2-Class
this 在类里面是指向类本身的指针,是每个成员函数都有的隐藏参数
Point 是姓, init 是名,因此 Point::init 共同构成了成员函数的名字,因此 void 需要放在函数名前面,即 void Point::init.
void Point::move(int dx, int dy); can be recognized as void Point::initialize(Point *this, int dx, int dy);
Object
Object = Attributes + Services,是一块内存区域
对象是一个类,类定义了对象,就像 1235 是一个 int,int 定义了 1235
Everything is an object.
Every object has a type.
Each object has its own memory made up of other objects.
A program is a bunch of objects telling each other what to do by sending messages.
同类型的对象可以接受相同的消息,可以接受相同消息的对象认为是同个类型
Constructor
对象离开其作用域时,析构会被自动调用,作用域以大括号为界
:: Resolver 预解析器
Destructor
进入函数,函数所有的本地变量的空间都已经被分配好了,但如果没有执行到具体的构造函数,是不会调用构造函数的
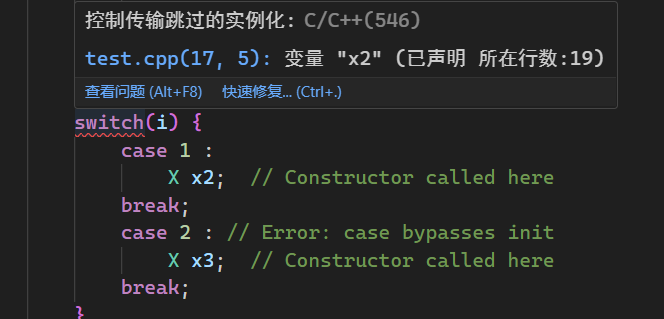
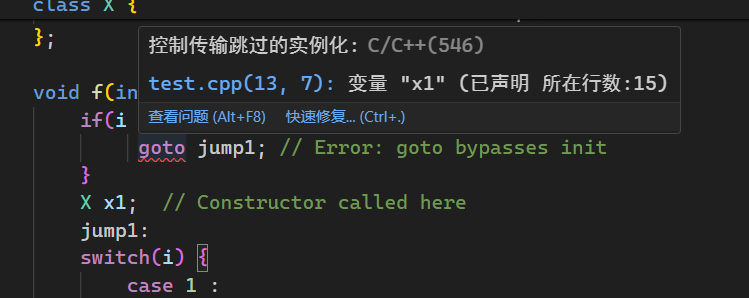
同理,当进入 switch case 语句时,对象的空间已经生成,但没有构造,这样析构时可能会出现问题,下面看个例子
void f(int i) {
if(i < 10) {
//! goto jump1; // Error: goto bypasses init
}
X x1; // Constructor called here
jump1:
switch(i) {
case 1 :
X x2; // Constructor called here
break;
//! case 2 : // Error: case bypasses init
X x3; // Constructor called here
break;
}
}
这里 jump1 跳过了 x1 的构造,但在进入函数 f 时空间已经被分配好了,当函数结束时,析构仍然会自动进行,如果没有默认零值的话析构会出问题,所以编译器会检查 ctor 有没有被跳过的可能,有就报错,保证 ctor 只要出现在代码里就 100% 会被执行
goto 可能导致 ctor 被跳过的报错:
case 可能导致 ctor 被跳过的报错: