Buffer Overflow
与 PL 比较相关,很多原因不会出现 Buffer Overflow
wiki 不适合作为文献被引用
背景知识
Type safety
type safety and type soundness are the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors.
Java 就是 type-safety 的,其会在运行时实时检查各类型变量是否越界,即超出定义范围,而 C 是 type-unsafe 的,可以对定义范围外的地址进行操作,所以会出现 Buffer Overflow
例如 int a[10]; a[10] = 3,Java 有Runtime Array Bounds Checking,会弹异常,C 是 No Array Bounds Checking
Memory Management
C 需要手动分配、释放内存
gets, fgets, strcpy
strncpy 中,src 过长会导致 dest 没有终结符 '\0',可能导致segmentation fault
所以一般长度设置为
sizeof(dest)-1,然后手动设置dest最后一个位置为终结符
Program Memory Layout
// on .data
int x = 100;
int main(){
// data stored on stack
int a = 2;
float b = 2.5;
// on .bss
static int y;
// allocate memory on heap, namely ptr on heap
int *ptr = (int*) malloc(2*sizeof(int));
// value 5 and 6 stored on heap
ptr[0] = 5;
ptr[1] = 6;
//deallocate memory on heap
free(ptr);
return 1;
}
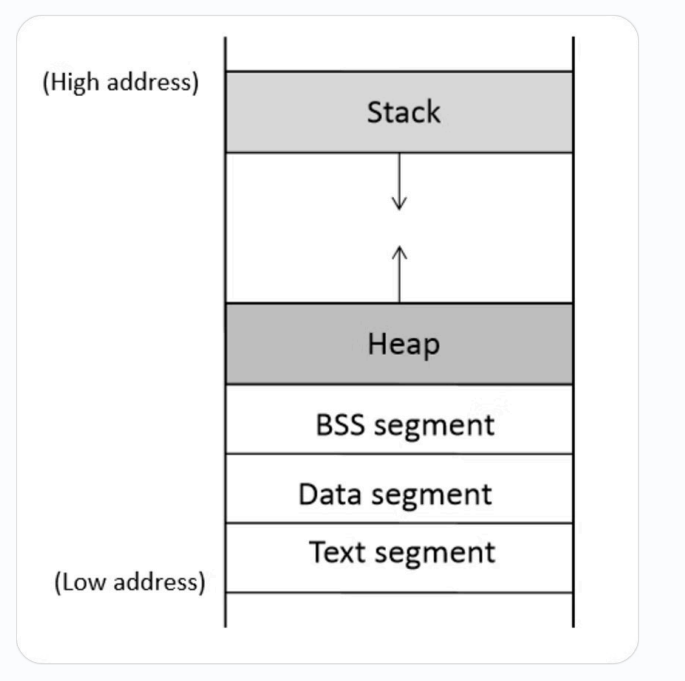
| 段名 | 主要作用 |
|---|---|
.text |
通常存放程序执行代码 |
.rodata |
通常存放常量等只读数据 |
.data |
通常存放已初始化的全局变量、静态变量 |
.bss |
通常存放未初始化的全局变量、静态变量 |
Stack Layout
看看函数被调用时栈如何变化,注意栈在内存里是从高往低增长,栈顶即最低地址处(fp)
func 被调用时,现在栈顶(即最低处)往下分配一块内存,然后依次压入
- 先压入参数,注意是逆序压入,先放 b 再放 a
- 返回地址即 caller 对 callee 的调用代码的下一行代码的地址,用于 callee 结束时返回 caller
- 然后压入 caller 的栈帧指针
ebp- 这个可以作为基地址,其加上偏移量可访问 retaddr,减去偏移量可访问 local var
- 不用实时 ESP 是因为运行时其在动态变化
