Lecture 11 | Query Processing
数据库系统2024-05-06第6-8节 (zju.edu.cn)
ch15 - Query Processing(3).pdf
查询处理
就是看数据库怎么处理SQL指令这么一个字符串的
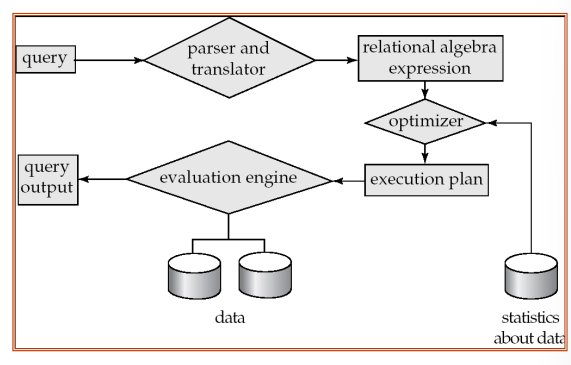
Basic Steps in Query Processing
- Parsing and translation
- 语法检查
- 转化为关系代数表达式
- Optimization
- 查询优化
- 最重要的一步、
- 关系代数等价变化化简
- 对代数里的每个算子选择合适的算法
- 每一个算子都有不同的实现方法
- 得到execution plan
- 这个是数据库内部的计划语言
- Evaluation
- execution plan交给引擎,搜索语言
给个例子语法检查和查询优化的
select name, title
from instructor natural join (teaches natural join course)
where dept_name=‘Music’ and year = 2009;
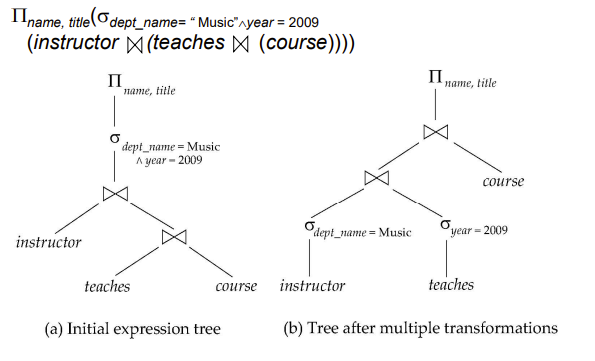
从叶子往上执行,右边这个不是最终优化结果,而是优化过程中根据某个规则得到的,这些规则一般都是经验规则
这里的规则是把选择运算推到了叶子节点,提前选择以减少后续运算量,用于第一次优化
优化后得到执行计划文件:
An evaluation plan defines exactly what algorithm is used for each operation, and how the execution of the operations is coordinated.
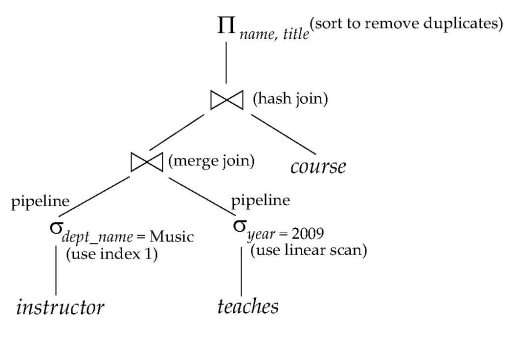
接下来我们看下,每个算子有哪些常见的算法,以及如何衡量、权衡
我们就将SELECT,JOIN,SORT三类
Measures of Query Cost
通常是磁盘访问时间作为cost的大头
- Number of seeks * average-seek-cost
- Number of blocks read * average-block-read-cost
- Number of blocks written * average-block-write-cost
一些细节
- Cost to write a block is greater than cost to read a block
- data is read back after being written to ensure that the write was successful
方便起见,我们只用磁盘块的读取数量以及寻找次数来衡量
- \(t_T\) - time to transfer one block
- \(t_S\) - time for one seek
这俩的比值相对稳定,用的比较多
还有一些细节
- We ignore CPU costs for simplicity
- We ignore cost to writing output to disk in our cost formulae
- 即我们约定忽略数据最终被写回磁盘的cost,因为流水线模式下数据不会被写回磁盘
- We often use worst case estimates, assuming only the minimum amount of memory needed for the operation is available
Algorithm
接下来看下都有啥子算法
Selection Operation
Algorithm A1 (linear search)
File scan
Scan each file block and test all records to see whether they satisfy the selection condition.
