Chapter 8: Main Memory
操作系统(本)2024-11-19 第 7-8 节 ch8 Main Memory.pdf
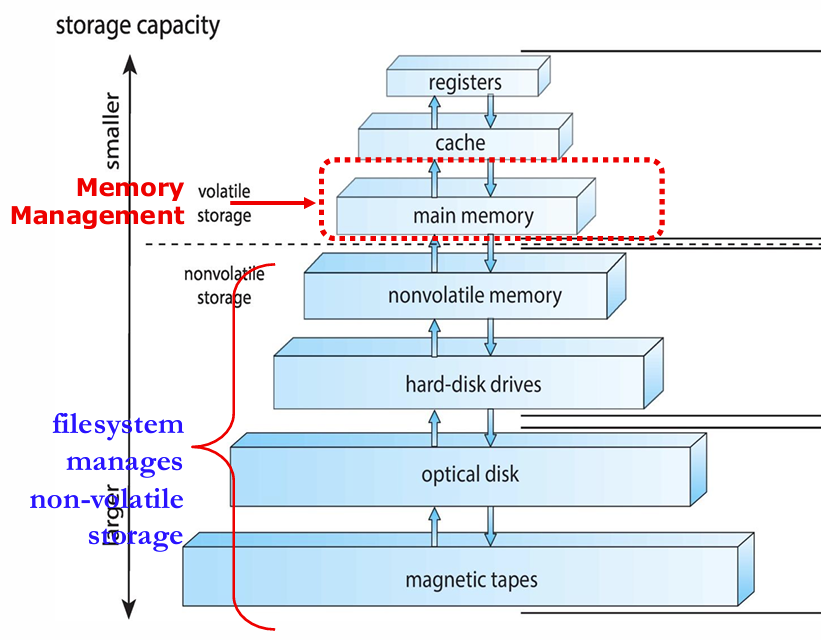
Background
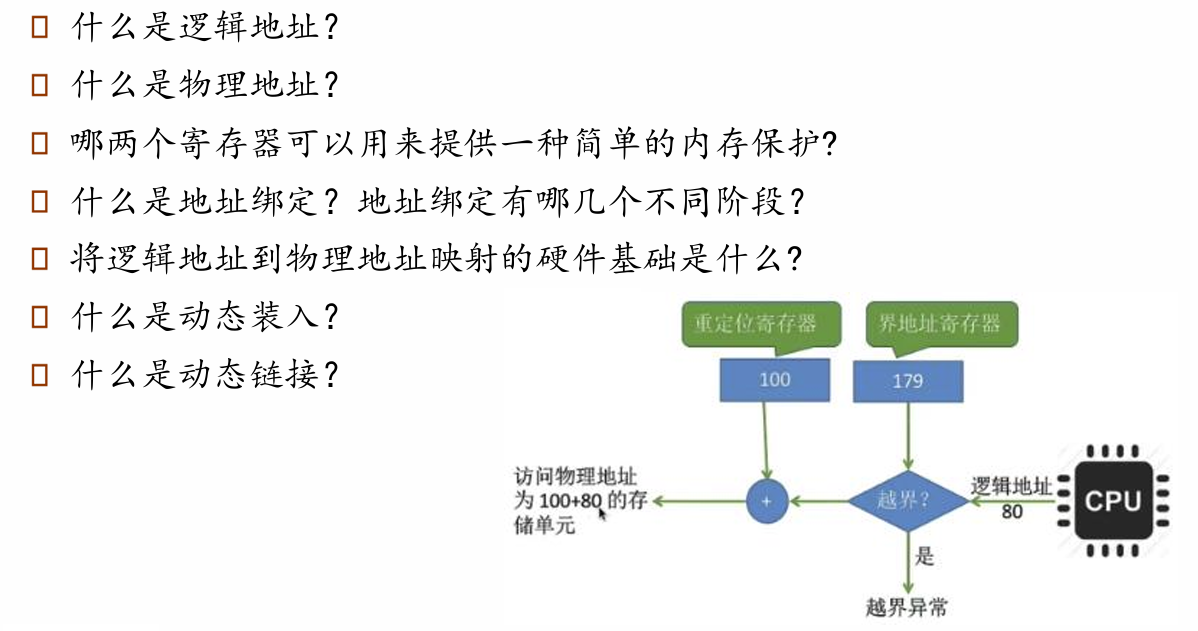
process 看到的地址都是逻辑地址,逻辑地址能映射到物理地址
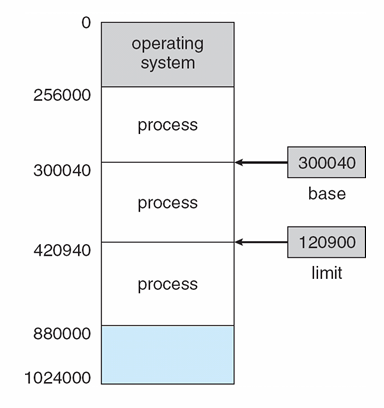
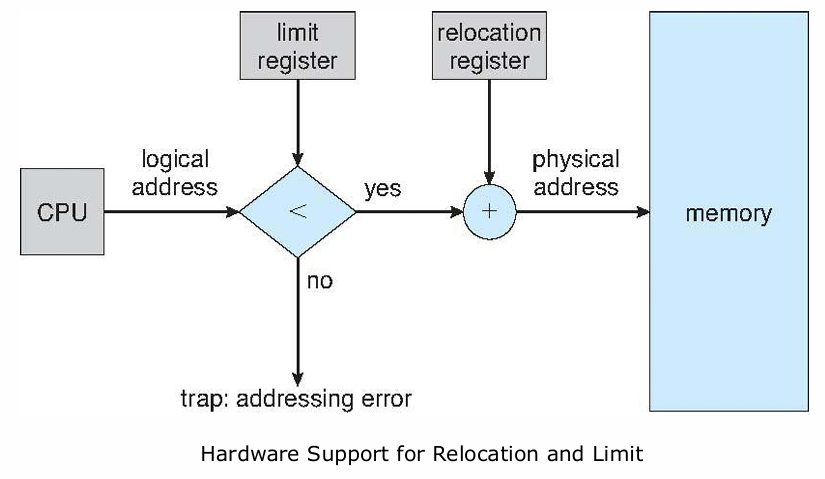
A pair of base and limit registers (基址寄存器和限长寄存器)define the logical address space
前者存储当前正在运行的 process 在内存中的起始地址
后者存储末尾地址或使用的内存大小
能实现简单的内存保护,避免越界
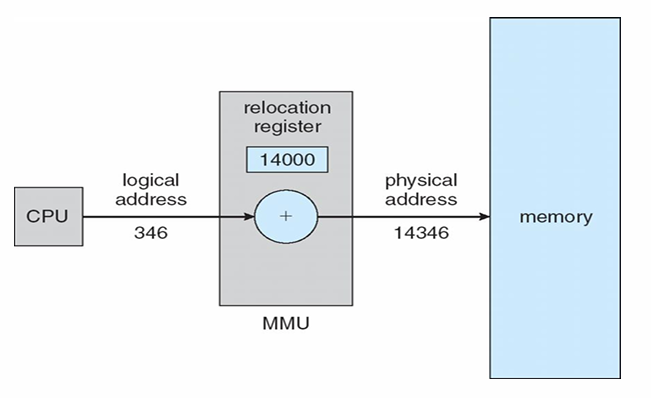
Address binding(地址绑定、地址映射、重定位)即计组学过的逻辑转物理
Address binding of instructions and data to memory addresses can happen at three different stages
Compile time, Load time, Execution time
Dynamic relocation(动态重定位)
Memory-Management Unit (MMU), hardware device that maps virtual to physical address
In MMU scheme, the value in the relocation register(重定位寄存器) is added to every address generated by a user process at the time it is sent to memory
