Activation Records
An invocation of function f is an activation of f,每次 f 被调用时,其内部变量会被创建新的实例,并在函数返回时被摧毁,我们该如何维护这些本地变量呢——用 stack
- Procedure calls and returns are usually managed by a run time stack called control stack
- Each live activation has an activation record (sometimes called a frame) on the control stack
- Each time a procedure(过程) is called, space for its local variables is pushed onto the stack
- Procedure calls are also called activations of procedures.
- 过程终止后对应的 space 就会 pop off
Stack Frames
栈如果只支持 push 和 pop 是还不能用于存储局部变量的
在实际使用中会将 stack 看成一个大数组,用 sp 指向栈顶
Stack Pointer– a special register that points at some location
Run-time stacks 由高地址向低地址增长
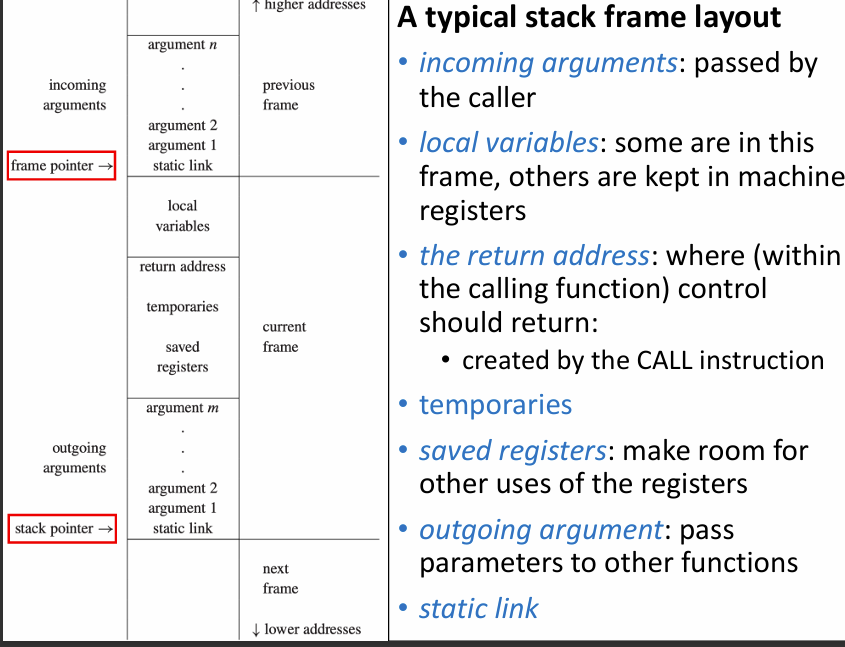
- Registers hold
- some parameters
- return address
- return value
- some local variables and temporaries
- Stack frame holds
- variables passed by reference or have their address taken (&)
- variables that are accessed by procedures nested within the current one
- variables that are too large to fit into register file
- array variables (address arithmetic needed to access array elements)
- spilled registers (too many local variables to fit into register file, so some must be stored in stack frame)
Frame Pointer
- Frame Pointer 指向 caller 帧头
- 当 caller call callee 时,sp 指向 caller 传递给 callee 的第一个参数
- 实际上是指向 static link
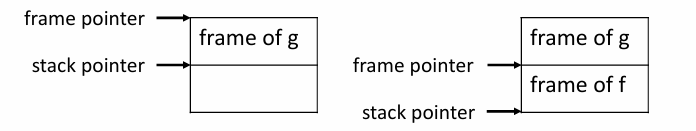
- When enter f:
- save the old frame pointer FP in memory in the frame
- let FP = SP
- SP = SP – framesize
- When f exits:
- let SP = FP
- let FP = saved old FP
Saved Registers
caller-save register: if the caller (in this case, f) must save and restore it
callee-save register: if it is the responsibility of the callee (in this case, g)
Parameter Passing
the first k arguments (for k = 4 or k = 6, typically) of a function are passed in registers rp, …, r(p+k−1), and the rest of the arguments are passed in memory.
但是,如果在函数中调用函数,那么这两个函数的第一个参数的值都在同一个寄存器中,前者会被后者覆盖,如果第二个函数返回后,第一个函数还用第一个参数,就会用到错误的值
解决方法如下:
- Parameter a is a dead variable at the point where h(z) is called. Then f can overwrite r1 without saving it.
- Leaf procedures need not write their incoming arguments to memory
- leaf procedures: the procedures that don’t call other procedures
- 分析全局,在每个地方进行抉择
- 每次分配新的寄存器
Return Address
略
Frame-Resident Variables
需要存在栈帧里的变量,如本地变量和临时变量,
Values are written to memory (in the stack frame) only when necessary for one of these reasons:
- the variable will be passed by reference, so it must have a memory address (e.g., & in the C language);
- the variable is accessed by a procedure nested inside the current one;
- the value is too big to fit into a single register;
- the variable is an array, for which address arithmetic is necessary to extract components;
- the register holding the variable is needed for a specific purpose, such as parameter passing (as described above); - 原先存储值的寄存器要用于新的用途,就得将其值存入栈帧
- or there are so many local variables and temporary values that they won’t all fit in registers, in which case some of them are “spilled” into the frame.
