)
- tracks(磁道)
- sectors(扇区)
- Disk controller(磁盘控制器)
- 读写头靠近 platter surface ,通过磁性质读写数据
- 一个磁盘有多个磁片
- 磁片表面分为多个磁道
- 一个磁道分为多个扇区,即磁盘的最小读写单位
Performance Measures of Disks
有以下几个概念
- Access time(访问时间)
- Seek time(寻道时间)
- Rotational latency (旋转延迟)
- Data-transfer rate(数据传输速率)
访问时间即磁盘读数据消耗的总时间,包含寻道时间和旋转延迟
寻道时间即读写头找到磁道的时间
旋转延迟即找到磁道后,磁片旋转到对应扇区的时间
- Average seek time is 1/2 the worst case seek time
- Average latency is 1/2 of the worst case latency
还有几个关于磁盘的概念:
- Sequential access pattern(顺序访问模式)
- Random access pattern(随机访问模式)
- I/O operations per second (IOPS ,每秒I/O操作数)
- Mean time to failure (MTTF,平均故障时间)
顺序访问意思是找到一个扇区后顺着读下去就完成了,随机访问就是读取多个不同位置的扇区,我们尽量避免后者,尽量将后者转化为前者
Optimization of Disk-Block Access
懒得看了,后面再看
- Buffering: in-memory buffer to cache disk blocks
- Read-ahead(Prefetch): Read extra blocks from a track in anticipation that they will be requested soon
- Disk-arm-scheduling algorithms re-order block requests so that disk arm movement is minimized
- 与controller相关
- elevator algorithm
-
File organization
- Allocate blocks of a file in as contiguous a manner as possible
- Allocation in units of extents(盘区)
- Files may get fragmented
- E.g., if free blocks on disk are scattered, and newly created file has its blocks scattered over the disk
- Sequential access to a fragmented file results in increased disk arm movement
- Some systems have utilities to defragment the file system, in order to speed up file access
-
Nonvolatile write buffers (非易失性写缓存) – speed up disk writes by writing blocks to a non-volatile RAM buffer immediately
- Non-volatile RAM: battery backed up RAM or flash memory
- Even if power fails, the data is safe and will be written to disk when power returns
- Controller then writes to disk whenever the disk has no other requests or request has been pending for some time
- Database operations that require data to be safely stored before continuing can continue without waiting for data to be written to disk
- Writes can be reordered to minimize disk arm movement
- Non-volatile RAM: battery backed up RAM or flash memory
-
Log disk(日志磁盘) – a disk devoted to writing a sequential log of block updates
- Used exactly like nonvolatile RAM
- Write to log disk is very fast since no seeks are required
- No need for special hardware (NV-RAM)
- Used exactly like nonvolatile RAM
Flash Storage
NAND flash 和 SSD(Solid State Disks)
。。。。。。
Storage Class Memory(NVM)
这部分没看
File Organization
数据库不是直接去管理上面说的硬盘,数据库引擎下面是OS,OS下面才是硬件
数据库是 files 的集合,每个文件是一序列的 records,record 是一序列的 fields
Fixed-Length Records
每个record分配统一的空间
Store record i starting from byte n * (i – 1), where n is the size of each record.
