Lecture 12 | Query Optimization
上节课学了基本运作框架,这节课优化一下
这节课我们会将有哪些经验规则用于优化
以及估算关系代数表达式的中间结果规模
举个例子:
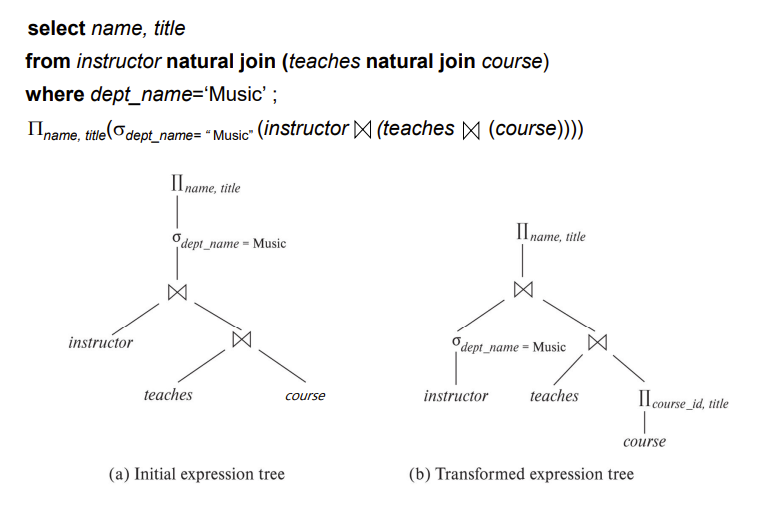
上面用到的规则是投影提前
An evaluation plan defines exactly what algorithm is used for each operation, and how the execution of the operations is coordinated
下图是一个执行计划的例子
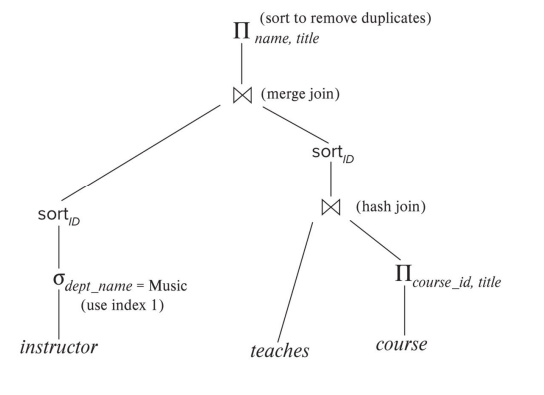
我们的优化基于经验规则与代价估算,生成最合适的执行计划
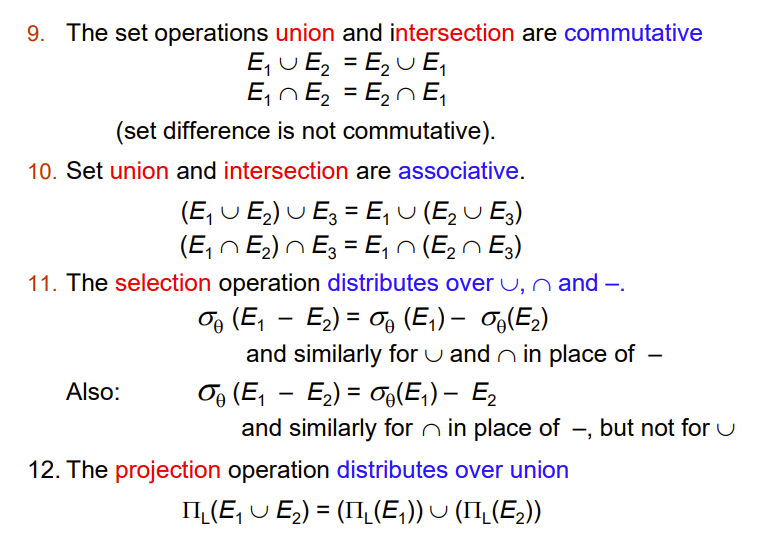
- Steps in cost-based query optimization
- Generate logically equivalent expressions using equivalence rules
- Annotate resultant expressions in alternative ways to get alternative query plans
- Choose the cheapest plan based on estimated cost
- Estimation of plan cost based on:
- Statistical information about relations
- number of tuples, number of distinct values for an attribute
- Statistics estimation for intermediate results
- Cost formulae for algorithms, computed using statistics
- Statistical information about relations
可以用
explain查询某条语句的执行计划
Generating Equivalent Expressions
等价变换
- Conjunctive selection operations can be deconstructed into a sequence of individual selections.
