Lecture 13 | Transactions
数据库系统2024-05-20第6-8节 (zju.edu.cn)
我们来到数据存储和索引,查询处理与优化,以及今天的并发控制与恢复
并发控制与恢复由事务管理模块实现,即其操作对象是事务
Transaction Concept
事务是一串SQL语句的执行序列,可以包含多条语句,用于完成一个目的。
A transaction is a unit of program execution that accesses and possibly updates various data items.
事务是要commit的
之前实验五的借书、还书都是一个个事务
- Two main issues to deal with:
- Failures of various kinds, such as hardware failures and system crashes
- 事务错误如何恢复
- Concurrent execution of multiple transactions
- 并发执行多条事务
- Failures of various kinds, such as hardware failures and system crashes
要完整描述一个事务,我们需要用到ACID Properties 这个概念
- ACID Properties
- Atomicity (原子性)
- 构成事务的操作被看成一个整体看待,要么全部成功,要么全不执行
- 数据库恢复功能能实现原子性
- Consistency (一致性)
- 就是不会错误地修改数据库,相互关联的数据应该进行更新。比如转账转完总的钱应该不变
- consistency requirements include
- Explicitly (显式) specified integrity constraints : primary keys , foreign keys
- 就是定义表时人为定义的
- Implicit (隐式)integrity constraints, e.g.– sum of balances of all accounts minus sum of loan amounts must equal value of cash-in-hand
- Explicitly (显式) specified integrity constraints : primary keys , foreign keys
- Isolation (隔离性)
- 要求各并行事务相互之间不能影响,就像虚拟内存的分块、
- 会影响的就不要并行了,改串行
- Durability (持久性)
- 对数据库的成功修改是永久性的,除非被其它事务再次修改
- even if there are software or hardware failures
- 出故障时,数据库恢复功能能实现持久性,比如用日志
- Atomicity (原子性)
A Simple Transaction Model
这个model的数据库只支持读写两种操作
我们后面的研究均基于此模型
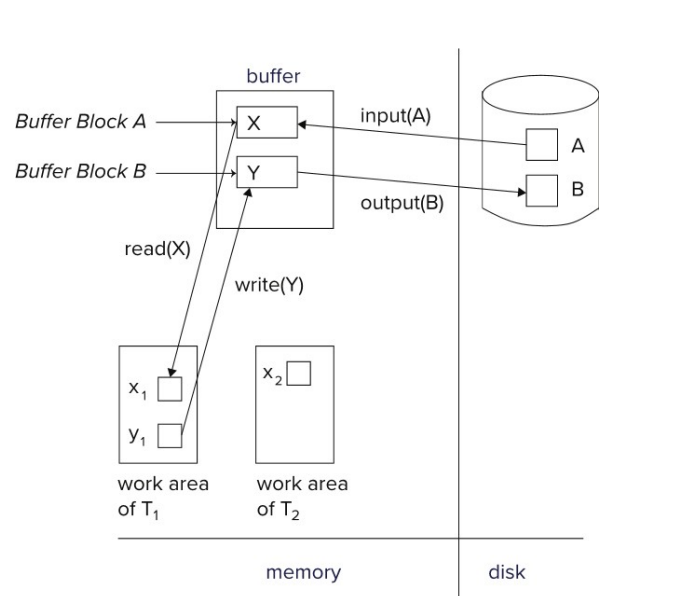
Transaction State
- Active
- the initial state
- it is executing
- Partially committed
- after the final statement has been executed
- 缓冲区,还没正式提交,可能会fail
- Failed
- after the discovery that normal execution can no longer proceed
- Aborted
- after the transaction has been rolled back and the database restored to its state prior to the start of the transaction
- Two options after it has been aborted:
- restart the transaction
- kill the transaction
- Committed