- worst cost = \(b_r * t_T + t_S\)
- \(b_r\) denotes number of blocks containing records from relation r
- average cost = \((b_r /2) t_T + t_S\)
If selection is on a key attribute, can stop on finding record
Note: binary search generally does not make sense since data is not stored consecutively except when there is an index available, and binary search requires more seeks than index search
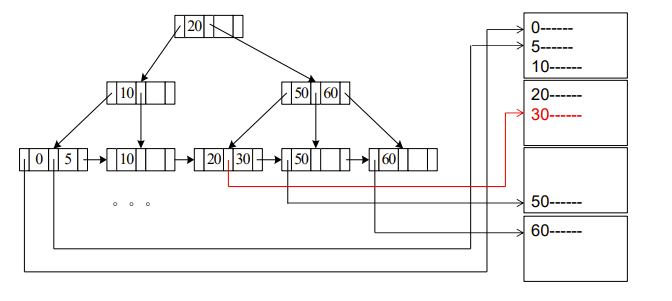
A2 (B+-tree index equality on key)
Index scan – search algorithms that use an index
A2 (primary B+-tree index / clustering B+-tree index, equality on key).
Cost = \((h_i + 1) * (t_T + t_S)\)
我们认为B+树在磁盘里,因为每个node占一个block,所以每个node都需要 一次seek + 一次transfer
A3 (B+-tree index equality on non-key)
equality 是等值查找的意思
A3 (primary B+-tree index/ clustering B+-tree index, equality on non-key)
Cost = \(h_i * (t_T + t_S) + t_S + t_T * b\)
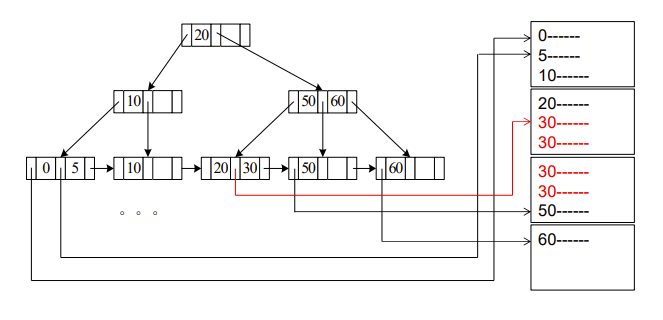
下面的是书上没有的,算是补充?
这个意思是n个record可能分散在m个block
乱序
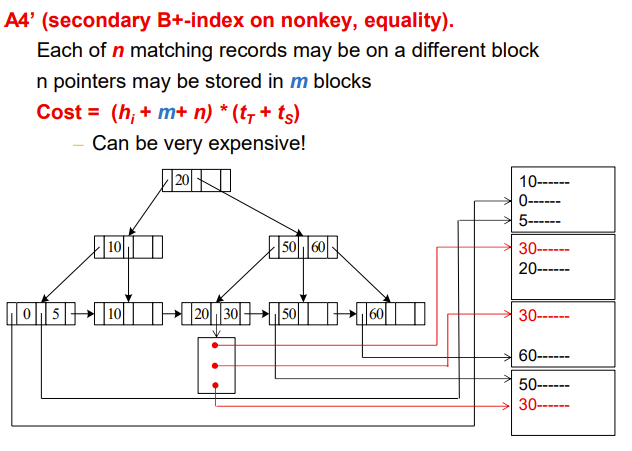
A5 (B+-index index, comparison)
之前是等值查询,这里是比较查询
- 分两种情况
- 找出大于V的,那就index出第一个大于V的,剩下的顺序找到结尾可,不用index