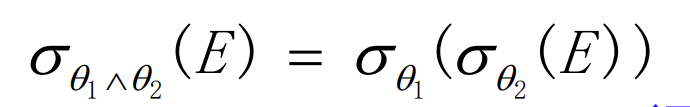
- Selection operations are commutative(可交换的).
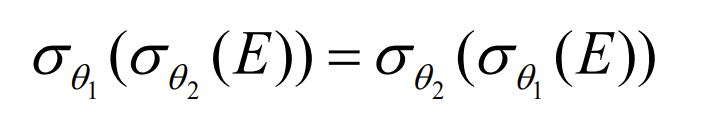
- Only the last in a sequence of projection operations is needed, the others can be omitted(可省略的).
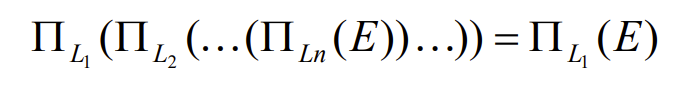
- Selections can be combined with Cartesian products and theta joins
- 因为我们希望尽量将选择转换为链接操作
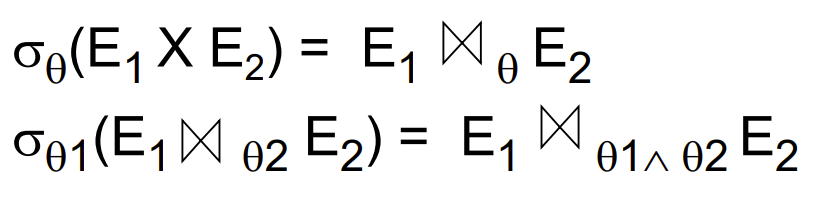
- Theta-join operations and natural joins are commutative(可交换的).
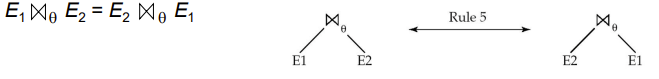
-
associative
- Natural join operations are associative(可结合的)
1.
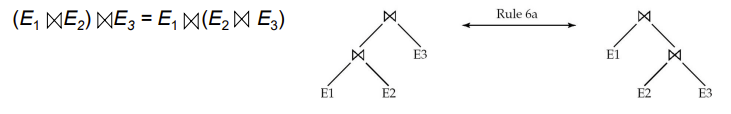
- Theta joins are associative in the following manner:
1.
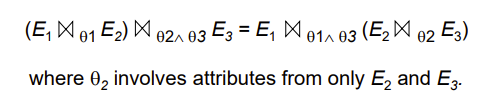
- Natural join operations are associative(可结合的)
1.
-
The selection operation distributes(分配)over the theta join operation under the following two conditions:
- When all the attributes in \(\theta_0\) involve only the attributes of one of the expressions (\(E_1\)) being joined.
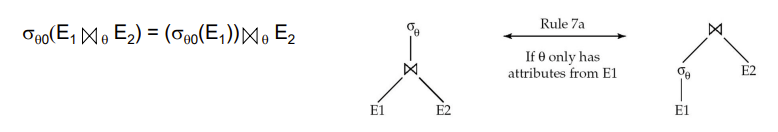
ii. When \(\theta_1\) involves only the attributes of \(E_1\) and \(\theta_2\) involves only the attributes of \(E_2\).
