Ch3-2 Tomasulo Algorithm
这个和 Scoreboard 一样也是一个 Dynamic Scheduling 算法,希望进一步减少 stall,同时减少编译器工作量,更多使用硬件优化
课前小测
- IS RO EX WB
- IS
- RO
- WB
Tomasulo Algorithm
我们主要针对浮点数运算
结构 hazard 改进
Scoreboard 有一个问题,结构竞争一定会有 stall,但是 stall 是后面所有指令都 stall,但是其他指令完全不用 stall 的,只有那一条结构 hazard 的指令需要 stall
相当于 Scoreboard 模型里所有指令都在 IS 这一个入口排队,一个一个进入,前面的人卡了后面的人只能跟着排队
但是,我们可以排队的地方换到每个组件那,即结构 hazard 时后面的指令还是可以继续进入其它组件执行,不用 stall,而卡住的指令相当于在组件前排队(即每个组件都设置入口用于排队)
这个每个组件前的排队队列叫 reservation stations,作用相当于缓冲区,大大缓解结构 hazard
而且 reservation stations 还能起到 register renaming 的作用,避免 WAR, WAW hazards
[!NOTE] Tomasulo 解决 WAR, WAW 的办法
Tomasulo 发生 WAW hazard 时总是把最新的值写进 reg,相对旧的值不会写进 reg,但是还是会在 CDB 广播,如果有指令需要就可以接收;
关于 WAR hazard,由于 Tomasulo 算法在指令 issue 的同时就会把能读取的 operand 先读取,所以并不会出现 WAR hazard
RO 改进
我们之前接触的流水线,访问寄存器都是通过 reg file
