Lecture 5 Advanced SQL
主要内容:
从高级程序设计语言(如C语言)访问关系数据库主要有API和嵌入式SQL两种方式。SQL和高级程序设计语言存在着基本数据类型和执行方式两方面的不匹配,嵌入式SQL通过游标(cursor)等方式处理这些不匹配的问题。讲授嵌入式SQL的基本原理、ODBC、JDBC,以及SQL的过程化扩展和触发器(trigger)。
JDBC and ODBC
没学过Java,基本不考
六种模式
- API (application-program interface) for a program to interact with a database server
- ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) works with C, C++, C#
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) works with Java
- Embedded SQL in C
- SQLJ - embedded SQL in Java
- JPA(Java Persistence API) - OR mapping of Java
JDBC
JDBC is a Java API for communicating with database systems supporting SQL.
......
SQL Injection(SQL 注入)
不要直接读入东西直接放在sql里面执行,要prepare一下,检查输入的玩意儿。可以提高效率和安全性。
Metadata Features
......
SQLJ
......
ODBC
Each database system supporting ODBC provides a "driver" library that must be linked with the client program
Code EXP
int ODBCexample()
{
RETCODE error;
HENV env; /* environment */
HDBC conn; /* database connection */
SQLAllocEnv(&env);
SQLAllocConnect(env, &conn);
SQLConnect(conn, “db.yale.edu", SQL_NTS, "avi", SQL_NTS, "avipasswd", SQL_NTS);
{ …. Do actual work … }
SQLDisconnect(conn);
SQLFreeConnect(conn);
SQLFreeEnv(env);
}
- Result tuples are fetched using
SQLFetch() SQLBindCol()binds C language variables to attributes of the query result
char deptname[80];
float salary;
int lenOut1, lenOut2;
HSTMT stmt;
char * sqlquery = "select dept_name, sum (salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name";
SQLAllocStmt(conn, &stmt);
error = SQLExecDirect(stmt, sqlquery, SQL_NTS);
if (error == SQL SUCCESS) {
SQLBindCol(stmt, 1, SQL_C_CHAR, deptname , 80, &lenOut1);
SQLBindCol(stmt, 2, SQL_C_FLOAT, &salary, 0 , &lenOut2);
while (SQLFetch(stmt) == SQL_SUCCESS) {
printf (" %s %g\n", deptname, salary);
}
}
SQLFreeStmt(stmt, SQL_DROP)
Embedded SQL
Embedded SQL(嵌入式SQL)
A language to which SQL queries are embedded is referred to as a host language(宿主语言), and the SQL structures permitted in the host language comprise embedded SQL.
Embedded SQL without cursor
main( )
{
EXEC SQL INCLUDE SQLCA; //声明段开始
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char account_no [11]; //host variables(宿主变量)声明
char branch_name [16];
int balance;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;//声明段结束
EXEC SQL CONNECT TO bank_db USER Adam Using Eve;
scanf (“%s %s %d”, account_no, branch_name, balance);
EXEC SQL insert into account
values (:account_no, :branch_name, :balance);
EXEC SQL delete from account where
account_number=:account_no;
EXEC SQL select balance into :balance:mask // 指示变量=0 正常
from account //指示变量<0 NULL
where account_number = :account_no; //指示变量 >0 截断
If (SQLCA.sqlcode ! = 0) printf ( “Error!\n”);
else printf (“Success!\n”);
}
Embedded SQL with cursor
select multiple records
main( )
{
EXEC SQL INCLUDE SQLCA;
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char customer_name[21];
char account_no [11];
int balance;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
EXEC SQL CONNECT TO bank_db USER Adam Using Eve;
EXEC SQL DECLARE account_cursor CURSOR for
select account_number, balance
from depositor natural join account
where depositor.customer_name = : customer_name;
scanf (“%s”, customer_name);
EXEC SQL open account_cursor;
for (; ;)
{
EXEC SQL fetch account_cursor into :account_no, :balance;
if (SQLCA.sqlcode!=0)
break;
printf( “%s %d \ n”, account_no, balance);
}
EXEC SQL close account_cursor;
}
Delete or update current record
where current of 游标名
//continue…
scanf (“%s”, customer_name);
EXEC SQL open account_cursor;
for (; ;)
{ EXEC SQL fetch account_cursor into :account_no, :balance;
if (SQLCA.sqlcode!=0)
break;
if (balance <1000)
EXEC SQL update account set balance=balance*1.05
