ILP: Branch Prediction&Hardware-based speculation
[!ABSTRACT]
我们已经解决了 Structural Hazard、Data Hazard,还有 Control Hazard 依旧得 satll
Dynamic Hardware Prediction
1-bit Branch-Prediction Buffer
就记录上一次有没有跳转,上一次跳了这次也跳
2-bit Branch-Prediction Buffer
有两个版本,一个如下

还有是两位计数器版本的
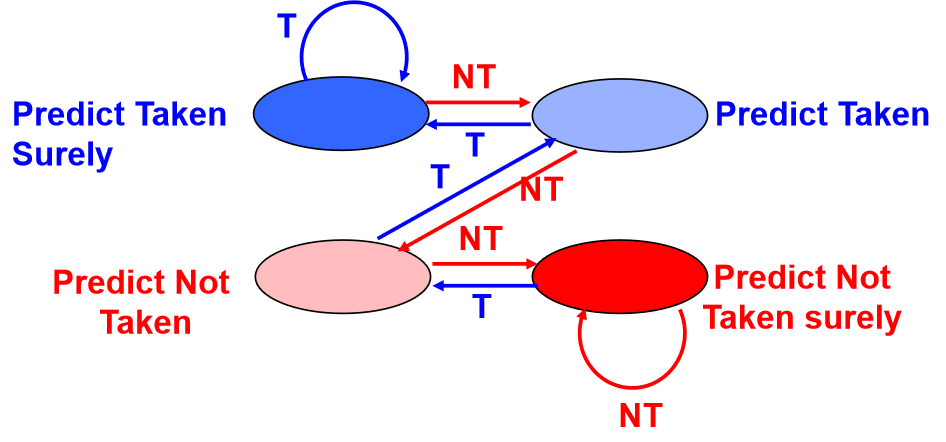
由两位预测器的思路可以延伸出 n bit predictor,但我们最常用的还是两位的
Correlating Branch Predictors
我们会发现,某次 branch 的结果会与之前 branch 的结果有关联,所以我们可以根据前 N 条指令的情况分别设置 Prediction Buffer
前 N 条 branch 的结果共同组成一个 key 来查询该访问哪个 Prediction Buffer
这种办法的准确性很高
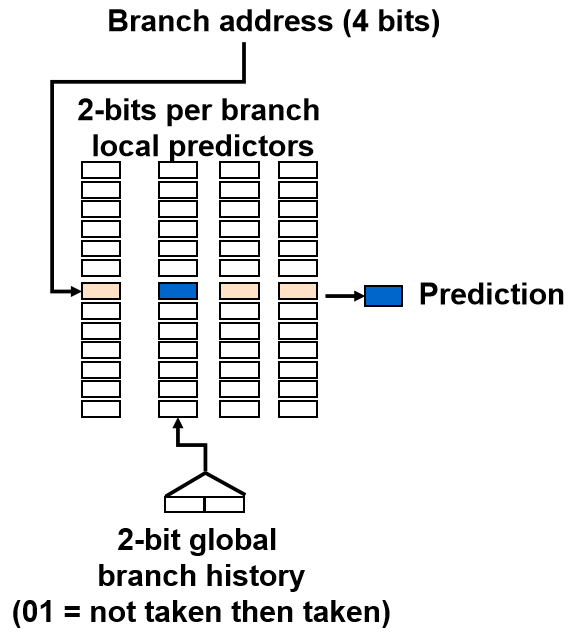
[!NOTE] (2,2) predictor: 2-bit global, 2-bit local
我们使用 Global History Register(GHR)来记录前两次 branch 的结果
例如 2-2 Correlating Branch Predictors , 有一个 2 位 GHR 和 4 个 2-bit Branch-Prediction Buffer,后者先初始化全为 0
我们根据 GHR 选择访问哪个的 Prediction Buffer,进行预测,然后再根据实际结果进行相应的状态转移,搞定
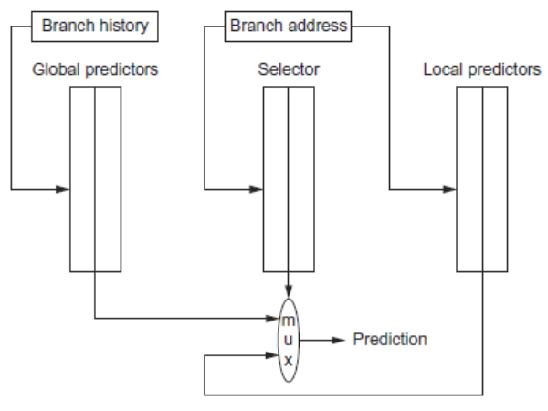
Tournament Predictors
[!INFO]
Correlating Predictors 属于 Global Predictor
Local Predictor,会为每个单独的分支指令维护一个 Local History Table, LHT,记录该分支指令的行为模式,根据每个分支指令的 LHT 来做出预测
Tournament Predictor 包含两个 Predictor,一个选择器,选择器在局部预测器与全局预测器中做出选择
- 基于全局信息的 Global Predictor
- 基于局部信息的 Local Predictor
Other
- PPM(Prediction by Partial Matching)
- Branch Target Buffer (BTB)
- 一个包罗万象的小玩意儿,比如提前把跳转后的指令地址存起来
- Integrated Instruction Fetch Units
- 预测器整合进 FU,指令直接预取
- Return Address Predictors
- 预测 ra,Return Addresses Buffer,加快 ret
Dynamic Branch Prediction Summary
- Prediction becoming important part of scalar execution
- Branch History Table: 2 bits for loop accuracy
- Correlation: Recently executed branches correlated with next branch.