Tomasulo 流水线加入了公共数据总线 Common Data Bus,而且 reservation stations 会自动监听,让每个 reservation stations 都实时知道哪些 reg 被读写了
而且 Common Data Bus 同时能起到 forwarding pass 的作用,改善 RAW
现在数据从被动访问变成了主动广播,reservation stations 主动获取数据
Tomasulo 流水线结构图
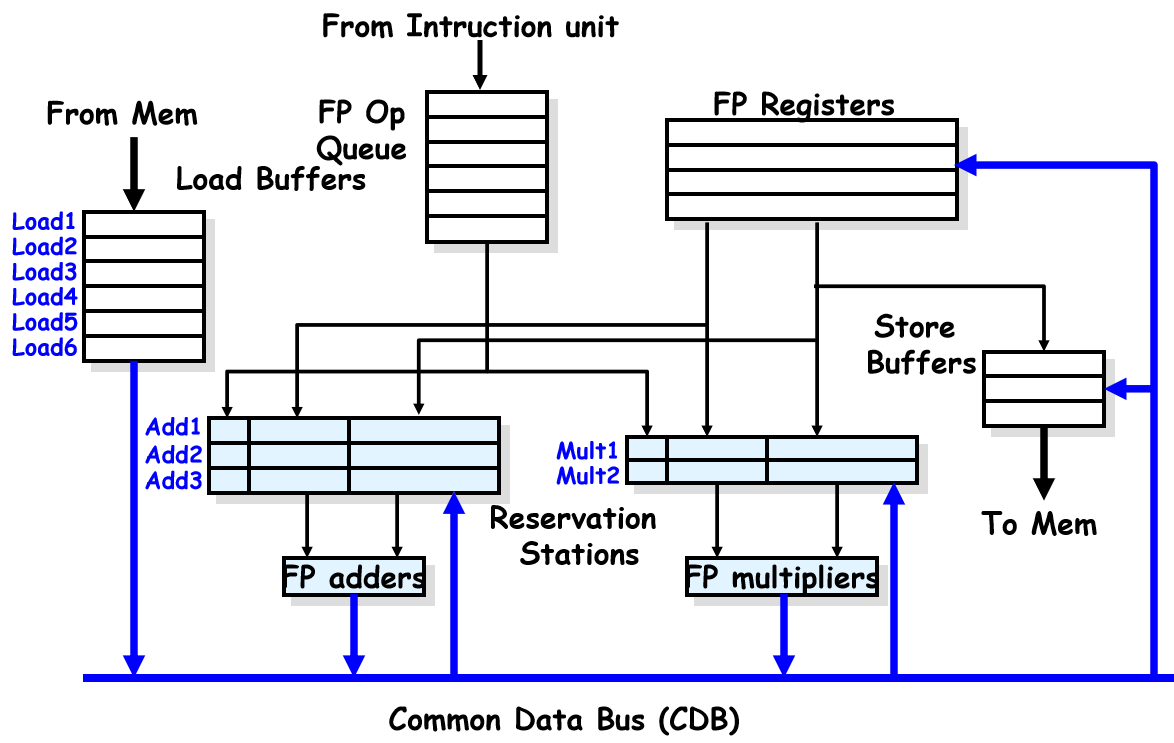
[!NOTE] load buffer
该 buffer 会根据
load指令的 addr 从 mem 读取相应的数据,并在 CDB 上广播实际上,load buffer 包含了很多专门用于
load操作的 FU相应的,要用的该数据的指令会将
Qj/Qk写为 load buffer 对应的序号(renaming)
reservation stations
每个保存站都有编号
- Op: Operation to perform in the unit
- Vj, Vk: Value of Source operands
- 从寄存器读过来,与 Scoreboard 不同的是,Tomasulo 是单个可读取就先读取,不用管另一个
- 如果还读取不了,说明要用到的是另一条指令的执行结果
- 如果 Register result status 对应的 reg 是空的,就直接读取 reg,如果是 mem 在写,就改为对应的 mem 标记
- Qj, Qk: Reservation stations producing source registers (value to be written)
- Note: Qj, Qk = 0 => ready
- Store buffers only have Qi for RS producing result
- 这里就会记录哪个需要的数据是哪个指令的结果,记的是对方的保存站编号
- 同时也是一种 forwarding,解决了 RAW
- 对应的 FU 算完之后会进行广播,然后 Qj, Qk 会被清空,同时 Vj, Vk 更新为对应的标记
- A: hold info. for memory address calculation
load和store的目标地址
- Busy: Indicates reservation station or FU is busy
- Register result status—Indicates which functional unit will write which register
- 使用后数据变成操作结果
Data path
一般我们的 bus 是“go to”模式,即给一个地址,给一个数据,数据会传输到该地址
Common data bus 是 data + source 进行广播,标记数据是从哪来的,是哪个组件产生的
所有接收端都会收到数据,然后根据 source 和 Qj, Qk 判断是否使用
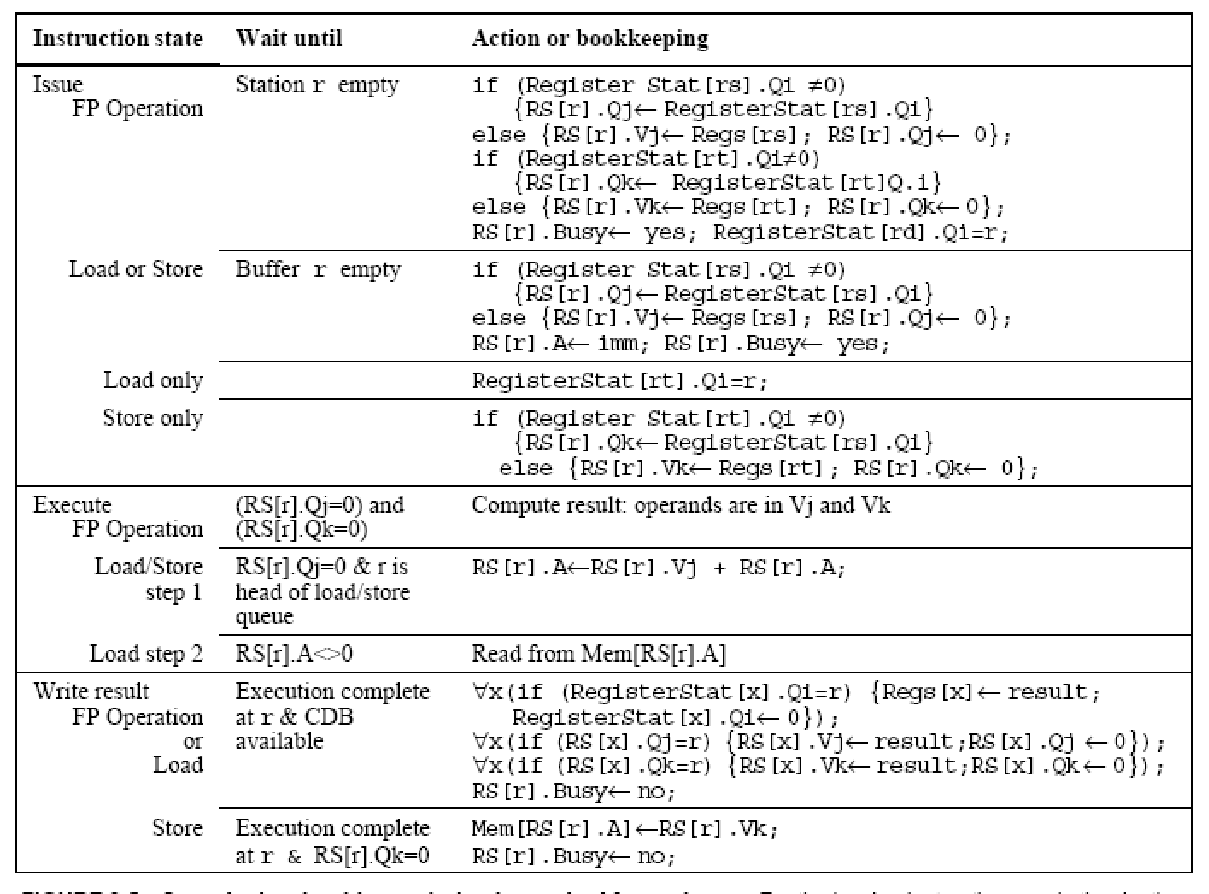
Stages of Tomasulo Algorithm
- Issue—get instruction from FP Op Queue
- If reservation station free (no structural hazard), control issues instr & sends operands (renames registers).
-
Execute—operate on operands (EX)
- When both operands ready then execute;
- if not ready, watch Common Data Bus for result
- Write result—finish execution (WB)