where current of account_cursor;
else
EXEC SQL update account set balance=balance*1.06
where current of account_cursor;
}
EXEC SQL close account_cursor;
}
Basic Steps in Query Processing
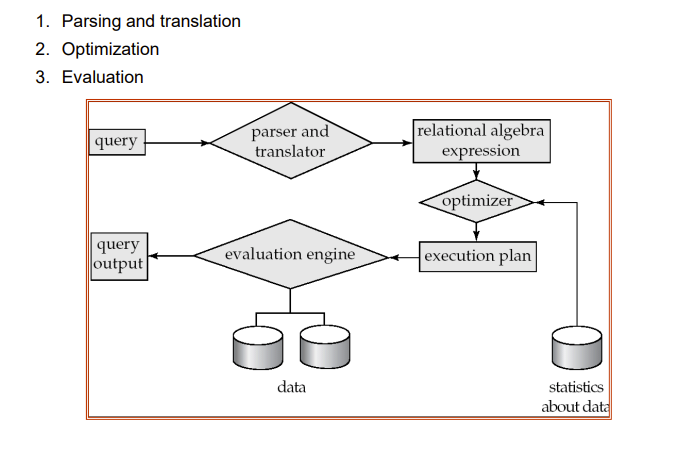
Procedural Constructs in SQL
SQL Functions
create function dept_count (dept_name varchar(20))
returns integer
begin
declare d_count integer;
select count (* ) into d_count
from instructor
where instructor.dept_name = dept_name
return d_count;
end
select dept_name, budget
from department
where dept_count (dept_name ) > 1
Table Functions
create function instructors_of (dept_name char(20) )
returns table ( ID varchar(5),
name varchar(20),
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2))
select *
from table (instructors_of (‘Music’)
SQL Procedures
create procedure dept_count_proc (in dept_name varchar(20), out d_count integer)
begin
select count(*) into d_count
from instructor
where instructor.dept_name = dept_count_proc.dept_name
end
declare d_count integer;
call dept_count_proc( ‘Physics’, d_count);
Procedural Constructs
While and repeat statements :
declare n integer default 0;
while n < 10 do
set n = n + 1
end while
repeat
set n = n – 1
until n = 0
end repeat
For loop: Permits iteration over all results of a query
declare n integer default 0;
for r as
select budget from department
where dept_name = ‘Music’
do
set n = n - r.budget
end for
Conditional statements (if-then-else)
if boolean expression
then statement or compound statement
elseif boolean expression
then statement or compound statement
else statement or compound statement
end if
Triggers
A trigger is a statement that is executed automatically by the system as a side effect of a modification to the database.
- Trigger - ECA rule
- E: Event ( insert, delete ,update)
- C: Condition
- A: Action
- To design a trigger mechanism, we must:
- Specify the conditions under which the trigger is to be executed.
- Specify the actions to be taken when the trigger executes.
account_log(account, amount, datetime)
-- event
create trigger account_trigger after update of account on balance
referencing new row as nrow -- for deletes and updates
referencing old row as orow -- for inserts and updates
-- condition
for each row
when nrow.balance - orow.balance > =200000 or
orow.balance -nrow.balance >=50000
-- action
begin
insert into account_log values (nrow.account-number,
nrow.balance-orow.balance , current_time() )
end
Statement Level Triggers
Instead of executing a separate action for each affected row, a single action can be executed for all rows affected by a transaction
- Use for each statement instead of for each row
- Use referencing old table or referencing new table to refer to temporary tables (called transition tables) containing the affected rows
Can be more efficient when dealing with SQL statements that update a large number of rows
create trigger grade_trigger after update of takes on grade
referencing new table as new_table
for each statement
when exists( select avg(grade)
from new_table
group by course_id, sec_id, semester, year
having avg(grade)< 60 )
begin
rollback
end
When Not To Use Triggers
- Triggers were used earlier for tasks such as
- maintaining summary data
- There are better ways of doing these now
Recursive Queries
find which courses are a prerequisite, whether directly or indirectly, for a specific course
with recursive rec_prereq(course_id, prereq_id) as (
select course_id, prereq_id
from prereq
union
select rec_prereq.course_id, prereq.prereq_id,
from rec_prereq, prereq
where rec_prereq.prereq_id = prereq.course_id
)
select ∗
from rec_prereq;
This example view, rec_prereq, is called the transitive closure of the prereq relation