9.1 Page Replacement & Allocation of Frames & Thrashing
Page Replacement (页面置换)
操作系统(本)2024-12-03 第 7-8 节 ch9 Virtual Memory.pdf
在进程运行过程中,如果发生缺页,此时内存中又无空闲块时,需要进行页置换
replacement policy 负责确定哪个 page 被置换出去,例如 LRU
reference string 指示一连串页操作的页号
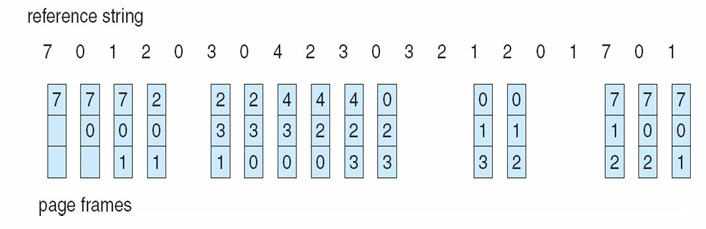
FIFO Page Replacement
FIFO Page Replacement 随着 page frame 增大 page faults 会逐渐减少,但是会出现局部回升的情况:
Belady’s Anomaly: more frames → more page faults

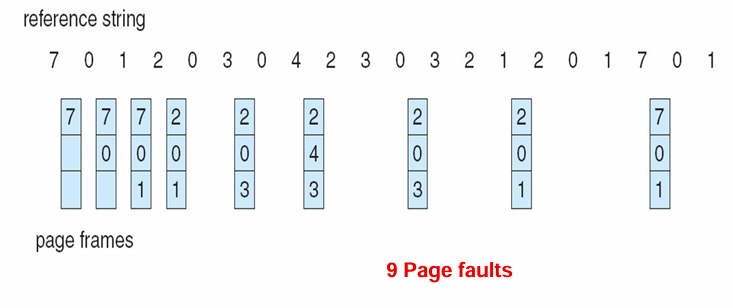
Optimal Page Replacement(最佳页面置换)
Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time
就是进行页置换时,目前已有的页中,在 reference string 下一次出现的地方离目前最远的那个页,就像开了上帝视角
Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs
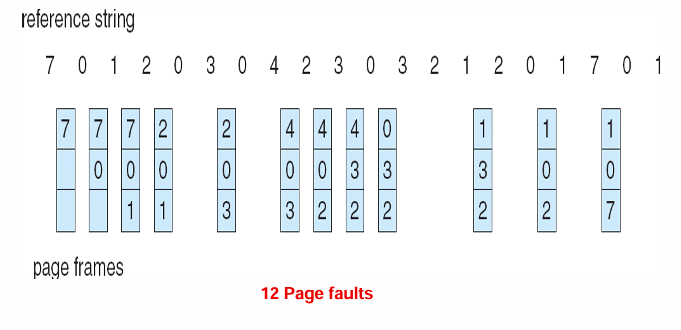
Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm (最近最久使用)
选择内存中最久没有引用的页面
性能接近最佳算法,但由于需要记录页面使用时间,硬件开销太大
[!NOTE] 如何获知“多长时间没引用”
计数器:每个页设立计数器,用于记录每一页最后使用的时间
栈:设置一个特殊的栈,把被访问的页移到栈顶, 于是栈底的是最久未使用页面
移位寄存器:被访问时左边最高位置 1,定期右移并且最高位补 0,于是寄存器数值最小的是最久未使用页面
LRU Approximation Algorithms (NRU)
Additional-Reference-Bits Algorithm
就是上面说过的移位寄存器方法
keep a byte for each page in a table in memory
被访问时左边最高位置 1,定期右移并且最高位补 0,于是寄存器数值最小的是最久未使用页面
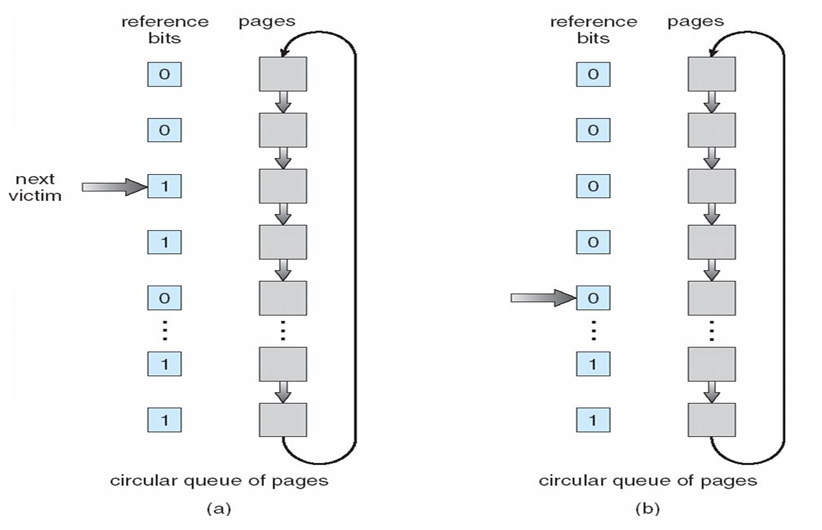
Second-Chance (clock) Algorithm
每个 page 设置一个 Reference bit(引用位或访问位),初始化为 0,被访问过就置 1,置换就置换这个 bit 为 0 的 page
当要选择一个页时,检查其引用位
- 如果其值为 0,那么就直接置换该页
- 如果该引用位为 1, 那么就给该页第二次机会,将其引用位置 0,并按 FIFO 选择下一个引用位为 0 的页
Enhanced Second-Chance Algorithm
