Chapter 4 Data-level Parallelism Vector, SIMD, and GPU
计算机体系结构(本)2024-11-25 第 3-4 节 PPT
这章重点掌握向量处理器及其优化、convey的判断
SIMD
SIMD 是一个能发挥数据并行性的架构
VECTOR Process
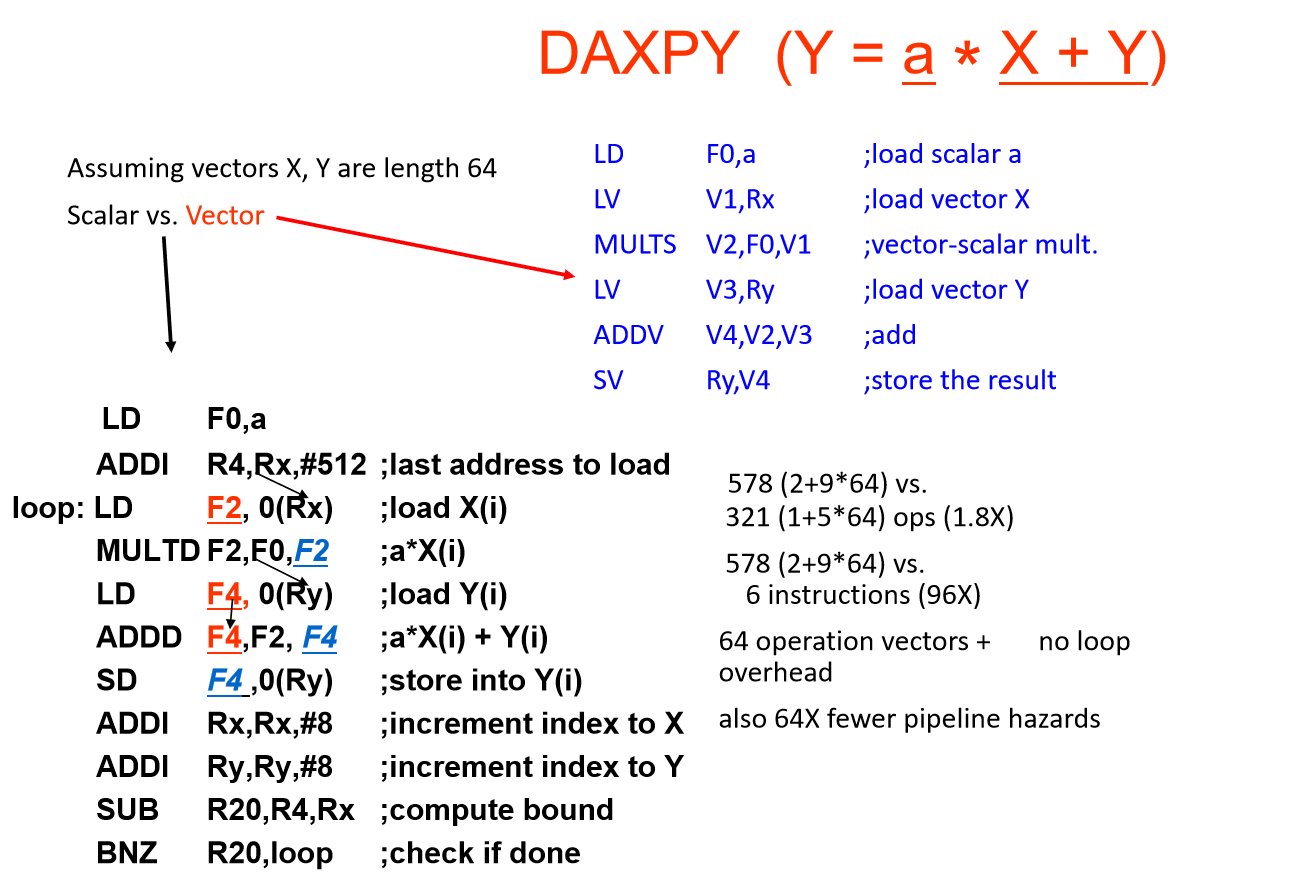
向量处理器架构下,单条指令能完成大量处理(类似 Python 的一些操作不需要循环?)