- 这个可以作为基地址,其加上偏移量可访问 retaddr,减去偏移量可访问 local var
- 最后算 callee 的本地变量
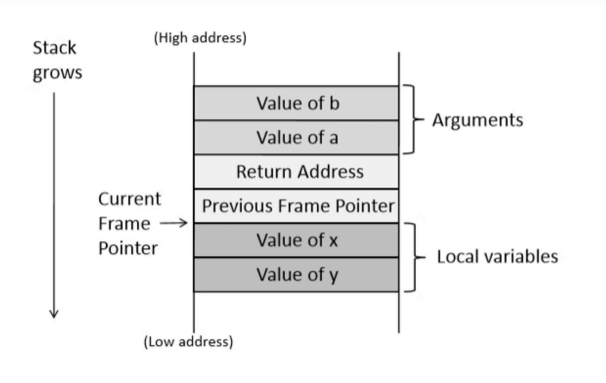
Stack Frame
- The stack pointer
- points to the top of the stack
RSPin Intel x86-64,ESPin intel x86-32
- The frame pointer
- points to the end of the current frame
- also called the base pointer
RBPin Intel x86-64,EBPin Intel x86-32
caller & callee
call 指令用于调用,会先往栈压入返回值
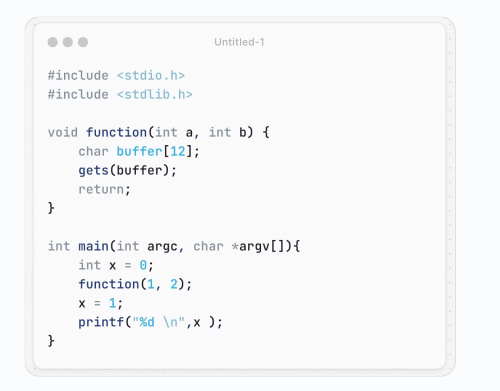
下面是 main 函数,红框即调用函数的部分,先逆序压入参数,再使用 call,这里的返回地址即 1205

经过 Function Call 后,栈形如:

下面是 function 函数
不同格式的汇编对
mov的定义不同
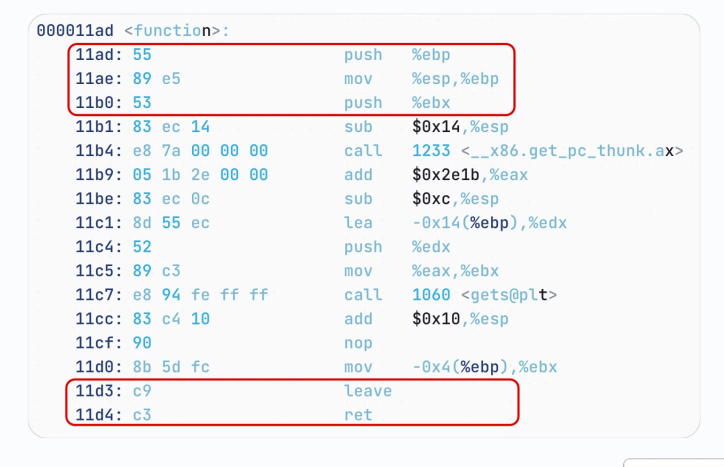
Prologue 部分,先把 ebp 压入栈,再把 esp 复制给 ebp
经过 Prologue 后,ebp 位置在 old ebp 底部,即可作为基地址使用
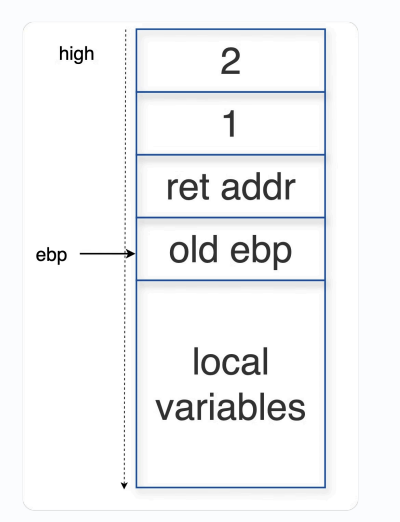
注意,old ebp 与 local var 之间是有空白空间的,别忘了 local var 是从低往高增长
Epilogue 部分,先 leave 再 ret,两个伪指令含义如下
即,先复位 esp 到 old ebp 底部,再通过 pop 弹出 old ebp,还给 ebp
eip 即 PC,相当于把 retaddr 交给 PC,回到 Caller
How to Exploit Buffer Overflow
我们针对的是栈上的 overflow,且是 32 位
A buffer overflow occurs when data is written outside of the boundaries of the memory allocated to a particular data structure
- modify
- return address on the stack
- function pointer
- local variable
- heap data structures
Smashing the Stack
Occurs when a buffer overflow overwrites data in the program stack
Successful exploits can overwrite the return address on the stack
Allowing execution of arbitrary code on the targeted machine