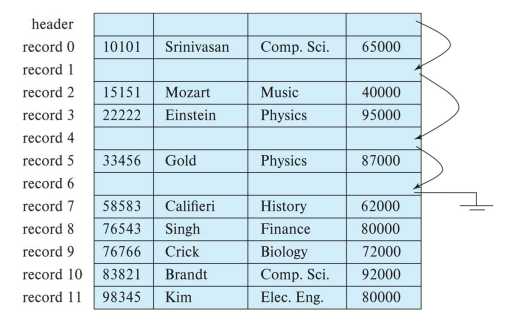
Variable-Length Records
每个record 被设计为 fixed length attributes 和 actual data 两部分,前者负责记录这个record的性质,比如position、length,后者则存放数据,前者可根据后者情况进行变化。
例如下图,前面三个部分是length-fixed的,第一段定义position,第二段定义length
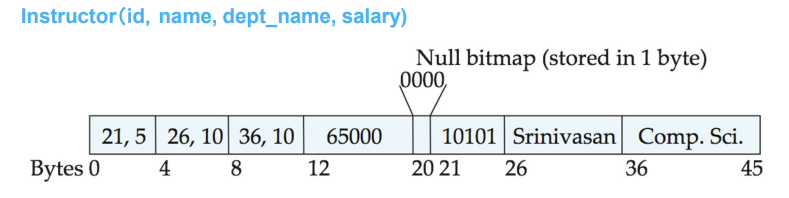
NULL数据是不会被储存的,所以我们需要一段 null bitmap,用于记录哪个位置是有NULL数据的
比如,如果一个record有4个数据,那就拿出4个bit,数据为NULL就让 null bitmap 对应的 bit 为
1
上面只是举个大概的例子,下面我们看看一种具体的格式规则
Slotted Page Structure
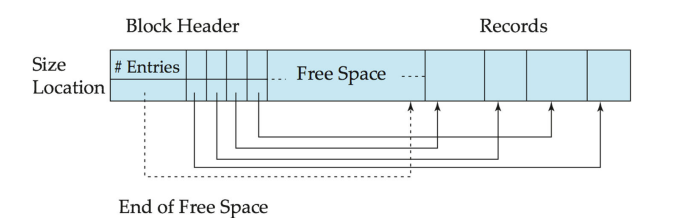
Slotted page(分槽页) 的 block header 有以下信息
- number of record entries
- end of free space in the block
- location and size of each record
我们需要保持维护,让数据连续地放在最后面以图方便,而所有空闲的空间都集中在中间
Organization of Records in Files
我们有以下几种 record 在一个文件里的组织方式
- Heap
- record 随便放,只要这里还有空间,放了就不要动他了,能跑就行
- Sequential
- 根据record 的 search key 值进行排序存储
- multitable clustering file organization
- 不同关系的 record 可以放同一个文件里
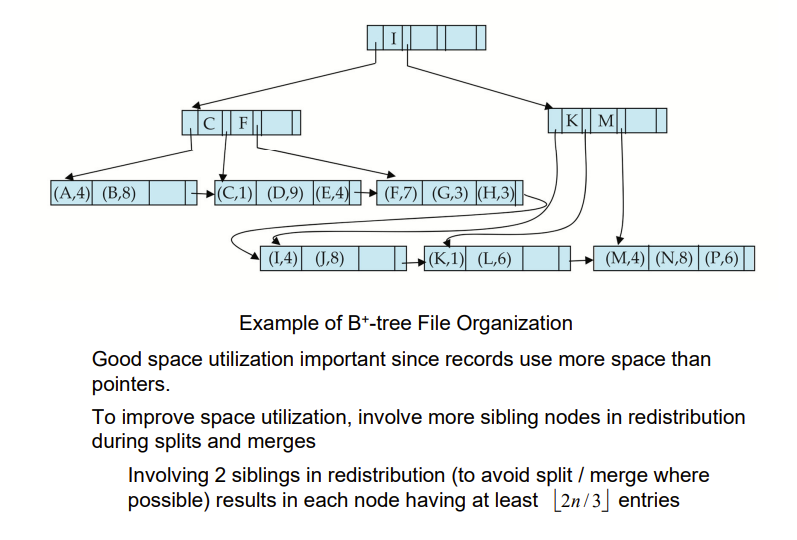
- B+-tree file organization