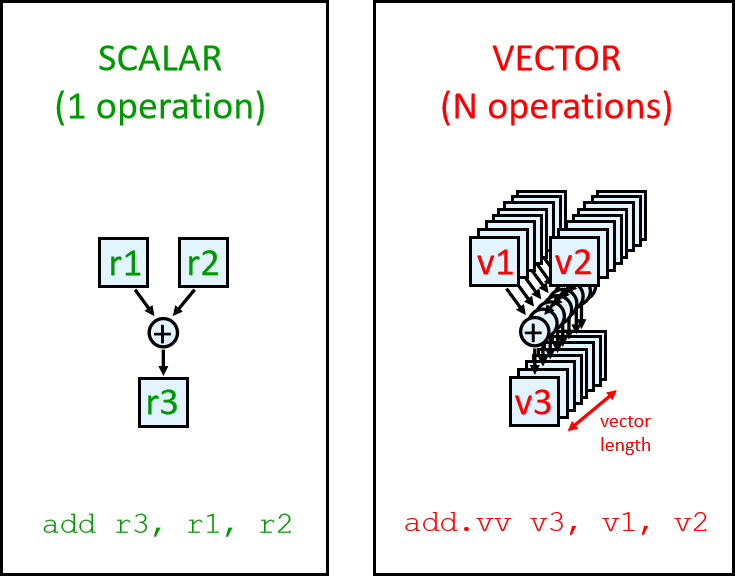
Single vector instruction implies lots of work ( loop),Each result independent of previous result
Vector instructions that access memory have a known access pattern,Reduces branches and branch problems in pipelines
Types of Vector Architectures
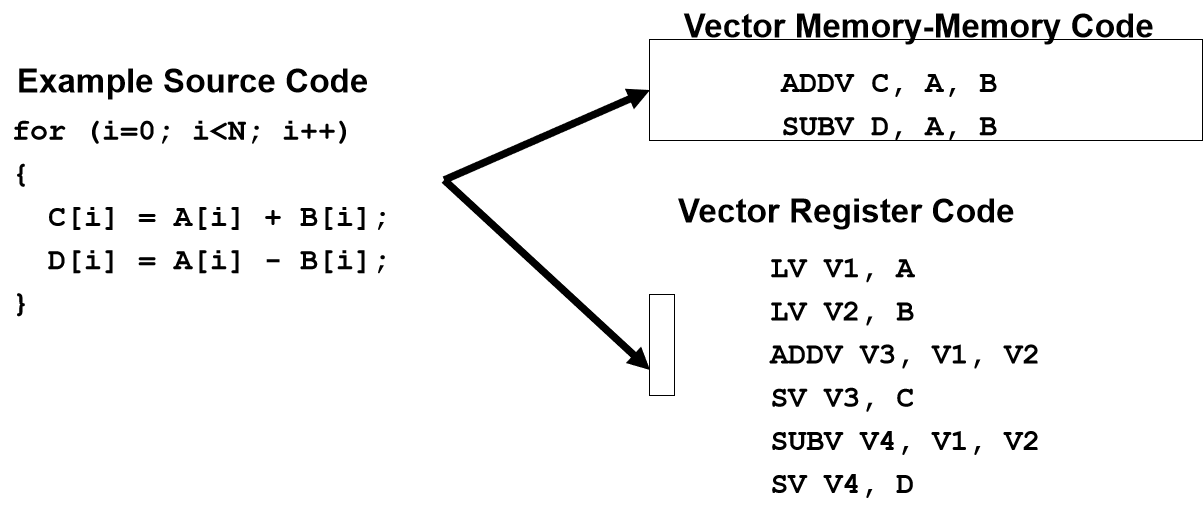
根据向量运算的操作数来源,分为两类:
- memory-memory vector processors
- 使用 Vector memory-memory architectures (VMMA)
- all vector operations are memory to memory
- require greater main memory bandwidth
- 不需要 load store 指令
- VMMA make if difficult to overlap execution of multiple vector operations
- Because it must check dependencies on memory addresses
- VMMAs incur greater startup latency
-
vector-register processors
- all vector operations between vector registers, except load and store)
- 需要先将操作数取到 reg 再用 reg 计算,需要 load store 指令
- 比 VMMA 更成功,也是我们后面讲的重点
Components of Vector Processor
- Vector Register
- Vector Functional Units (FUs)
- Fully pipelined, start new operation every clock
- Vector Load-Store Units (LSUs)
- fully pipelined unit to load or store a vector
- Multiple elements fetched/stored per cycle
- may have multiple LSUs
- Scalar registers
- single element for FP scalar or address
- Cross-bar to connect FUs , LSUs, registers
优缺点
Pro.
- No dependencies within a vector
- Each instruction generates a lot of results
- Regular Memory access pattern
- Fewer branches in the instruction sequence
Cons.
- Very inefficient if parallelism is irregular
- Memory bandwidth can become a bottleneck
[!EXAMPLE] VECTOR vs. SCALAR
Vector Length
A vector register can hold some maximum number of elements for each data width (maximum vector length or MVL)
Vector-length (VL) register controls the length of any vector
VL can be anything from 0 to MVL
Strip Mining
when application vector length > MVL
Strip mining: Generation of a loop that handles MVL elements per iteration
就是说,实际的 VL 超过了 MVL(机器能处理的最长的向量长度),就把这个向量切成一段一段的分别处理
[!EXAMPLE]
Example: vector daxpy of N elements
First loop handles (N mod MVL) elements, the rest handle MVL