因为本地变量是从低往高增长,所以我们有机会往高覆盖掉 ret addr
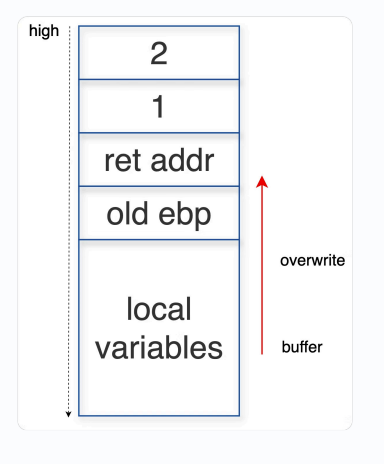
- The user input buffer will overwrite the return address on the stack
- Case I: the overwritten return address is invalid -> crash (why?)
- Case II: the overwritten return address is valid but in kernel space
- Case III: the overwritten return address is valid, but points to data
- Case IV: the overwritten return address happens to be a valid one
我们得精确地覆盖到 retaddr,且精确控制新的 retaddr 往哪跳
How To Exploit
We can overwrite the return address on the stack to shellcode
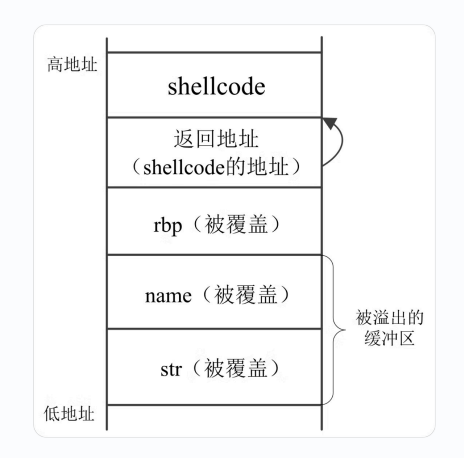
Shellcode
略
shellcode =
b'\x6a\x42\x58\xfe\xc4\x48\x99\x52\x48\xbf\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x57\x54\x5e\x49\x89\xd0\x49\x89 \xd2\x0f\x05'
Defense
- 三种思路
- 避免程序本身有漏洞
- 承认程序有漏洞,提高攻击代价
- 限制权限,降低攻击效果
ASLR
Address space layout randomization (ASLR) 地址空间随机化
ASLR randomly arranges the address space positions of key data areas of a process, including the base of the executable and the positions of the stack, heap and libraries.
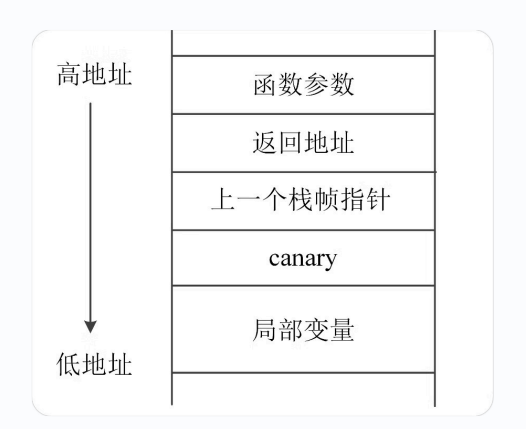
Stack Guard
Put a canary between the return address
- Canary should be random
- The canary value should not be on the stack
- to prevent it from being checked
When returned to the caller, the canary will be checked
QUIZ