- Write on Common Data Bus to all awaiting units;
- mark reservation station available
- 即清空 reservation stations 表格对应的数据
具体实现要点
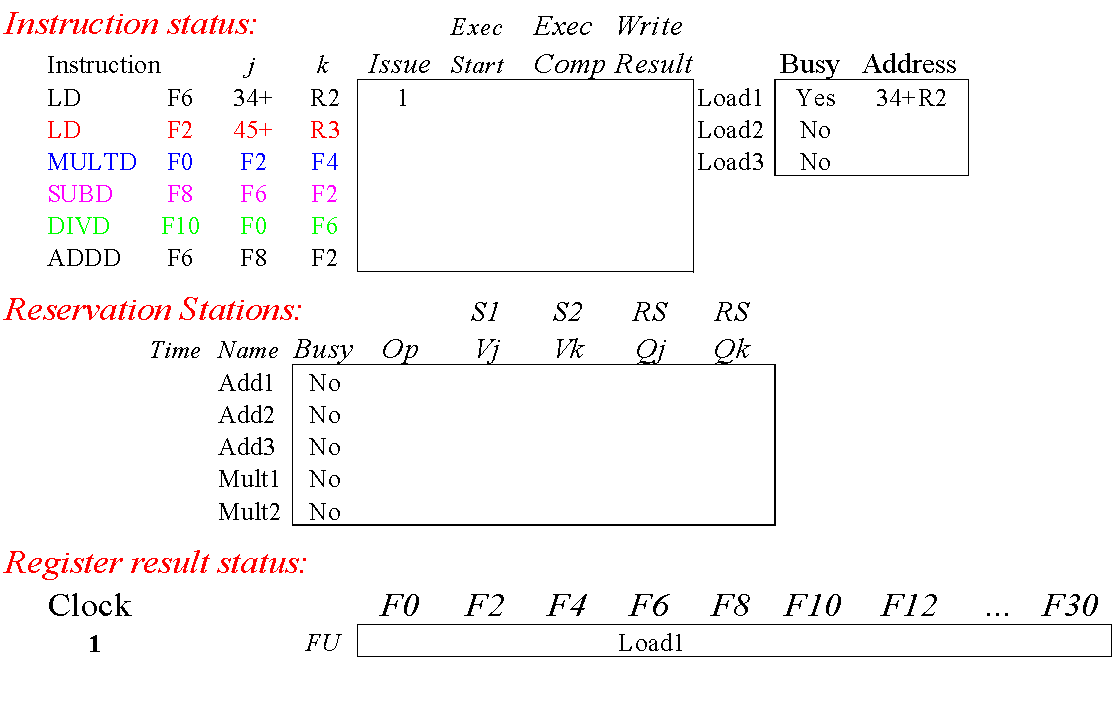
Tomasulo Example
注意指令状态表 Tomasulo 是没有的,PPT 里是为了方便看懂
PPT 11 页
Loop Example
Tomasulo 可以让 循环的迭代 部分地并行执行,因为解决了很多的数据依赖问题
[!TIP]
左上角六行指令是两轮迭代的展开,右下角才是原指令
这里实现的就是第一轮迭代里的MUL与第二轮的MUL可以同时运行
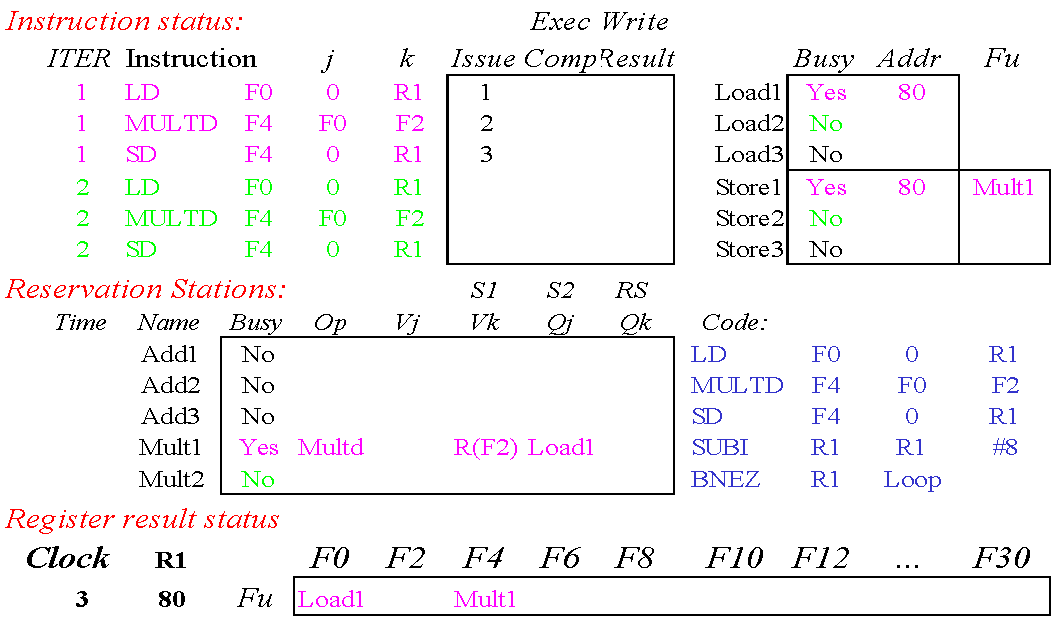
[!NOTE] store buffer
这里也有一个隐式 renaming,我们注意到 MUL 与 SD 发生了 WAW hazard,但是我 store buffer直接指示我要的是Mult1的结果(而不是直接要F4的值)
PPT 36 页,需要看一下什么玩意儿,没搞明白
Summary of Tomasulo Algorithm
Reservations stations
- implicit register renaming to larger set of registers + buffering source operands
- Prevents registers as bottleneck
- Avoids WAR, WAW hazards of Scoreboard
- Allows loop unrolling in HW
Tomasulo had: In-order issue, out-of-order execution, and out-of-order completion