- B+树yyds
- Hashing
- 根据 search key 的哈希值决定 record 放file里的哪个block
Heap File Organization
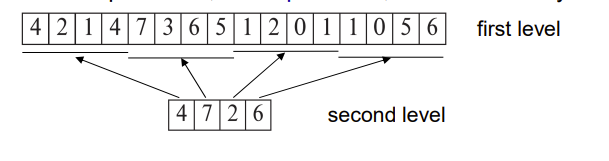
最关键的地方就是快速寻找空的位置,我们使用 Free-space map
这个方法要求每个 block 多几个bit来记录自己的空闲情况,例如下面这图用3bit记录,格子表示一个block,最左边上面数字 4表示这个block有 4/8 的空闲位置
如果block很多,我们还可以分层以加快速度,第一层记录每个block的空闲情况,第二层将block分组,记录每组里面最大的空闲情况
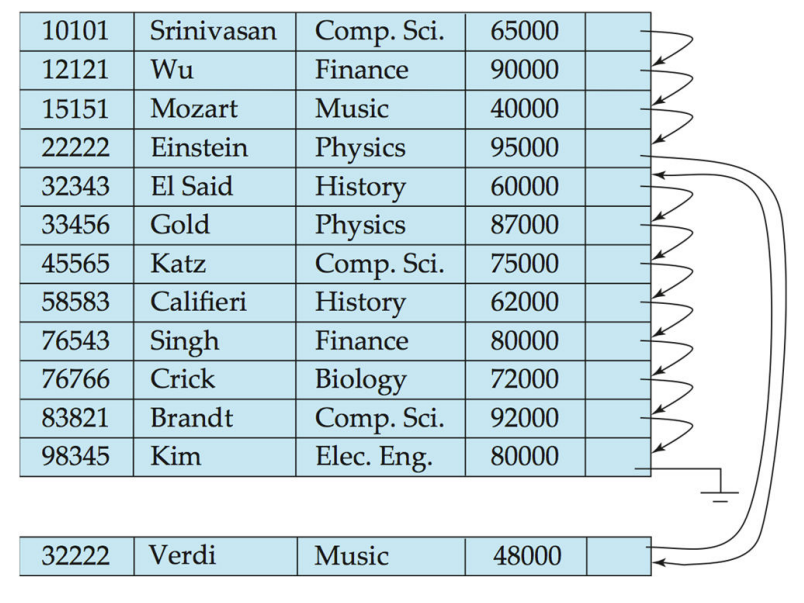
Sequential File Organization
最关键的地方是维护顺序,为了方便,一次插入后我们通过指针保存顺序信息,而不是每次插入都维护严格的物理有序
但是我们还是需要定期维护一次,实现物理有序,以提高储存和访问效率
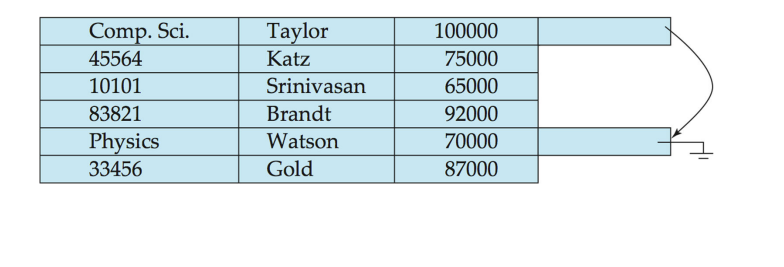
Multitable Clustering File Organization
如果多个表有类型相同的属性,此组织方式可以让这些属性的值物理上聚集在一起
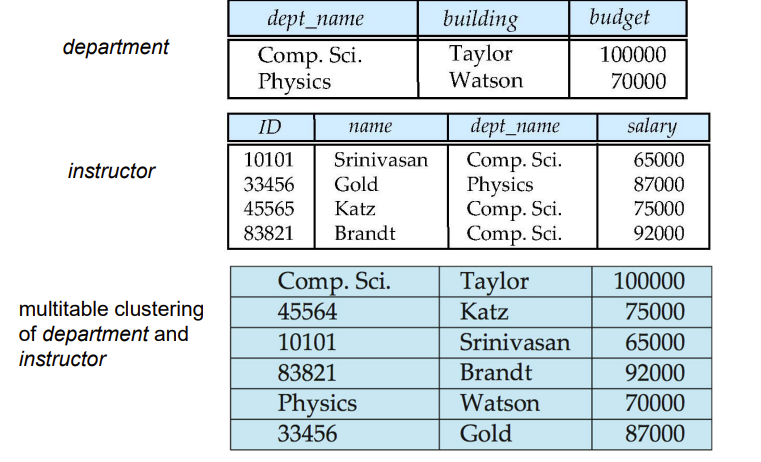
我们可以通过指针串联同一个关系的数据
B+-Tree File Organization
叶子结点存储record,而不是指针,而且根据B+树的性质应该至少半满
其它(会考的,只是比较零散,放一起了)
Table Partitioning
一张表可以拆分为多张表存储在多个文件里
transactionintotrans_2018,trans_2019
Data Dictionary Storage
Data dictionary 又叫 system catalog,存储 metadata
元数据是一些记录数据整体信息的数据,比如关系的名称,管理员用户名与密码,关系简介,tuple数量,等等
