8.2 Segmentation
操作系统(本)2024-11-26 第 7-8 节 ch8 Main Memory.pdf
Segmentation (分段,段式管理)
A program is a collection of segments
A segment is a logical unit such as main program, procedure, function, method , object, local variables, global variables, common block, stack , symbol table , arrays
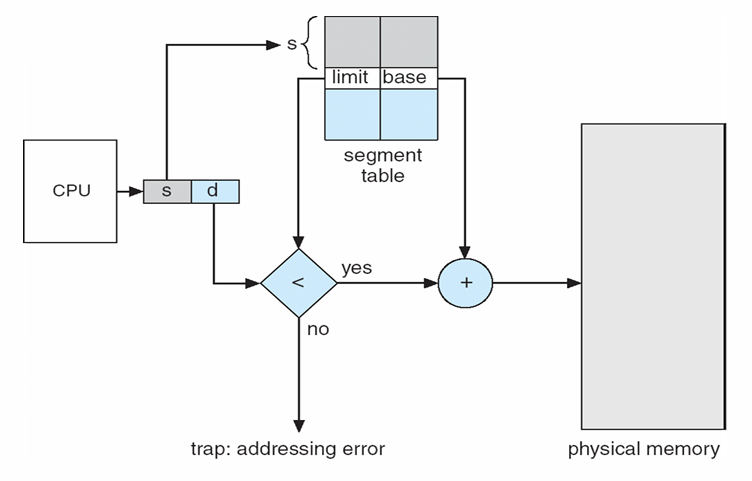
Segmentation Architecture
Logical address consists of a two tuple:
Segment table(段表)– maps two-dimensional physical addresses; each table entry has
- base – contains the starting physical address where the segments reside in memory
- limit – specifies the length of the segment
Segment-table base register (STBR) (段表基址寄存器)points to the segment table’s location in memory
Segment-table length register (STLR) (段表限长寄存器)indicates number of segments used by a program; 用于防止越界
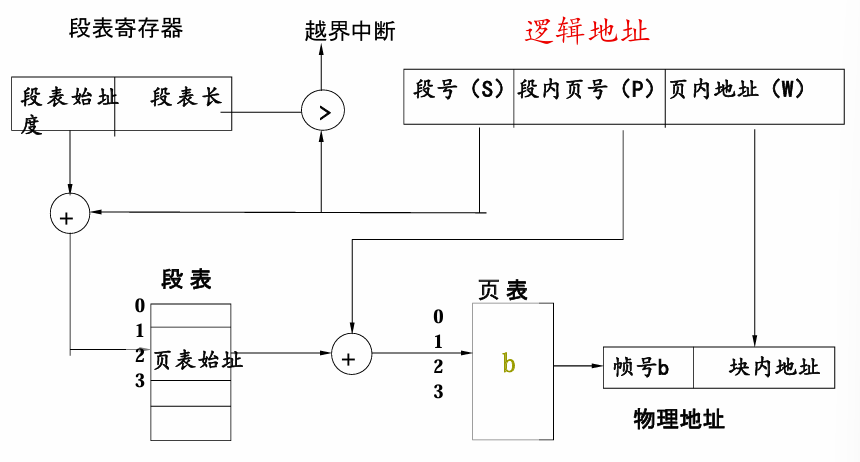
Segmentation with Paging
程序(逻辑内存)首先被划分成若干程序段,每一段给予不同的分段标识符, 每一分段又分成若干个固定大小的页
地址变换至少要访问主存三次:段表、页表、指令或数据
地址结构现在变为:<段号,页号,页内地址>
[!QUESTION] 分页和分段的区别
本章内容
内存管理基本概念:源程序的常规处理流程,地址绑定,逻辑地址空间与物理 地址空间;内存保护;MMU,动态加载,动态链接,交换,地址管理模型,模 型指标。 交换技术。 连续分配管理方式:单一连续分配算法,基地址寄存器,界限寄存器;动态分 区管理,动态存储分配算法,外部碎片,内部碎片。 分页管理方式:页,页帧,页表,地址映射流程,硬件支持,页表实现,TLB ,有效访问时间,页式管理的模型指标分析,页表结构,多级页表,哈希页表 ,反向页表