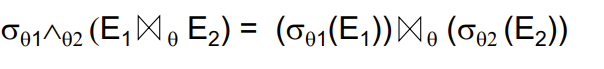
- The projection operation distributes(分配) over the theta join operation as follows:
- if \(\theta\) involves only attributes from \(L_1 \cup L_2:\)
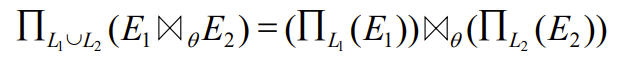

怎么这么多啊我超

Statistics for Cost Estimation
下面这些信息对于估算有用
- \(n_r\) 关系 \(r\) 中的元组个数
- \(b_r\) 关系 \(r\) 占用的块个数
- \(l_r\) 关系 \(r\) 有多长(大小)
- \(f_r\) 关系 \(r\) 占用的块,一块能放多少记录
- \(V(A,r)\) 关系 \(r\) 在某个属性上有几个值
- 比如性别有两个值

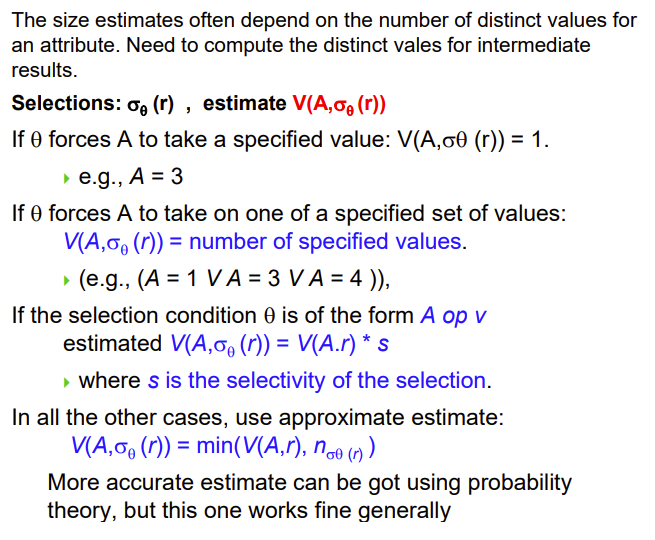
Selection Size Estimation
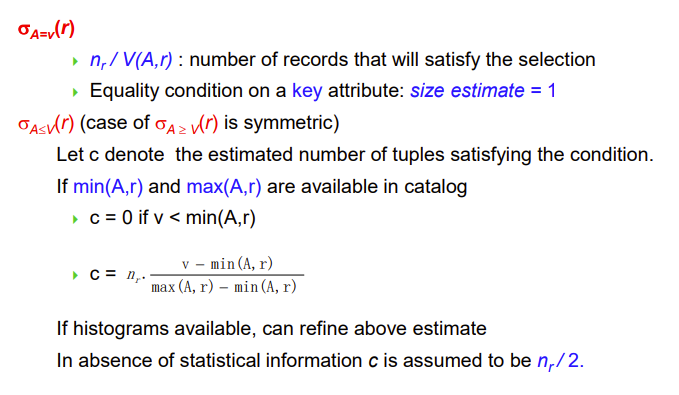
注意这里是在估计,所以看着很奇怪
max和min是这个属性里面的最大值和最小值
这里是假设这个属性均匀分布,我们可以根据实际权重进一步优化
Size Estimation of Complex Selections
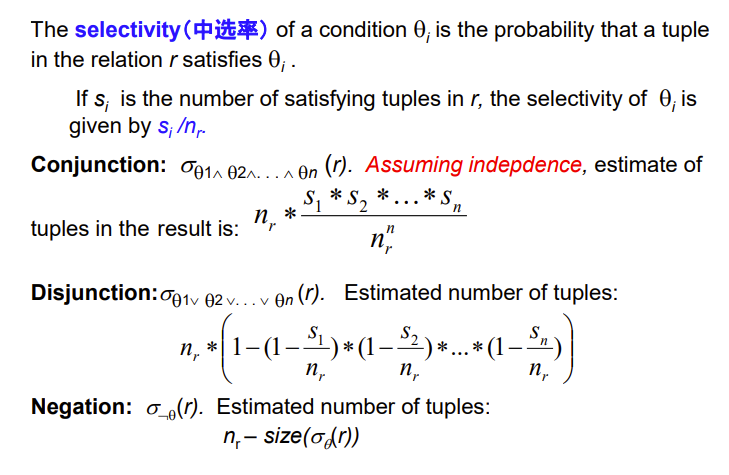
这里是假定各属性独立分布的,实际上很复杂,我们不考虑
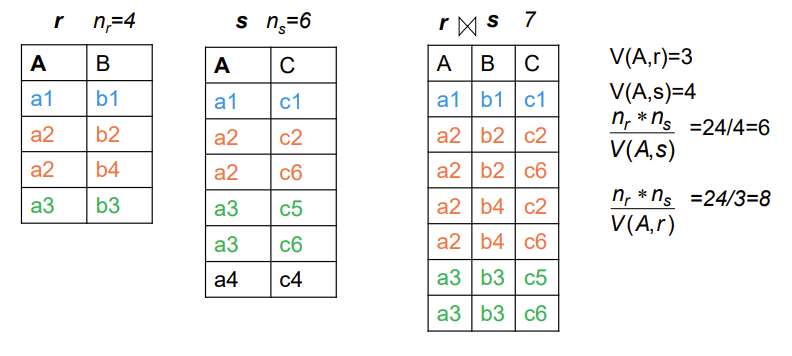