- after successful completion
Concurrent Executions
并行处理会遇到以下问题
- Anomalies in Concurrent Executions
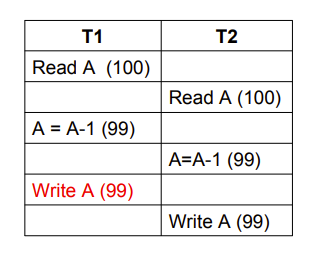
- Lost Update( 丢失修改 )
- 出现了交叉修改,其中一个被覆盖了
- 比如两个人同时买票
- Dirty Read (读脏数据)
- 比如一个人预定票结果没钱又退了
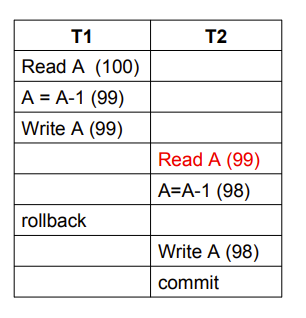
- 比如一个人预定票结果没钱又退了
- Unrepeatable Read(不可重复读)
- 我们要求事务的隔离性,这里T1的第二次read被T2影响了,这是我们不希望出现的
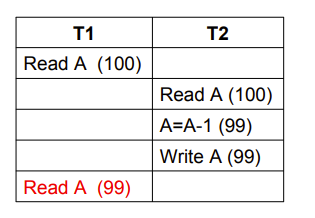
- 我们要求事务的隔离性,这里T1的第二次read被T2影响了,这是我们不希望出现的
- Phantom Problem (幽灵问题)
- 和上一个类似,不过这里是指T1里面的第二次select由于收到T2影响,多了一个entity

- 和上一个类似,不过这里是指T1里面的第二次select由于收到T2影响,多了一个entity
- Lost Update( 丢失修改 )
Schedules(调度)
就是一组排好序以防止出现并行问题的事务,注意是一组事务
Schedule – a sequences of instructions that specify the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed
a schedule for a set of transactions must consist of all instructions of those transactions
must preserve the order in which the instructions appear in each individual transaction
Schedule 1
一个串行调度(serial schedule),先执行一个再执行另一个,肯定能保证正确

Schedule 2
一个交叉调度,与Schedule 1等价
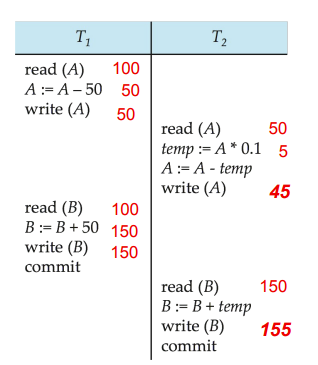
可见这个交叉调度实际上是根据操作对象进行分类的串行执行,等价于串行调度
这种能变化到串行调度的调度叫 Serializability( 可串行化 ) 的
Serializability
关于Serializability我们会从冲突的角度来看,先看看什么是冲突
- Conflicting Instructions
- 两条操作对象相同的操作,只要不都是读,一定是冲突的
- 或者说,操作对象相同,只要有写操作,就是冲突的
- 操作对象不相同肯定不冲突啦
- Conflict Serializability (冲突可串行化)
- If a schedule S can be transformed into a schedule S´ by a series of swaps of non-conflicting instructions, we say that S and S´ are conflict equivalent.
- 即,能通过交换非冲突指令变成另一个调度,就说这两调度是冲突等价的
- We say that a schedule S is conflict serializable if it is conflict equivalent to a serial schedule
Testing for Serializability
Precedence graph(前驱图)— a directed graph where the vertices are the transactions
有向边指示两者有一对冲突的操作,被指向的事务的指令时间上在后
这玩意儿是理论研究用的,实际实现不会用这个
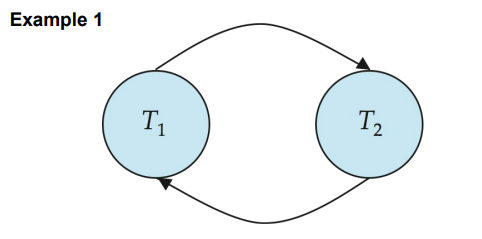
注意,冲突的操作是不能交换次序的
所以如果两个事务能形成一个有向闭环,那肯定不能转化为串行
