Virtual Memory
Demand Paging(按需调页、请求调页)
复习下来发现,实验做下来是真的很有用,只要写过基本一看就懂
Demand Paging 模式下的页表
在请求分页系统中的每个页表项为:
- 状态位 P(存在位):用于指示该页是否已调入内存,供程序访问时参考。
- 访问字段 A:用于记录本页在一段时间内被访问的次数,或最近已有多长时间未被访问,提供给置换算法选择换出页时参考。
- 修改位 R/W:表示该页在调入内存后是否被修改过。
- 外存地址:用于指出该页在外存上的地址,供调入该页时使用。
Page Fault 缺页
缺页处理过程
- 检查进程的页表,确定该访问请求是合法还是非法的
- 如果非法,那么终止进程;如果有效但是尚未调入页面,那么现在应调入。
- 找到一个空闲帧
- 调度磁盘操作,将所需要的页调入刚分配的帧
- 修改进程的内部表和页表,以表示该页已在内存中。
- 重新开始因非法地址陷阱而中断的指令
Demand Paging Performance
page fault rate p
p = 0 表示不会发生 page fault,p = 1 表示每次访问都会 page fault
The effective memory-access time (EAT) is:
(1 – p) x physical-memory-access + p x ( page-fault-overhead + swap-page-out + swap-page-in + restart-overhead )

为什么缺页时不用再加一次内存访问时间
Process Creation
Virtual memory allows some benefits during process creation
Copy-on-Write (COW)
Copy-on-Write allows both parent and child processes to initially share the same pages in memory
如果父子进程都只读一个 page,就共享这个 page
直到有一方要写某个 page,才将该 page 进行复制,让双方各自拥有一份这个 page
Page Replacement
在进程运行过程中,如果发生缺页,此时内存中又无空闲块时,需要进行页置换
- replacement policy 负责确定哪个 page 被置换出去,例如 LRU
- reference string 指示一连串页操作的页号
FIFO Page Replacement
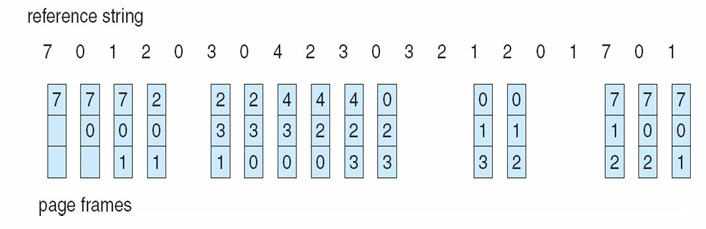
随着 page frame 增大,page faults 会逐渐减少,但是会出现局部回升的情况,即 Belady’s Anomaly: more frames → more page faults
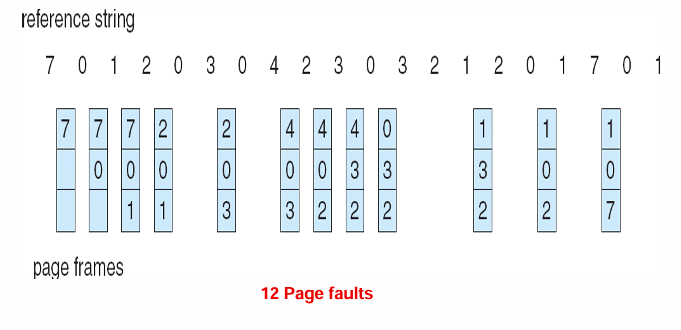
Optimal Page Replacement(最佳页面置换)
Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time
在目前已有的页中,找出这么一个页进行替换:其下一次使用的时间是已有页中最后的,就是看 reference string 中哪个下一次出现的更靠后
就像开了上帝视角,这个是无法实现的
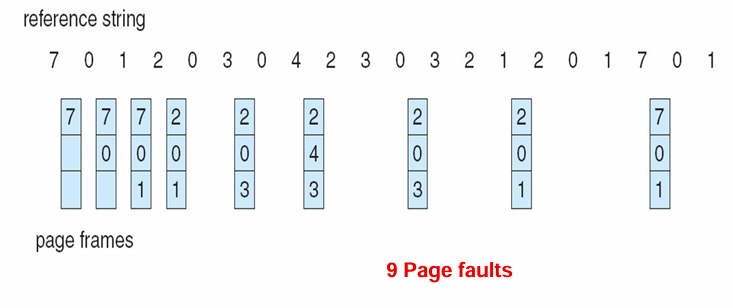
Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm (最近最久使用)
选择内存中最久没有引用的页面
性能接近最佳算法,但由于需要记录页面使用时间,硬件开销太大
如何获知“多长时间没引用”
- 计数器:每个页设立计数器,用于记录每一页最后使用的时间