Estimation of the Size of Joins
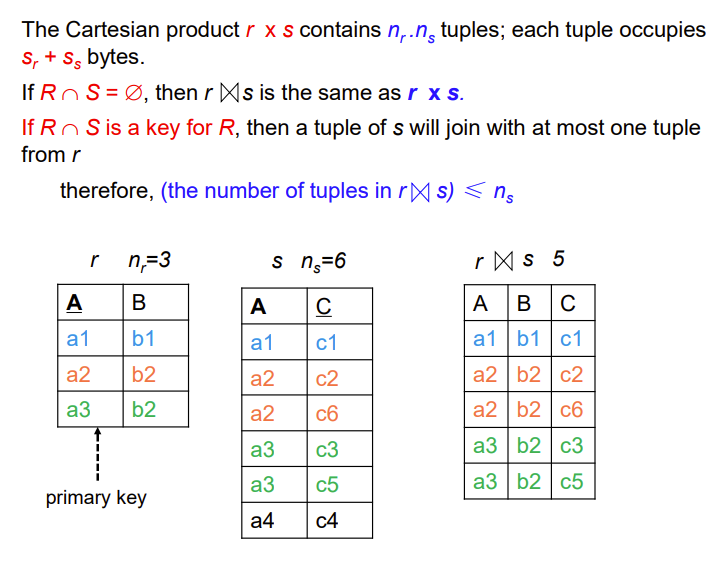
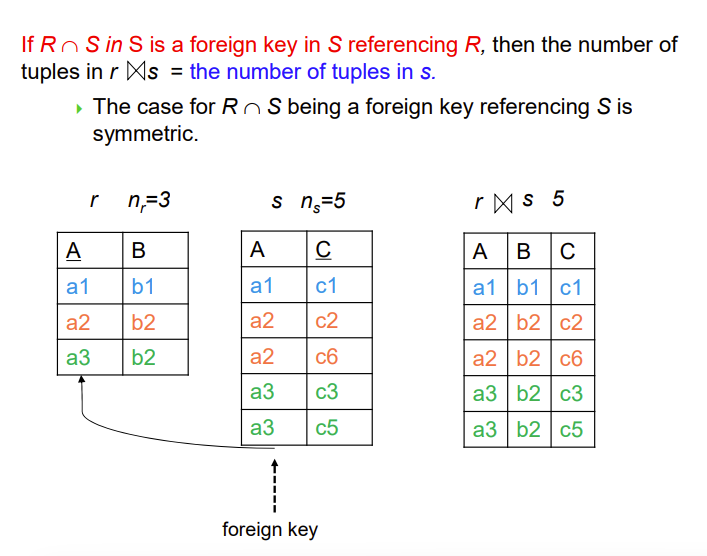

下面的没讲
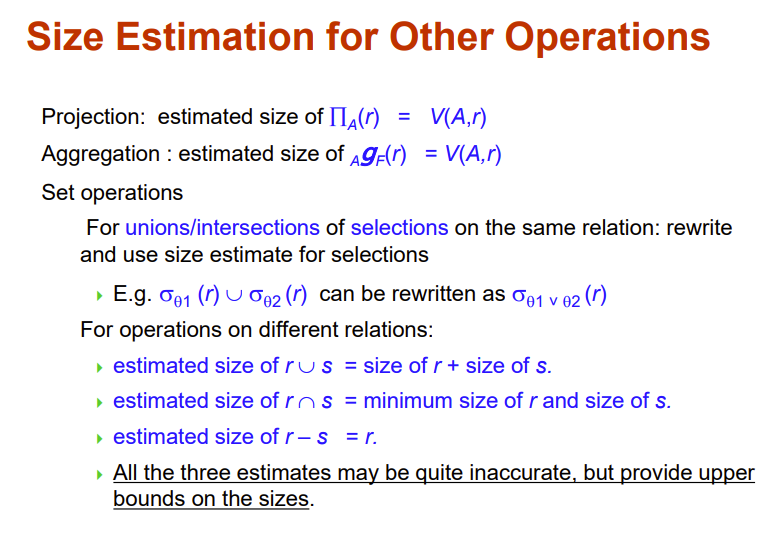
Estimation of Number of Distinct Values
即中间结果在某个属性上有几个值
就讲了概念

这两章是考试重点,必考
- 典型的算子的算法,必考
- 关系代数表达式等价规则,考小题
- 规模估算,必考
Choice of Evaluation Plans
如何选出最好的计划
最好的可能很难找,但是找稍微差一点的就会简单很多
Cost-based Optimizer
举个例子Selection

穷举数量太大了,我们可以动态规划一下
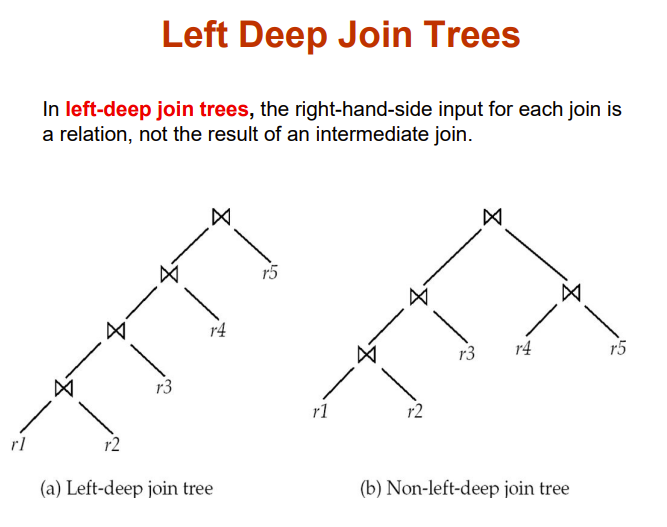
Join Order Optimization Algorithm

procedure findbestplan(S)
if (bestplan[S].cost )
return bestplan[S]
// else bestplan[S] has not been computed earlier, compute it now
if (S contains only 1 relation)
set bestplan[S].plan and bestplan[S].cost based on the best way
of accessing S using selections on S and indices (if any) on S