这个操作叫做
Dynamic Loading(动态装入)
Using dynamic loading, external libraries are not loaded when a process starts
Libraries are stored on disk in relocatable form, loaded into memory only when needed
Dynamic Linking(动态链接)
Using dynamic linking, external libraries can be preloaded into (shared) memory
When a process calls a library function, the corresponding physical address is determined
stub - small piece of code - used to locate the appropriate memory-resident library routine
Stub replaces itself with the address of the routine, and executes the routine
就是运行时要用到再链接
Dynamically Linked Library 动态链接库, also known as shared libraries
Review Questions
Swapping(交换技术)
A process can be swapped temporarily out of memory to a backing store(备份区), and then brought back into memory for continued execution
Roll out, roll in(调出,调进)
将展示不执行的 process 内存空间从内存换出到外存,将要执行的从外存换入内存
交换技术很慢
Contiguous Allocation(连续分配)
单一连续区分配
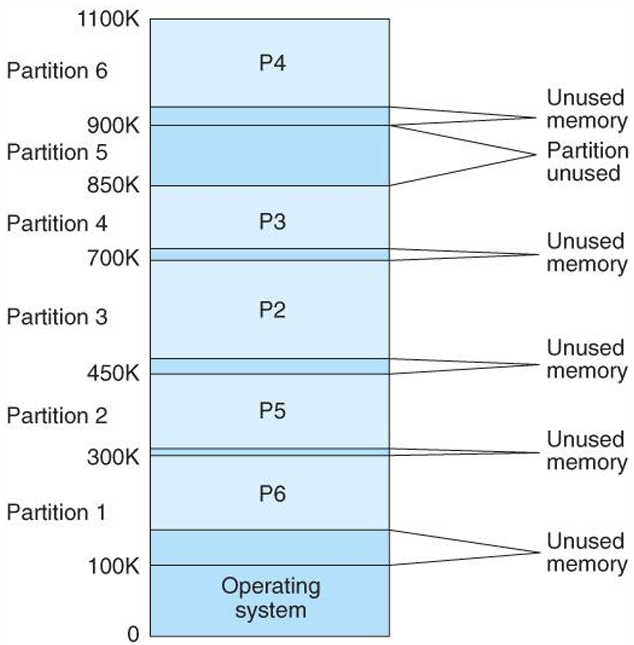
Main memory usually into two partitions(单分区)
- Resident operating system, usually held in low memory
- User processes then held in high memory

Relocation registers used to protect user processes from each other, and from changing operating-system code and data:Base register,Limit register,MMU
多分区分配
Multiple-partition allocation,基本思想是将内存划分成若干个连续区域,称为分区,每个分区只能存放一个进程,具体又分为以下几类:
Fixed Partitioning (固定分区)
Main memory is partitioned and allocated to the resident OS and processes
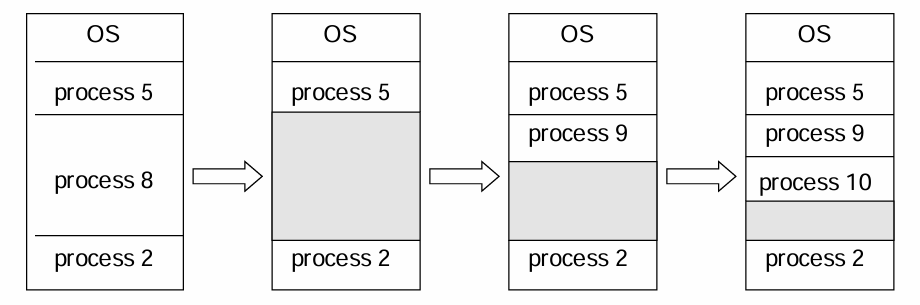
Dynamic Partitions (动态分区)
在程序装入内存时把可用内存“切出”一个连续的区域分配给该进程,且分区 大小正好适合进程的需要
OS maintains information about allocated partitions & free partitions (hole)
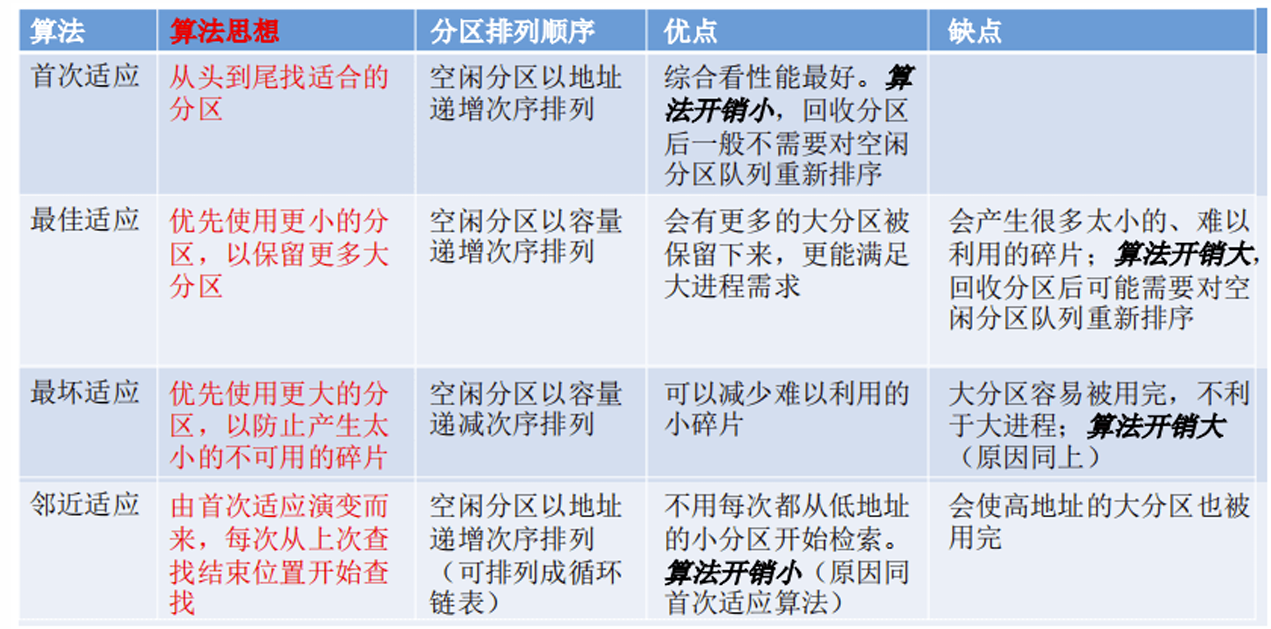
Dynamic Storage-Allocation Problem
How to satisfy a request of size n from a list of free holes
- First-fit: Allocate the first hole that is big enough
-
Best-fit: Allocate the smallest hole that is big enough
- must search entire list, unless ordered by size
- Produces the smallest leftover hole
-
Worst-fit: Allocate the largest hole
- must also search entire list
- Produces the largest leftover hole
First-fit and best-fit better than worst-fit in terms of speed and storage utilization
死去的 ADS 开始攻击我
Next Fit(下次适应):想象我们将内存首尾相接,然后总是从上次查找结束的地方开始,找一个足够大的空白区即可,这样开销很小
Fragmentation
Memory is wasted due to fragmentation, which can cause performance problems
- Internal fragmentation is wasted memory within a single process memory space
- 分配给了 process,但 process 没有用上
- External fragmentation can reduce the number of runnable processes
- 所有 hole 加起来大小是够分配给新 process 的,但 hole 是零散分布,用不了
Reduce external fragmentation by compaction or defragmentation (紧缩,拼接),defragmentation is expensive
Review Questions

- 几个 Fit
- 不知道
- 略