- Cost = \(h_i * (t_T + t_S) + t_S + t_T * b\)
- 找出小于V的,那都不用index了,直接从头找,找到大于V的停止即可
- 找出大于V的,那就index出第一个大于V的,剩下的顺序找到结尾可,不用index
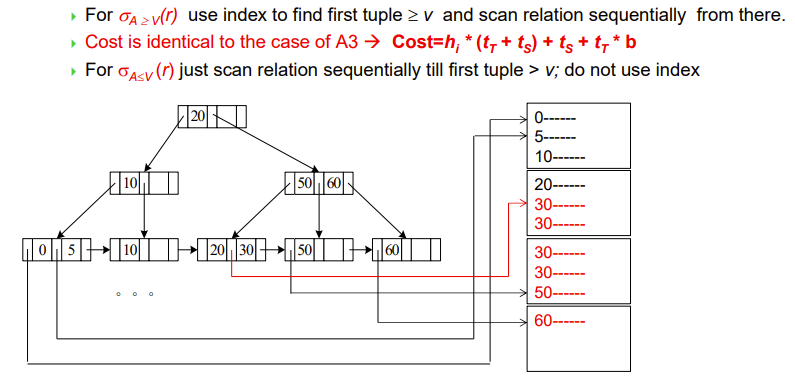
Implementation of Complex Selections

External Sort-Merge
我们考虑的是内存不够大的情况,即需要用到外部排序
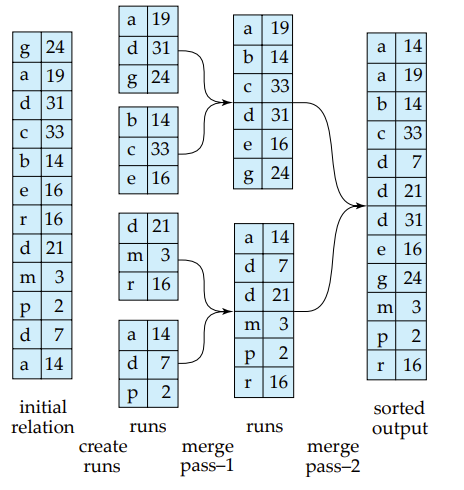
Let \(M\) denote memory size (in pages).
mem有M个page
- Create sorted runs(归并段)
- Let \(i\) be \(0\) initially.
- Repeatedly do the following till the end of the relation: 1. Read \(M\) blocks of relation into memory 2. Sort the in-memory blocks 3. Write sorted data to run \(R_i\) ; increment \(i\).
- Let \(N\) be the final value of \(i\) - 这个N是指有几个run
- Merge the runs (N-way merge).
- IF \(N < M\), single merge pass is required (如果归并段少于可用内存页 ) 1. Use \(N\) blocks of memory to buffer input runs, and 1 block to buffer output. Read the first block of each run into its buffer page 2. repeat 1. Select the first record (in sort order) among all buffer pages 2. Write the record to the output buffer. 1. If the output buffer is full, write it to disk 3. Delete the record from its input buffer page. 1. If the buffer page becomes empty then read the next block (if any) of the run into the buffer 3. until all input buffer pages are empty
- If \(N \ge M\), several merge passes are required. 1. In each pass, contiguous groups of \(M - 1\) runs are merged. 2. A pass reduces the number of runs by a factor of \(M - 1\), and creates runs longer by the same factor. 1. E.g. If M=11, and there are 90 runs, one pass reduces the number of runs to 9, each 10 times the size of the initial runs 3. Repeated passes are performed till all runs have been merged into one
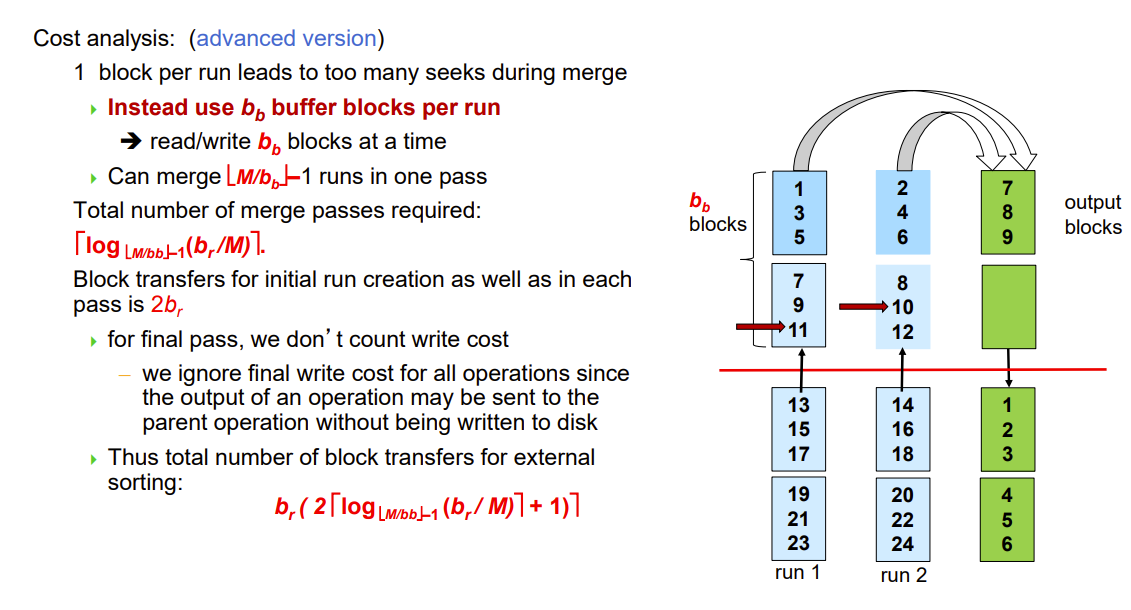
cost分析

br是数据占的block,M是内存buffer有的block
M-1是一次能归并的block,还有一个留来输出

Join Operation
有五种典型算法
- Nested-loop join
- Block nested-loop
- join Indexed
- nested-loop join
- Merge-join Hash-join
Nested-Loop Join
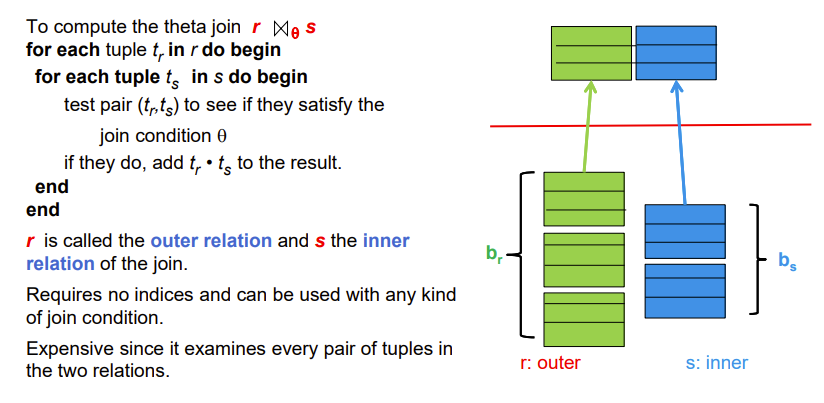
两重循环,遍历r和s的tuple
外循环的叫outer relation,内循环的叫inner relation
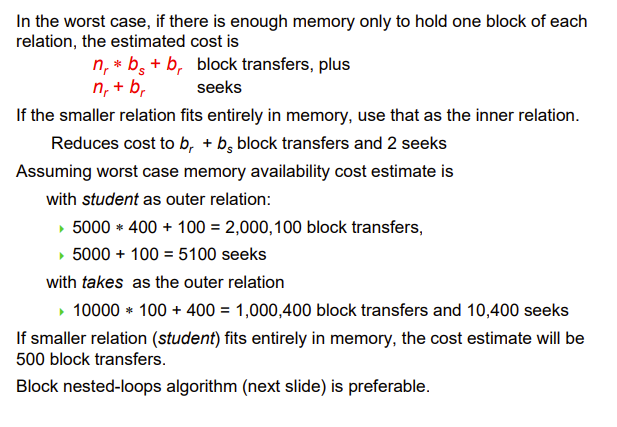
Block nested-loop
循环基本单位改成块,然后块与块再一个嵌套循环
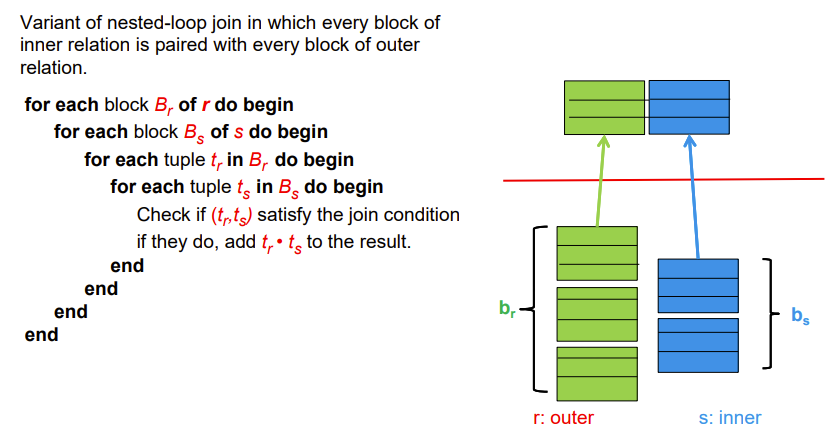
Worst case estimate: $ b_r+b_r * b_s$ block transfers + \(2 * b_r\) seeks
- Each block in the inner relation \(s\) is read once for each block in the outer relation
可见小关系放外循环比较好
Best case: \(b_r + b_s\) block transfers + \(2\) seeks
即内存足够大,r和s一次性进去即可
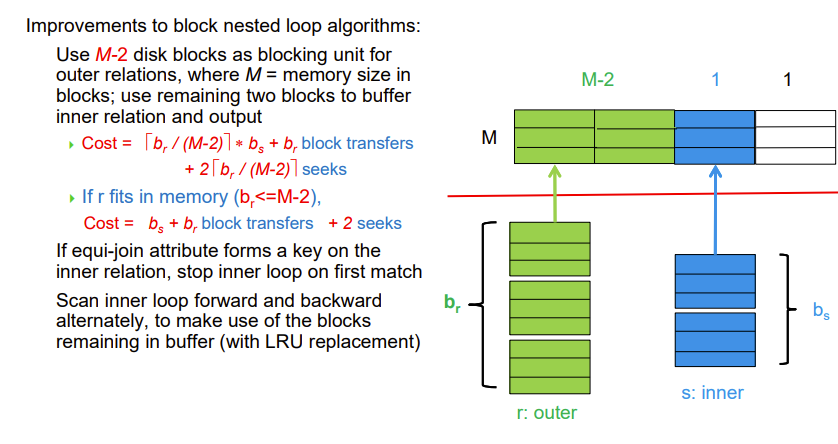
注意,上面是只有2个buffer block的情况,实际上我们有很多buffer block,下面讲多个buffer的情况
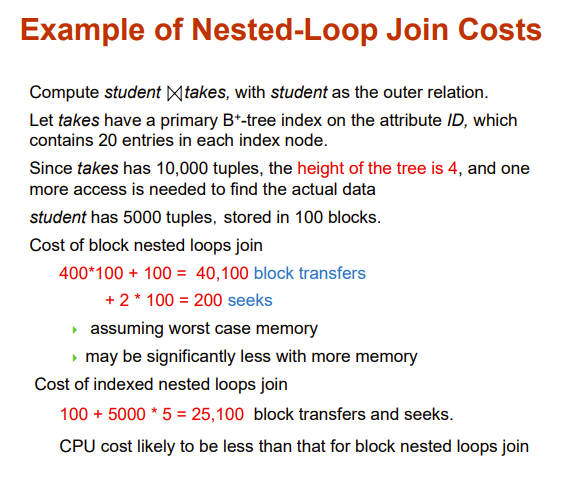
Indexed Nested-Loop Join
我们之前的思路都是外循环与内循环一一匹配
我们尝试通过索引替代内循环
- Index lookups can replace file scans if
- join is an equi-join or natural join
- and an index is available on the inner relation’s join attribute
对于每个r的tuple,我们通过索引查找满足条件的s的tuple
Worst case: buffer has space for only one page of r, and, for each tuple in r, we perform an index lookup on s.
Cost of the join: \(b_r (t_T + t_S) + n_r * c\)
- Where c is the cost of traversing index and fetching all matching s tuples for one tuple or r
- c can be estimated as cost of a single selection on s using the join condition.
If indices are available on join attributes of both r and s, use the relation with fewer tuples as the outer relation.
Merge-Join
Join step is similar to the merge stage of the sort-merge algorithm.