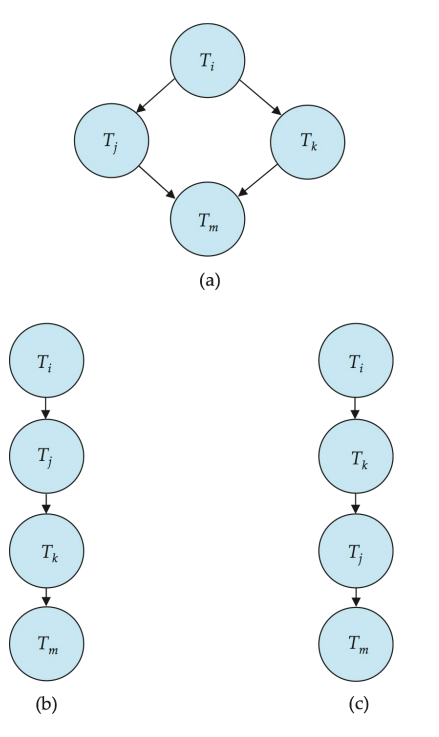
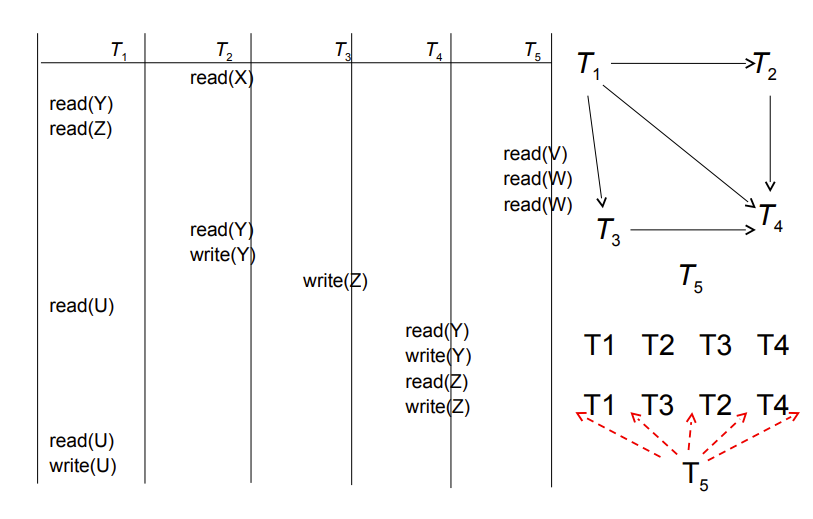
注意T5没有冲突,但是也要放进图里
T5可以放在串行调度里的任意位置(见右下角示意图)
Different forms of Serializability
view serializability(视图可串行)
这里不管冲突的概念了
- view serializability
- 我们要求两个调度,只要读操作获得的数值一致,且写操作写出去的数值也是一样的即可
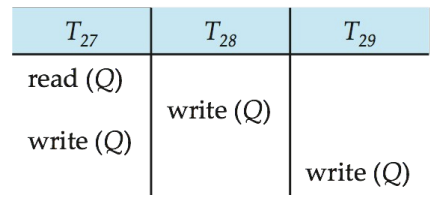
比如从这个角度出发,这个等价于串行调度 T21-T28-T29
Other Notions of Serializability
这里讲的只看输出结果是不是一样即可
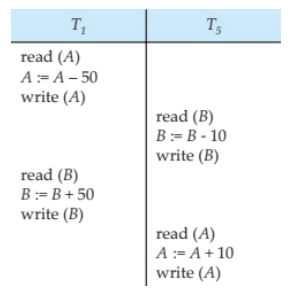
即,(B-10)+50 = (B+50)-10
Recoverable Schedules
可恢复与可串行是等级别的性质
- Recoverable schedule (可恢复调度)
- 比如,T1先写了A,T2再读了A,那么如果T1的commit先于T2,这就是可恢复调度
- 如果T2先commit,那么T1如果rollback就会导致T2读的是不一致的
我们下面看一下这部分常见的问题
Cascading Rollbacks
cascade是连锁的意思
- Cascading rollback
- 即多个事务都一个接一个读和写,第一个错了就会导致后面的全部都要rollback
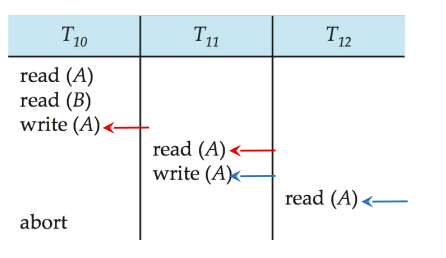
none of the transactions has yet committed (so the schedule is recoverable)
一个简单的解决办法就是规定不读脏数据,我们管采用这种规则的调度叫 Cascadeless schedules (无级联调度)
脏数据即改了还没commit的数据
Concurrency Control & Serializability
- 数据库必须提供机制以保证调度都是
- either conflict or view serializable
- recoverable and preferably cascadeless
Weak Levels of Consistency
上面是理论,是理想的
下面是实际,用一些牺牲换取性能
Transaction Isolation Levels
- Serializable
- Repeatable read
- only committed records to be read, repeated reads of same record must return same value.
- 不关心幽灵问题
- Read committed
- 不读脏数据
- Read uncommitted
- 能读脏数据
Concurrency Control Protocols
通过什么机制决定事务的串行机制

- Lock-Based Protocols
- 访问数据前需要申请相应的锁,一个数据同一时间只有一个锁
- 读数据申请共享锁
- 写数据申请派那锁?
- 共享锁之间可以容纳,其它情况不能相容
- 访问数据前需要申请相应的锁,一个数据同一时间只有一个锁
- Timestamp-Based Protocols
- 给每个事务一个时间戳,类似出生日期,且十分精确
- 根据时间戳决定次序
上面两种都是悲观的,即针对会出现问题的情况进行设计
下面这个是乐观的
- Validation-Based Protocols
- Each transaction must go through 3 phases:
- Read phase Validation phase Write phase
- Each transaction must go through 3 phases:
Lecture 13 | Concurrency Control
怎样的并发控制能让事务都产生可并发调度:1. 可串行 2. 可联级调度
数据库系统2024-05-20第6-8节 (zju.edu.cn) 02:07:31
等PPT