逃逸 escapes
A variable escapes if :
- it is passed by reference,
- its address is taken (e.g., using C’s & operator),
- it is accessed from a nested function
逃逸就是指其被“复制”了,其被修改不会影响原来的值
嵌套函数变量访问问题
对于支持嵌套函数的语言,内部函数可能需要访问外部函数的变量,即访问外部函数的栈帧
Static Links
简单来说,如果 f 是 g 内部的嵌套函数,那么调用 f 时需要把 g 最近一次的 activation record 的地址传递给 f 作为 Static Links,也就是说 Static Links 是一个指向外部函数栈帧的指针
如此内部函数就能通过 Static Links 访问外部函数栈帧
确切说,是把调用它的那个函数的栈帧地址传过去,比如递归调用自己
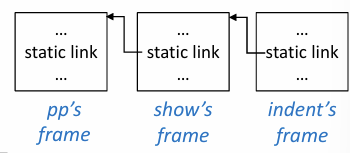
这个方法有个缺点就是只能遍历链表查询,如果离得很远就很麻烦
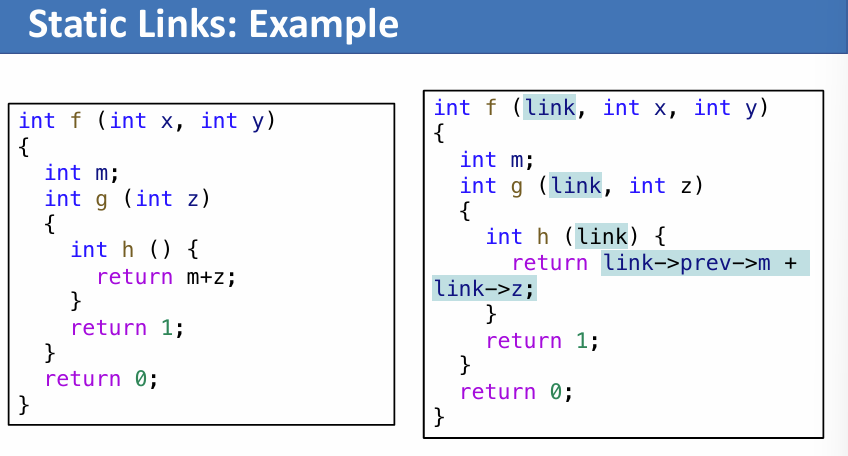
Display
先给每一个函数标记静态嵌套深度,然后设置一个全局数组,以嵌套深度为 index 存储该深度函数的最近一次调用的栈帧地址
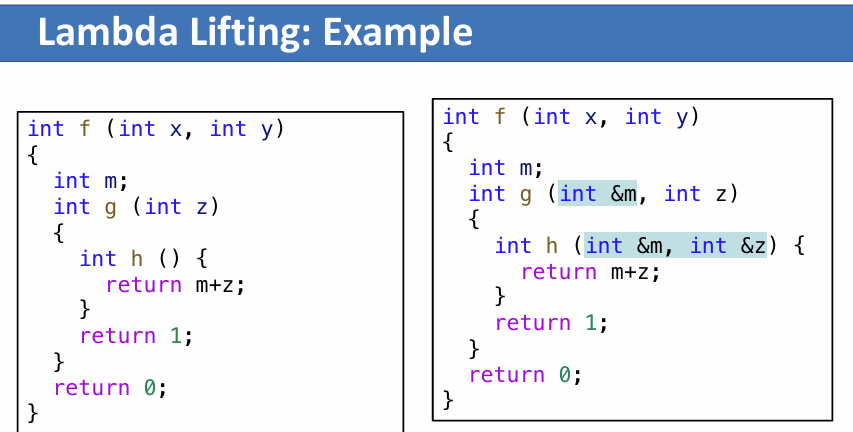
Lambda Lifting
编译时直接看调用的函数会用到哪些外部变量,直接当参数传进去
Higher-Order Functions
我们之前讨论的都是基于栈帧的存储方法,使用栈帧有个要求是:函数退出后需要释放其内部的所有信息(包括内部函数的栈帧)
但是这样就不支持高阶函数了,高阶函数将函数作为返回值
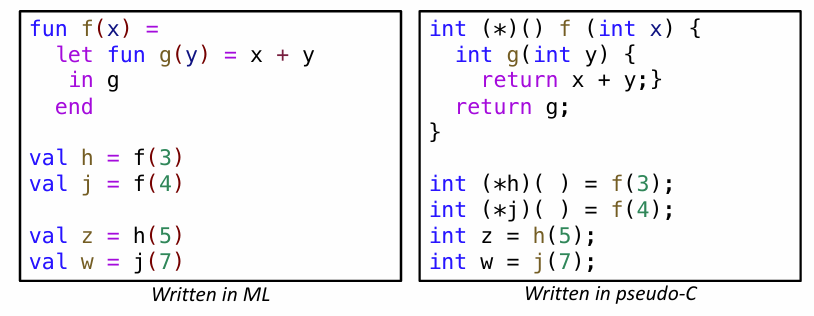
调用
f(3)后,传入的3不应该被销毁