Main difference is handling of duplicate values in join attribute — every pair with same value on join attribute must be matched
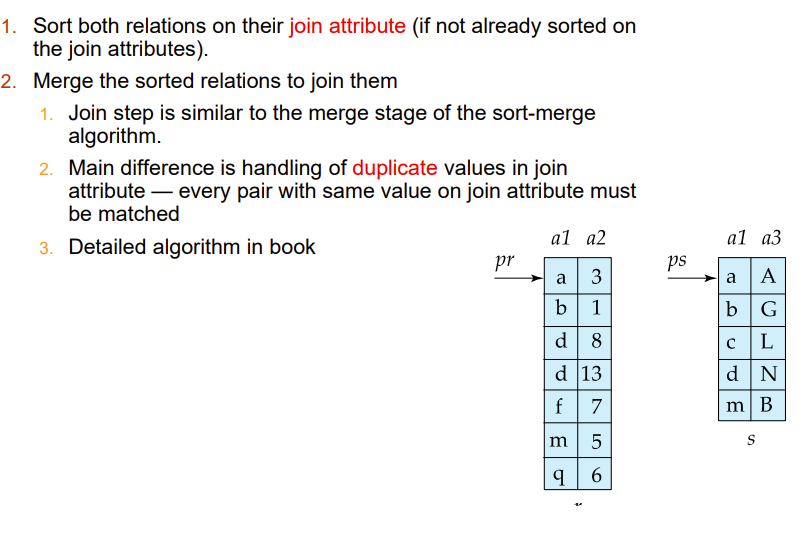
注意这个merge-join需要表先排好序

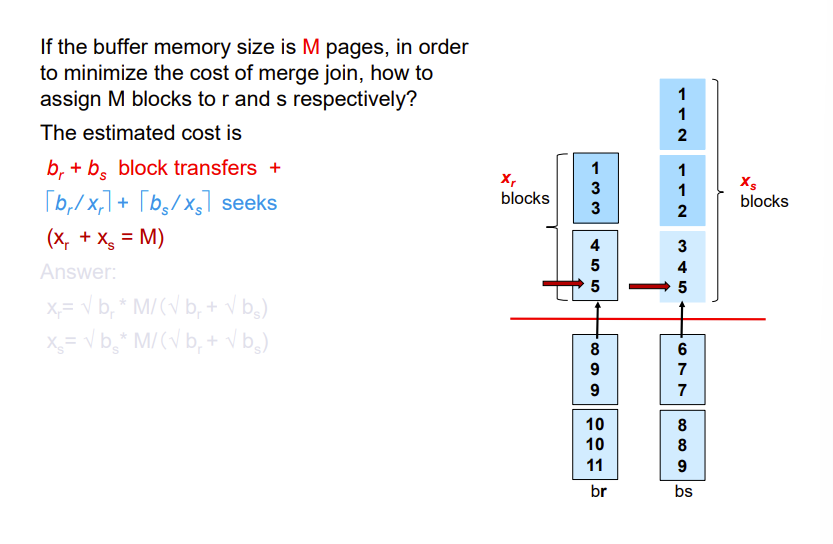
下面这个方法允许一个表无序

Hash-Join
引入哈希函数,函数值相同的归为一个集合
然后在这个集合内进行两重循环
至于哈希函数的稀疏成都取决于buffer多大,至少能让一个集合整体读入


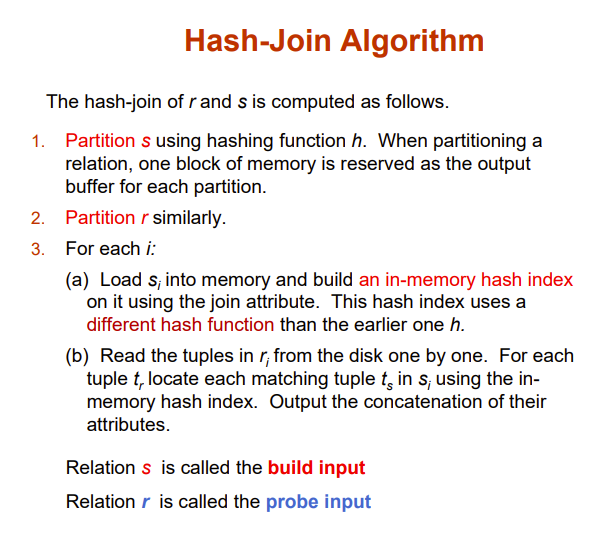
build input是能一次性读入内存的

Recursive partitioning

上面那个不等式很重要,决定要不要递归partition
嵌套partition,即patition太大了放不进buffer,就建一个新的哈希函数将patition拆分,还是大就再分别拆分