- 栈:设置一个特殊的栈,把被访问的页移到栈顶, 于是栈底的是最久未使用页面
LRU Approximation Algorithms (NRU)
LRU 开销大,我们可以改进为 LRU 近似算法
Additional-Reference-Bits Algorithm
每个页都设置一个 byte,作用类似移位寄存器
被访问时左边最高位置 1,定期右移并且最高位补 0,于是寄存器数值最小的是最久未使用页面
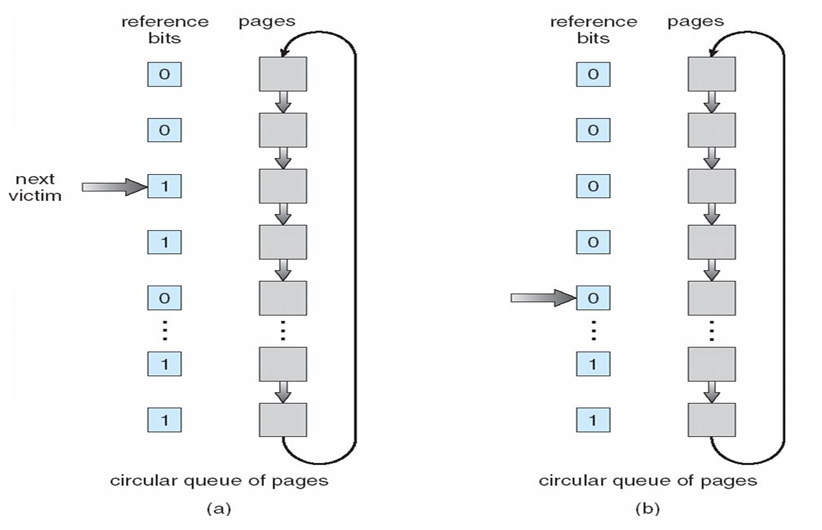
Second-Chance (clock) Algorithm
每个 page 设置一个 Reference bit(引用位或访问位),初始化为 0,被访问过就置 1
要置换时,按顺序检查页的引用位:
- 如果其值为 0,那么就直接置换该页
- 如果该引用位为 1, 那么就给该页第二次机会,将其引用位置 0,并按 FIFO 选择下一个引用位为 0 的页
Enhanced Second-Chance Algorithm
使用引用位和修改位:引用过或修改过置成 1
淘汰次序:(Reference bit, modified bit) = (0,0) → (0,1)→(1,0)→(1,1)
Allocation of Frames(帧分配)
分配策略
Fixed Allocation(固定分配)
Equal allocation(平均分配)– For example, if there are 100 frames and 5 processes, give each process 20 frames.
Proportional allocation(按比例分配)– Allocate according to the size of process
Priority Allocation(优先级分配)
Use priorities rather than size
置换策略
Global replacement(全局置换)– process selects a replacement frame from the set of all frames; one process can take a frame from another
Local replacement(局部置换)– each process selects from only its own set of allocated frames
Thrashing (颠簸、抖动)
Thrashing = a process is busy swapping pages in and out
\(\Sigma\) size of locality > total memory size
Thrashing 解决方法
- 局部置换算法能限制
- L = S 准则,L:产生缺页的平均时间,S:系统处理进程缺页的平均时间
- 在 cpu 调度中引入工作集算法
- 挂起若干进程
Working-Set Model 工作集模型
新的概念:
- 记 \(\Delta\) = working-set window(工作集窗口) = 最近 Δ 个页面引用
- 工作集 WS(Working set):最近 Δ 个引用的页集合
- WSSi (working set size of Process Pi 工作集尺寸) = 某进程最近所引用的所有页面的总数
- D = \(\Sigma\) WSSi = total demand frames
- m = total available frames
如果 D 大于可用帧数量 m,那么有的进程就得不到足够帧,从而会出现 Thrashing
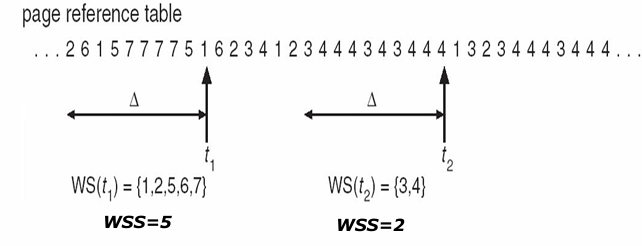
如上图,\(\Delta\) 都是 10,但 WSS 及 WS 不同