- Either different branches
- Or different executions of same branches
- Tournament Predictor: more resources to competitive solutions and pick between them
- Tagged Hybrid Predictors: have predictor for each branch and history
- Branch Target Buffer: include branch address & prediction
- Predicated Execution can reduce number of branches, number of mispredicted branches
- Return address stack for prediction of indirect jump
ILP Hardware Based Speculation
就是 Tomasulo with ROB,原来是我提前学过了。。。
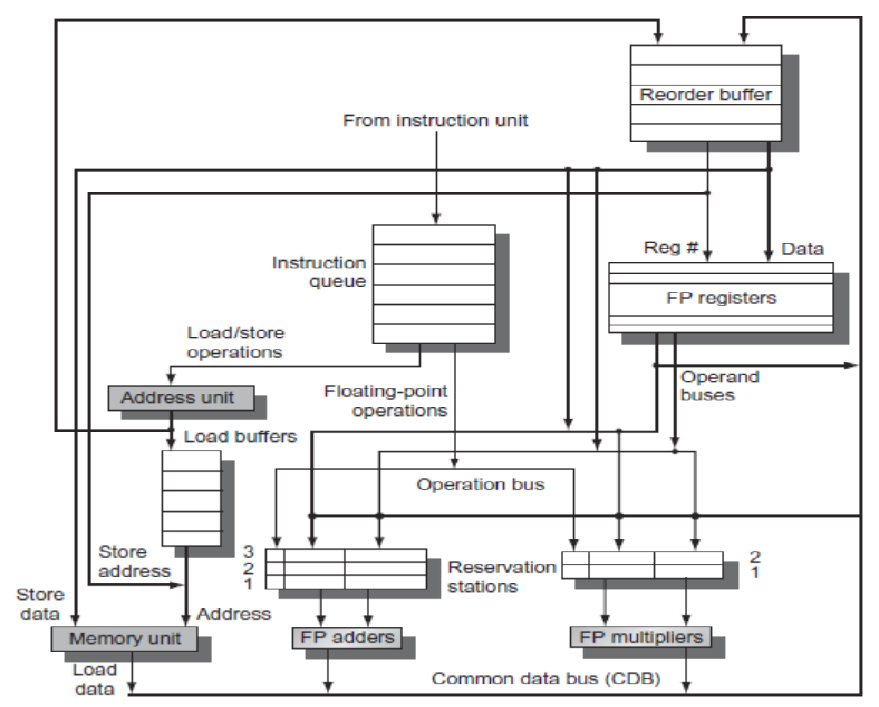
先不管怎么预测,我们看看 branch 指令是怎么在这里运作的
我们会先预测 branch 跳转后的指令,并和 branch 一起乱序执行,但会先在 IS 阶段按序计入 ROB
然后 ROB 在 commit 时,如果检测到是 branch,就会先看预测正确没,正确了就太好了,一切正常
如果错了,则 ROB 里这条 branch 后的所以指令都清空,并重新开始执行 branch 真正跳转的指令
PPT 55页有例子
Difference from Tomasulo Algorithm
- Reorder Buffer is added
- ROB hold the instruction results and supply operands in the interval between completion of instruction execution and instruction commit.
- Eliminate store buffer (Mem write is ordered in Reorder buffer)
- Register renaming is done via reorder buffer instead of reservation station
- Reservation only for storing opcodes and operands during the instruction flying between issue and execution.
4 Steps of Speculative Tomasulo Algorithm
- Issue—get instruction from FP Op Queue - If reservation station and reorder buffer slot free, issue instr & send operands & reorder buffer no. for destination (this stage sometimes called “dispatch”) , update control entries “in use”.
- Execution—operate on operands (EX) - When both operands ready then execute; - if not ready, watch CDB for result; when both in reservation station, execute; - checks RAW
- Write result—finish execution (WB) - Write on Common Data Bus to all awaiting FUs & reorder buffer; - mark the reservation station available.
- Commit—update register with reorder result - When instruction at head of reorder buffer & result present, update register with result (or store to memory) and remove instr from reorder buffer. - Mispredicted branch flushes reorder buffer (sometimes called “graduation”)


cycles per loop iteration are lost to branch overhead,是指跳转指令的fetch周期 和第二轮循环第一条指令的fetch周期之间的差值减1,即若跳转指令fetch后第二轮循 环第一条指令在下一周期立马fetch,视为0 overhead.