使用引用位和修改位:引用过或修改过置成 1
淘汰次序:(Reference bit, modified bit) = (0,0) → (0,1)→(1,0)→(1,1)
其它基于计数的算法
LFU(Least Frequently Used) Algorithm(最不经常使用算法)
MFU(Most Frequently Used) Algorithm(经常使用算法):考虑到那些没用过几次的可能还会多用几次,用过很多次的就滚吧
Page Buffering Algorithm 页面缓冲算法,加个垃圾桶,允许你把换出去的再恢复回来
想看就看 ch9 Virtual Memory.pdf 59 页
Allocation of Frames(帧分配)
分配策略
Fixed Allocation(固定分配)
Equal allocation(平均分配)– For example, if there are 100 frames and 5 processes, give each process 20 frames.
Proportional allocation(按比例分配)– Allocate according to the size of process
Priority Allocation(优先级分配)
Use priorities rather than size
置换策略
Global replacement(全局置换)– process selects a replacement frame from the set of all frames; one process can take a frame from another
Local replacement(局部置换)– each process selects from only its own set of allocated frames
Thrashing (颠簸、抖动)
Thrashing = a process is busy swapping pages in and out
\(\Sigma\) size of locality > total memory size
Thrashing 解决方法
- 局部置换算法能限制
- L = S 准则,L:产生缺页的平均时间,S:系统处理进程缺页的平均时间
- 在 cpu 调度中引入工作集算法
- 挂起若干进程
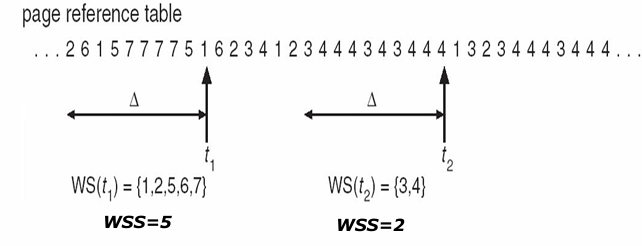
Working-Set Model 工作集模型
新的概念:
- 记 \(\Delta\) = working-set window(工作集窗口) = 最近 Δ 个页面引用
- 工作集 WS(Working set):最近 Δ 个引用的页集合
- WSSi (working set size of Process Pi 工作集尺寸) = 某进程最近所引用的所有页面的总数
- D = \(\Sigma\) WSSi = total demand frames
- m = total available frames
如果 D 大于可用帧数量 m,那么有的进程就得不到足够帧,从而会出现 Thrashing
[!EXAMPLE]
如上图,\(\Delta\) 都是 10,但 WSS 和 WS 不同