else for each non-empty subset S1 of S such that S1 S
P1= findbestplan(S1)
P2= findbestplan(S - S1)
for each algorithm A for joining results of P1 and P2
… compute plan and cost of using A (see next page) ..
if cost < bestplan[S].cost
bestplan[S].cost = cost
bestplan[S].plan = plan;
return bestplan[S]
可以优化一下
for each algorithm A for joining results of P1 and P2
// For indexed-nested loops join, the outer could be P1 or P2
// Similarly for hash-join, the build relation could be P1 or P2
// We assume the alternatives are considered as separate algorithms
if algorithm A is indexed nested loops
Let Pi and Po denote inner and outer inputs
if Pi has a single relation ri and ri has an index on the join attribute
plan = “execute Po.plan; join results of Po and ri using A”,
with any selection conditions on Pi performed as part of
the join condition
cost = Po.cost + cost of A
else cost = ; /* cannot use indexed nested loops join */
else
plan = “execute P1.plan; execute P2.plan;
join results of P1 and P2 using A;”
cost = P1.cost + P2.cost + cost of A
Cost of Optimization

Heuristic Optimization(启发式优化)
经验

Additional Optimization Techniques
嵌套查询怎么执行,怎么优化
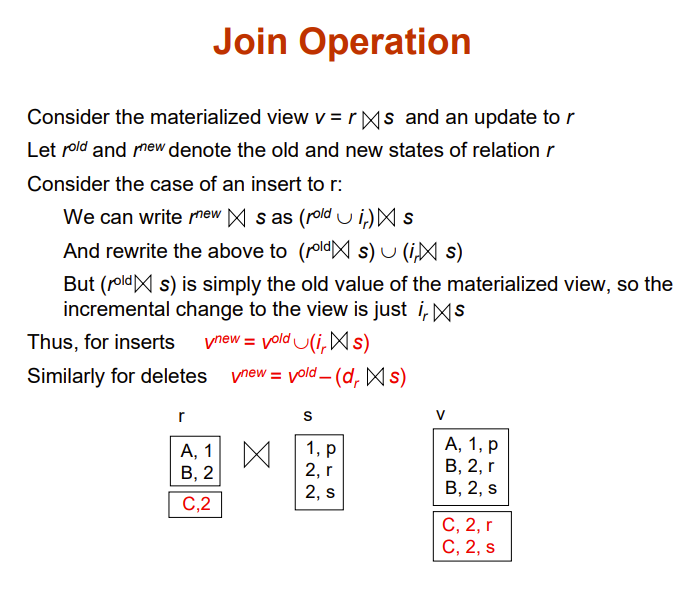
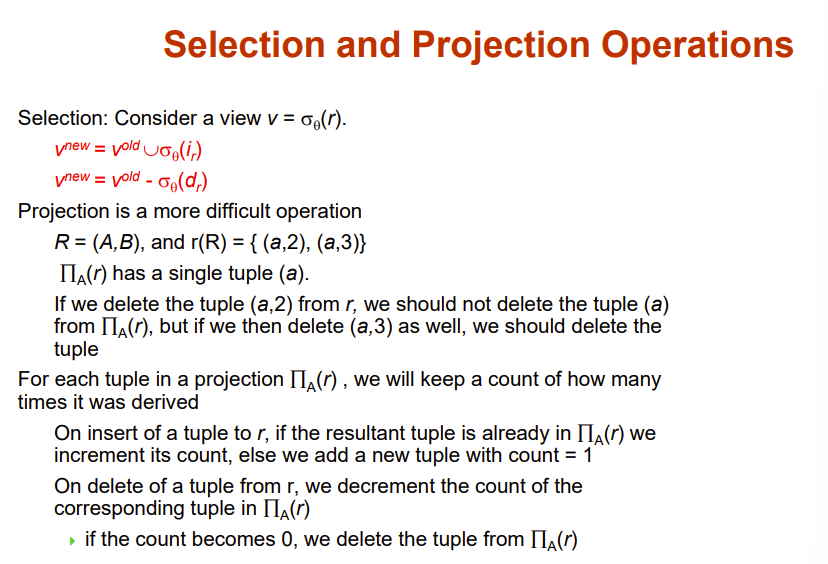
例化视图怎么实现
select name
from instructor
where exists (select *
from teaches
where instructor.ID = teaches.ID and teaches.year = 2022)
在找2022年上过课的老师
这有一个嵌套循环
可以改成下面这种不带嵌套的连接
但有个问题,上面那个name是distinct的,这里会重复
可以name加distinct,但这样的话同名就会出问题
这种优化可以归纳为以下的系统性算法,即将嵌套查询转化为半连接



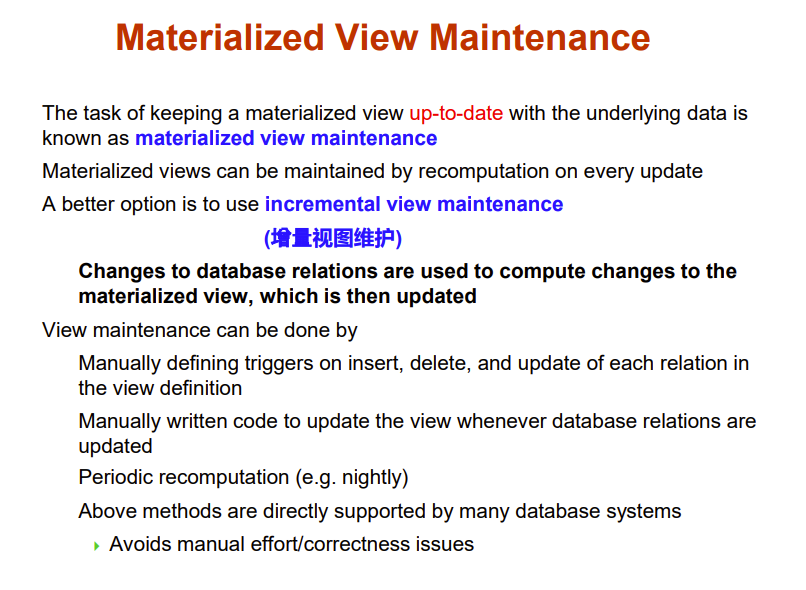
Materialized Views