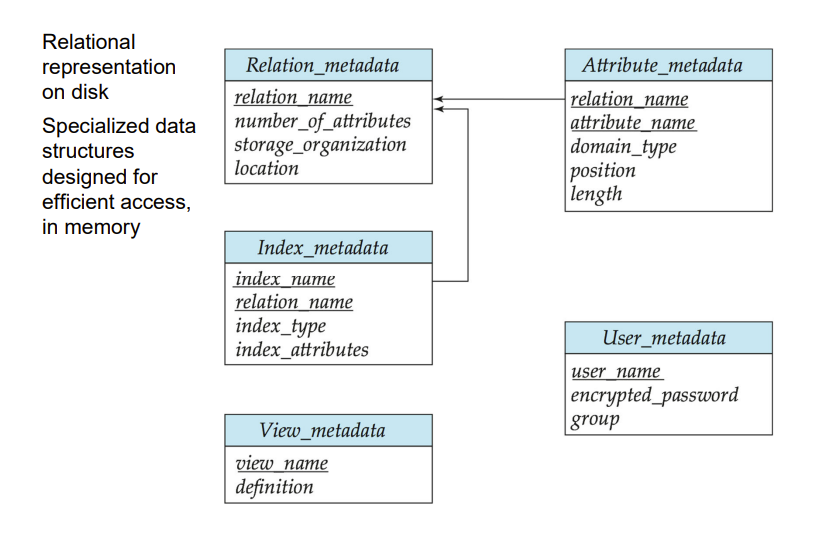
Storage Access
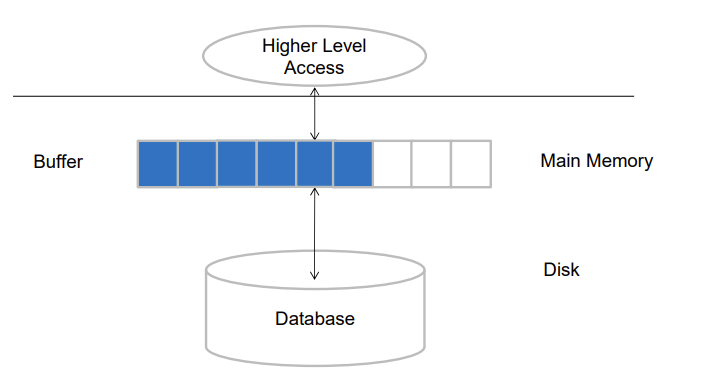
一个块从硬盘读取后会暂时放在内存,确切说是放在内存的缓冲区,以便短时间内的再次使用
所以程序会先通过 buffer manager 看内存里有没有,没有就先在buffer留个空间,然后从硬盘取出块放到buffer里,有的话 buffer manager 会返回相应的内存地址
buffer满了就腾出最久未使用的块,这是计组的LRU policy
这部分计组和数据库知识直接重叠了,学了两遍
Clock: An approximation of LRU
每个block多一个pin_count 和 reference_bit,后者在前者不为 0 时标记为禁用,为 0 时标记为启用,启用时初始化为 1
pin_count 记录此时这个block被多少个程序访问,没程序访问就为 0,此时会让这个block的 reference_bit 启用,并初始化为 1
我们将所有block的reference_bit排成一个环,一个指针恒速转动,依次检查,未启用的不管。对于启用的 reference_bit,遇到 1 先将其置为 0,遇到 0 则将其标记为可替换出去
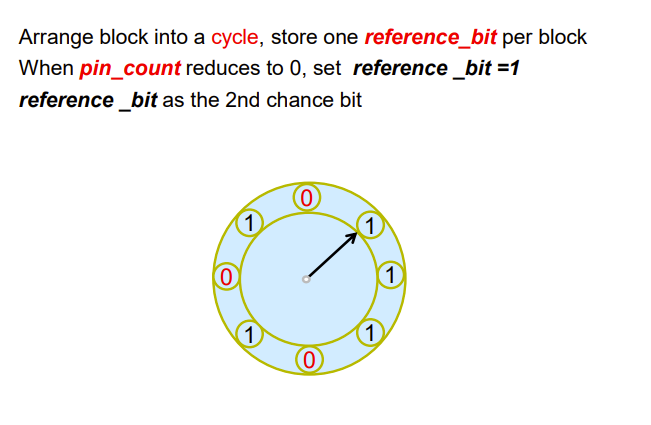
这个可用于miniSQL,我们不需要实现严格的LRU,用这个可以非常非常非常非常简单地近似实现LRU
Column-Oriented Storage
我们之前一条条 tuple 是 row-oriented representation,一个tuple 是一行
Column-Oriented Storage 也叫 columnar representation,就是把一张表的每列数据(即每个属性的所有数据)分来存放

好处(2022期末考过)是只获取部分属性值时能大大减少IO消耗,提升性能,适应CPU的 Vector processing
坏处是表的构建消耗大,删除和更新都麻烦